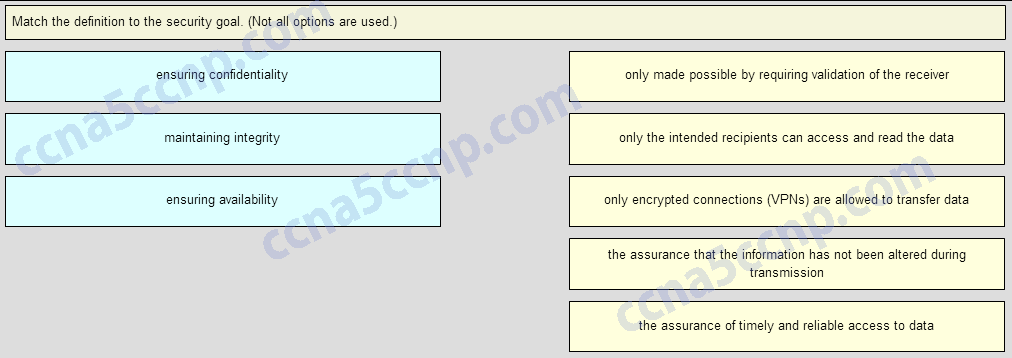
1. During a routine inspection, a technician discovered that
software that was installed on a computer was secretly collecting data
about websites that were visited by users of the computer. Which type of
threat is affecting this computer?
6. An employee at a branch office is creating a quote for a customer. In order to do this, the employee needs to access confidential pricing information from internal servers at the Head Office. What type of network would the employee access?
10. What two criteria are used to help select a network medium from various network media? (Choose two.)
25. What are three characteristics of an SVI? (Choose three.)
28. Match the definitions to their respective CLI hot keys and shortcuts. (Not all options are used.)
29. In the show running-config command, which part of the syntax is represented by running-config?
37. Which name is assigned to the transport layer PDU?
42. Which PDU format is used when bits are received from the network medium by the NIC of a host?
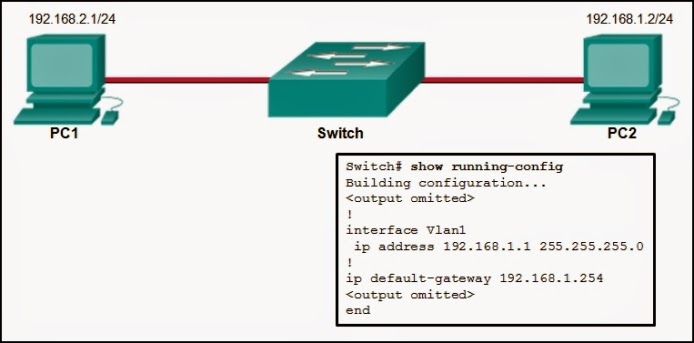
What is the IP address of the switch virtual interface (SVI) on Switch0?

80. A network administrator is measuring the transfer of bits across the company backbone for a mission critical financial application. The administrator notices that the network throughput appears lower than the bandwidth expected. Which three factors could influence the differences in throughput? (Choose three.)



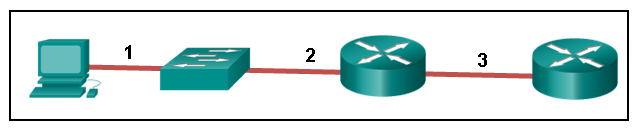
Which port does Switch0 use to send frames to the host with the IPv4 address 10.1.1.5?
169. What information does the loopback test provide?
185. A new network administrator has been asked to enter a banner message on a Cisco device. What is the fastest way a network administrator could test whether the banner is properly configured?
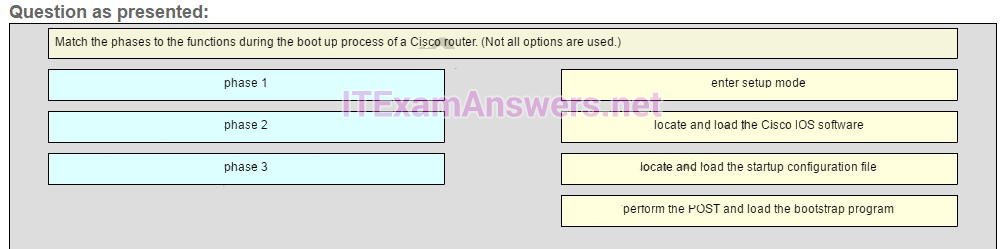
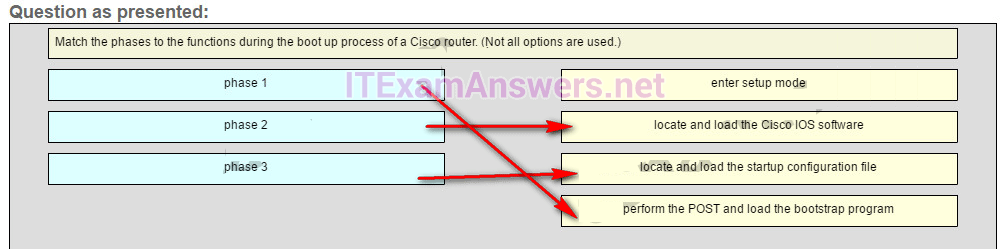
187. Match the phases to the functions during the boot up process of a Cisco router. (Not all options are used.)
188. Match the command with the device mode at which the command is entered. (Not all options are used.)
189. What are two functions of NVRAM? (Choose two.)
195. Which three commands are used to set up secure access to a router through a connection to the console interface? (Choose three.)
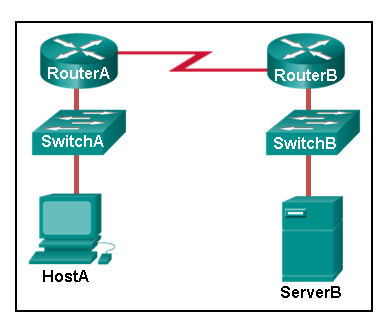
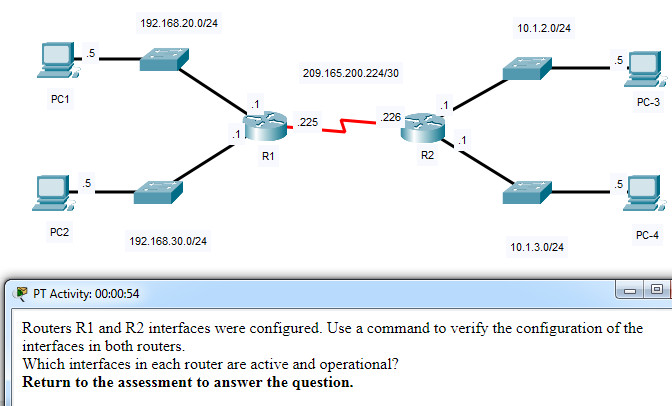
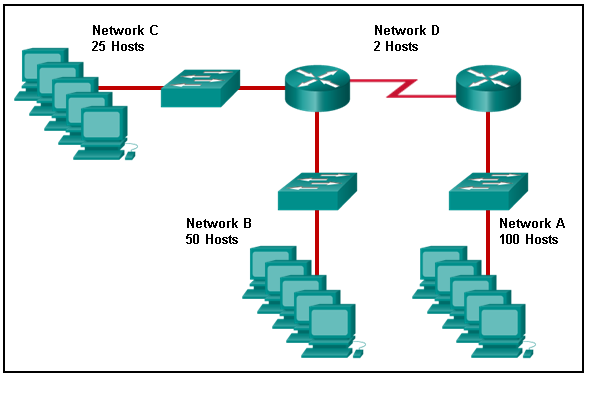
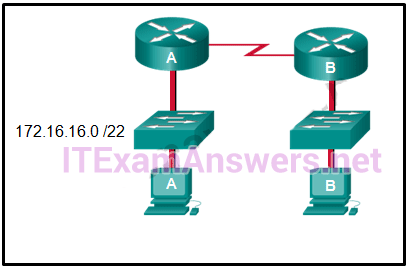
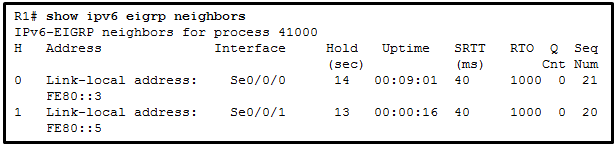
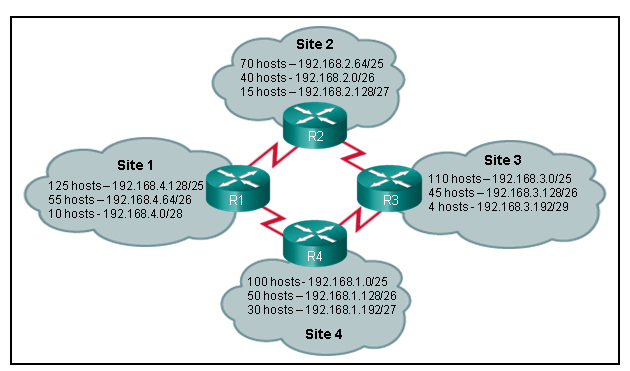
Which interfaces in each router are active and operational?
Which interfaces in each router are active and operational?
 R1: G0/0 and S0/0/1
R1: G0/0 and S0/0/1
R2: G0/1 and S0/0/1
R1: G0/1 and S0/0/1
R2: G0/0 and S0/0/1
R1: G0/0 and S0/0/0
R2: G0/1 and S0/0/0
R1: G0/0 and S0/0/0
R2: G0/0 and S0/0/0
231. What is the prefix length notation for the subnet mask 255.255.255.224?
236. An administrator wants to create four subnetworks from the network address 192.168.1.0/24. What is the network address and subnet mask of the second useable subnet?
241. What three blocks of addresses are defined by RFC 1918 for private network use? (Choose three.)
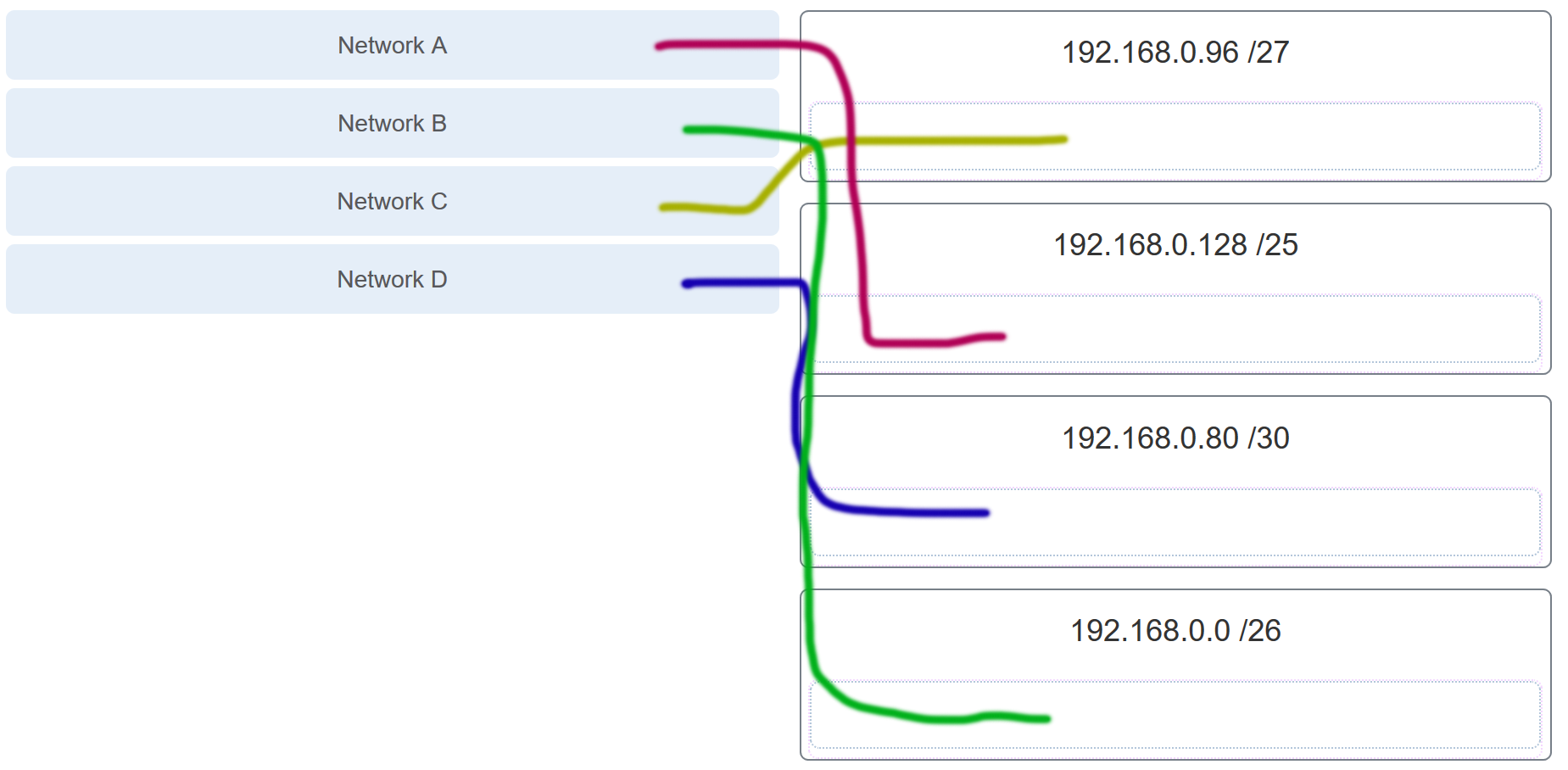
248. A high school in New York (school A) is using videoconferencing technology to establish student interactions with another high school (school B) in Russia. The videoconferencing is conducted between two end devices through the Internet. The network administrator of school A configures the end device with the IP address 209.165.201.10. The administrator sends a request for the IP address for the end device in school B and the response is 192.168.25.10. Neither school is using a VPN. The administrator knows immediately that this IP will not work. Why?
3FFE:1044:0000:0000:00AB:0000:0000:0057?
2001:0DB8:BC15:00A0:0000::
2001:0DB8:BC15:00A1:0000::
2001:0DB8:BC15:00A2:0000::
…
2001:0DB8:BC15:00AF:0000::
The prefix-length for the range of addresses is /60 .
257. What type of IPv6 address is FE80::1?
263. Which IPv6 prefix is reserved for communication between devices on the same link?
269. A technician uses the ping 127.0.0.1 command. What is the technician testing?

277. A user issues a ping 192.135.250.103 command and receives a response that includes a code of 1. What does this code represent?
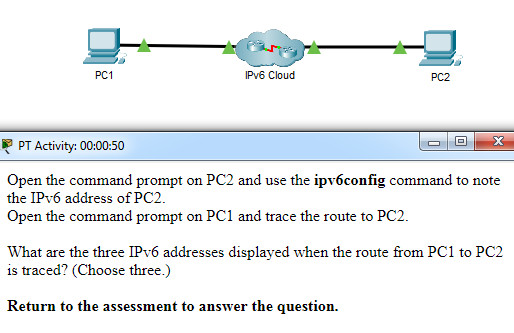 What are the three IPv6 addresses displayed when the route from PC1 to PC2 is traced? (Choose three.)
What are the three IPv6 addresses displayed when the route from PC1 to PC2 is traced? (Choose three.)
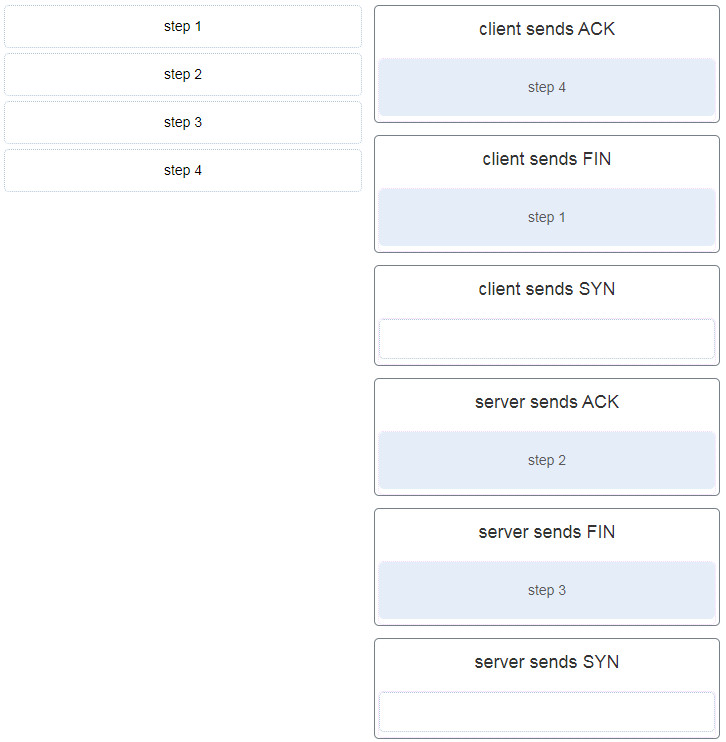
321. Which flag in the TCP header is used in response to a received FIN in order to terminate connectivity between two network devices?

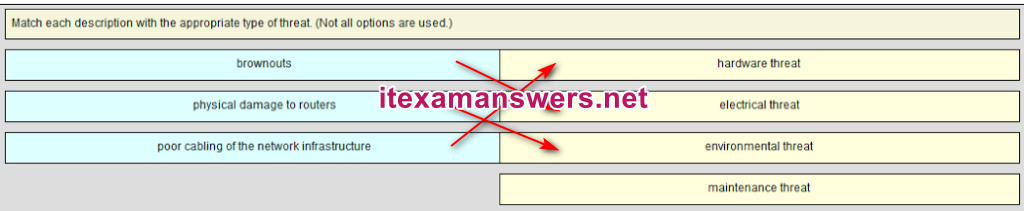
382. Match the type of information security threat to the scenario. (Not all options are used.)

383. Which example of malicious code would be classified as a Trojan horse?

388. What is the purpose of the network security authentication function?

392. What feature of SSH makes it more secure than Telnet for a device management connection?



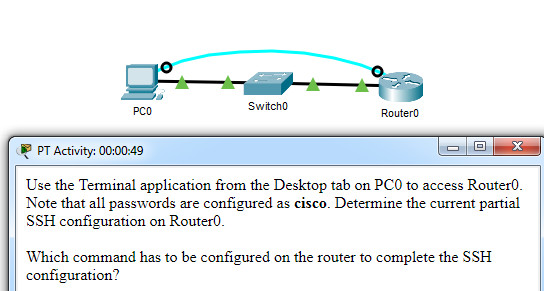 Which command has to be configured on the router to complete the SSH configuration?
Which command has to be configured on the router to complete the SSH configuration?
* minimum of 8 characters, preferably 10.
* use complex combinations of numbers, special characters, and upper and lower case letters.
* avoid repetition, common dictionary words, letter or number sequences.
* avoid names of children, relatives, pets, birthdays, or any easily identifiable personal information.
* can be created by misspelling words or replacing vowels with numbers or special characters.
434. A network technician is troubleshooting an issue and needs to verify the IP addresses of all interfaces on a router. What is the best command to use to accomplish the task?


Place the options in the following order.
— not scored —
locale and load the Cisco IOS software -> phase 2
locate and load the startup configuration file -> phase 3
perform the POST and load the bootstrap program -> phase 1
48. What three blocks of addresses are defined by RFC 1918 for private network use? (Choose three.)
Question
Answer
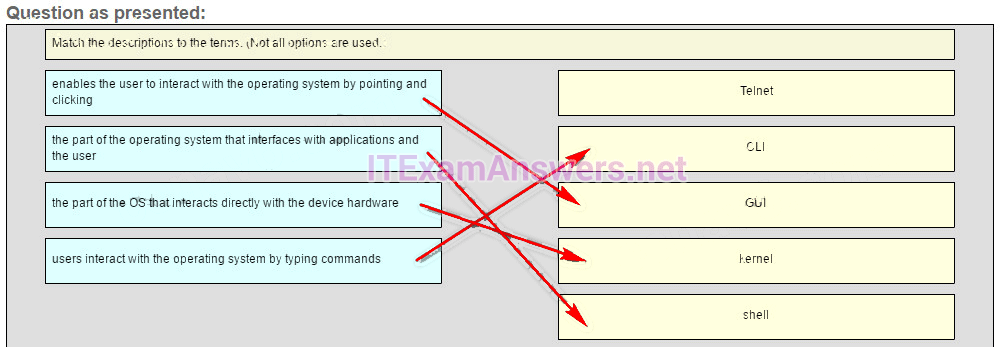
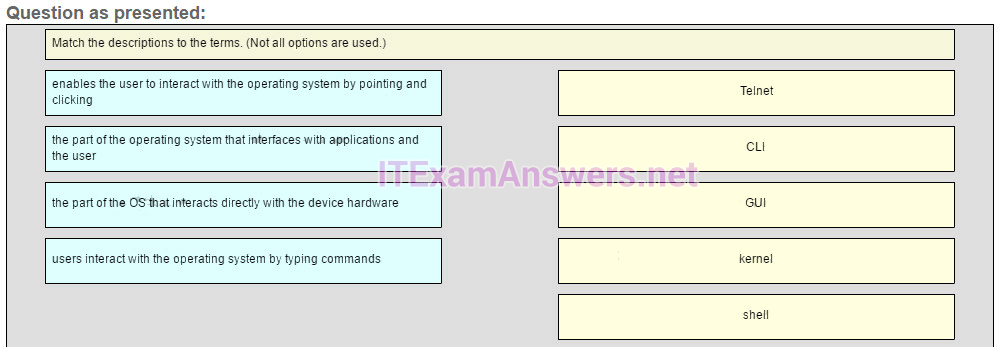
Place the options in the following order.
— not scored —
CLI -> users interact with the operating system by typing commands
GUI -> enables the user to interact with the operating system by pointing and clicking
kernel -> the part of the OS that interacts directly with the device hardware
shell -> the part of the operating system that interfaces with applications and the user
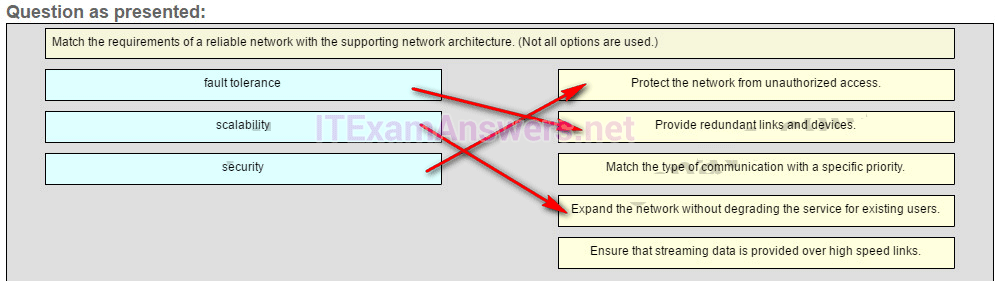
51. Match the requirements of a reliable network with the supporting network architecture. (Not all options are used.)
Question
Answer
Place the options in the following order.
Protect the network from unauthorized access. -> security
Provide redundant links and devices. -> fault tolerance
— not scored —
Expand the network without degrading the service for existing users. -> scalability
— not scored —
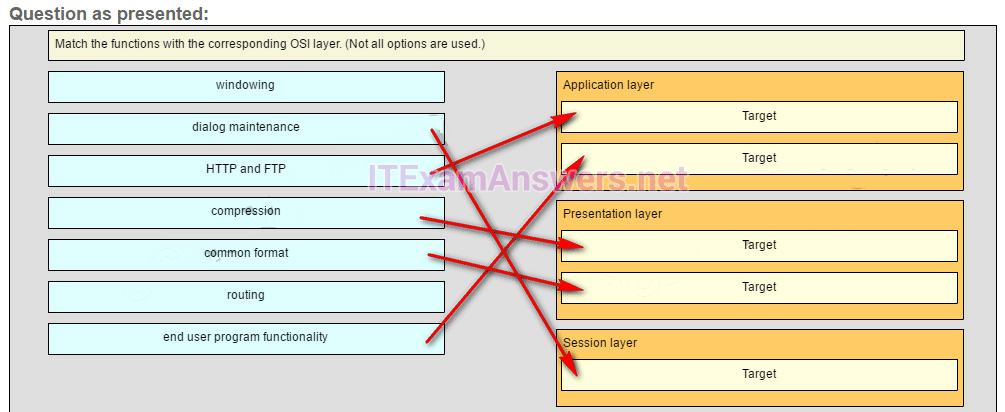
52. Match the functions with the corresponding OSI layer. (Not all options are used.)
Question
Answer
Place the options in the following order.
Application layer
HTTP and FTP
end user program functionality
Presentation layer
compression
common format
Session layer
dialog maintenance
53. What subnet mask is required to support 512 subnets on networks 172.28.0.0/16?


Which interface configuration mode command puts a Layer 3 switch interface into Layer 3 mode? no switchport
96. Fill in the blank.
A nibble consists of 4 bits.
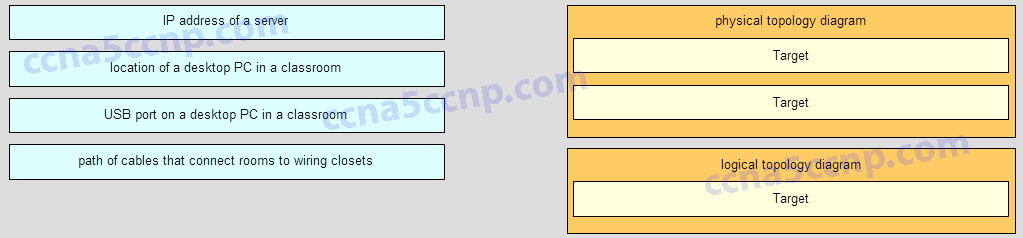
97. Match each item to the type of topology diagram on which it is typically identified. (Not all options are used.)
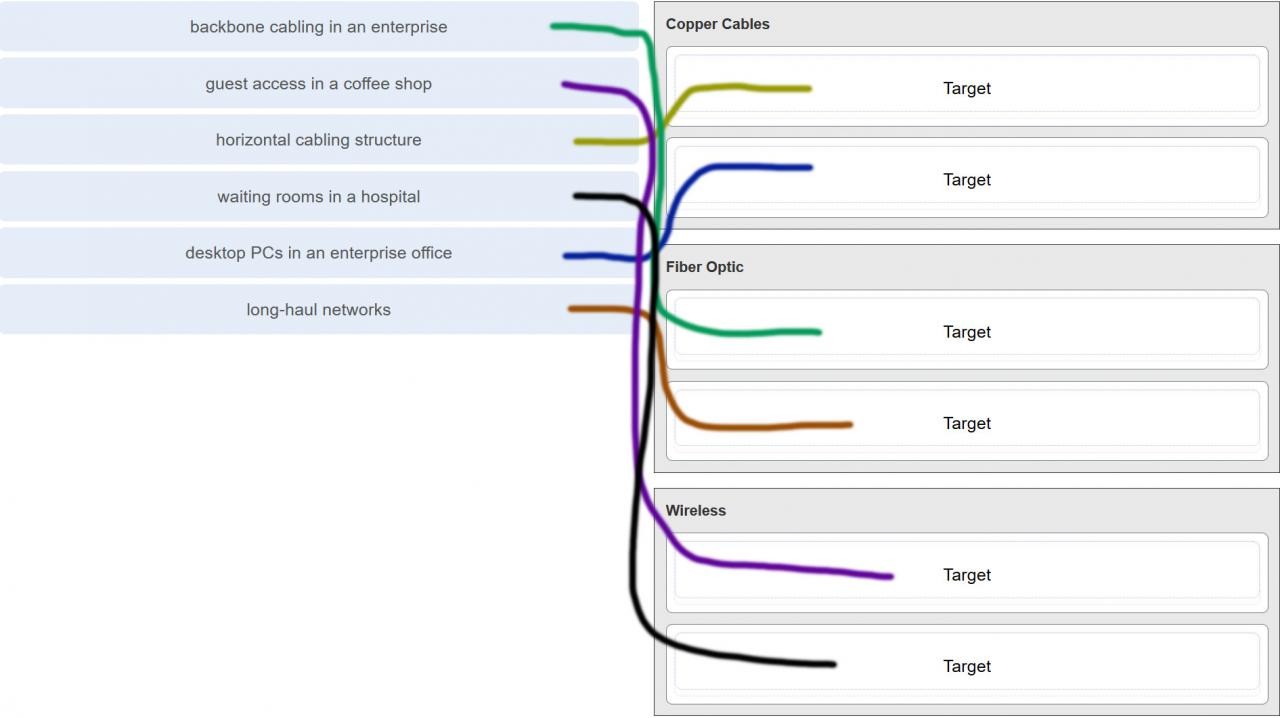
98. Match the situation with the appropriate use of network media.
99. Match the subnetwork to a host address that would be included within the subnetwork. (Not all options are used.)
100. Open the PT activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then fill in the blank.
The Server0 message is winner.?
101. Which two statements are correct in a comparison of IPv4 and IPv6 packet headers? (Choose two.)
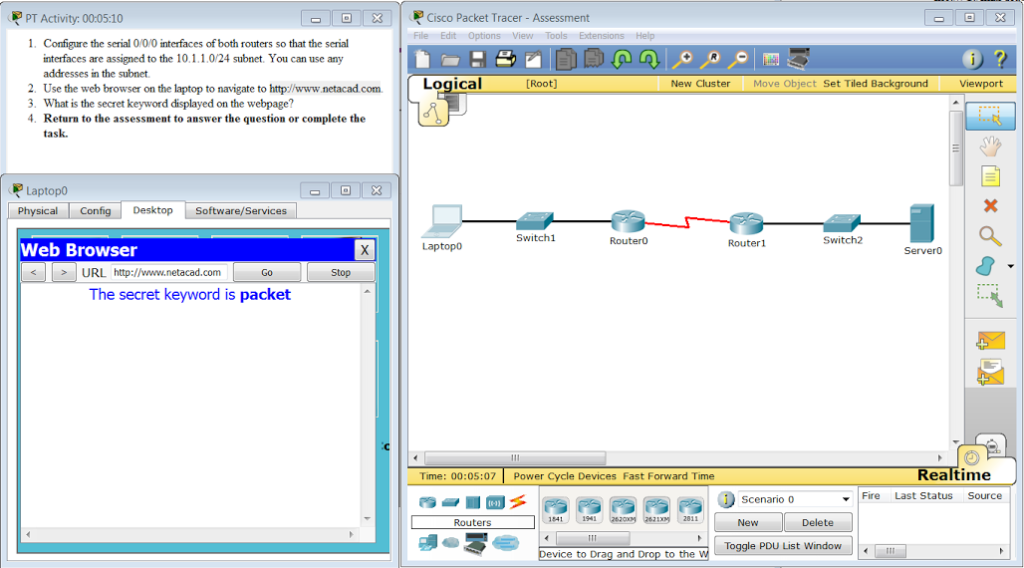
What is the secret keyword that is displayed on the web page?
In dotted decimal notation, the IP address “172.25.0.126” is the last host address for the network 172.25.0.64/26.
106. What are two characteristics of a scalable network? (Choose two.)
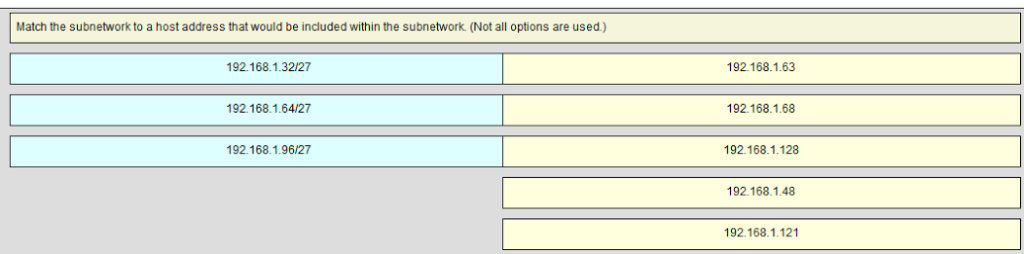
Subnet 192.168.1.32/27 will have a valid host range from 192.168.1.33 – 192.168.1.62 with the broadcast address as 192.168.1.63
Subnet 192.168.1.64/27 will have a valid host range from 192.168.1.65 – 192.168.1.94 with the broadcast address as 192.168.1.95
Subnet 192.168.1.96/27 will have a valid host range from 192.168.1.97 – 192.168.1.126 with the broadcast address as 192.168.1.127
108. What information is added during encapsulation at OSI Layer 3?
The minimum Ethernet frame size is “64” bytes. Anything smaller than that should be considered a “runt frame.”
114. What three statements describe features or functions of media access control? (Choose three.)
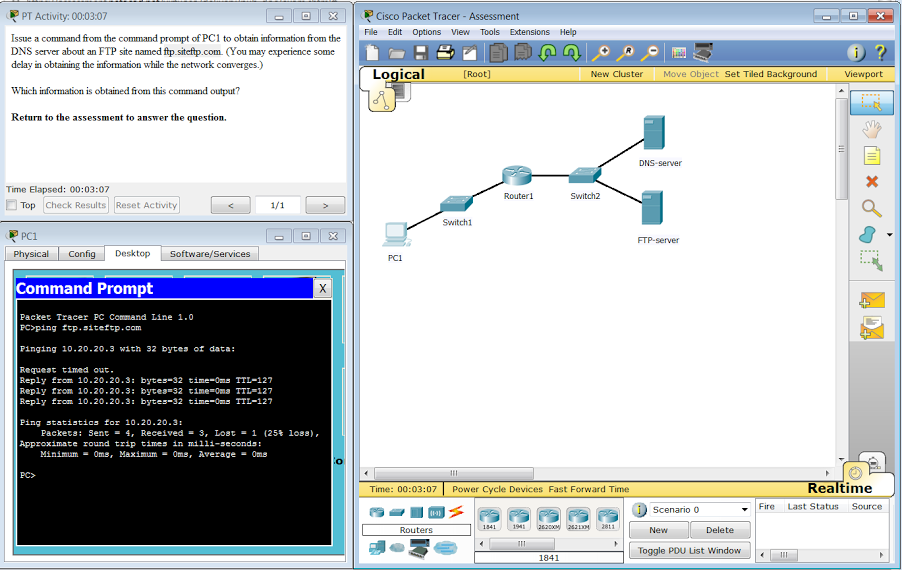
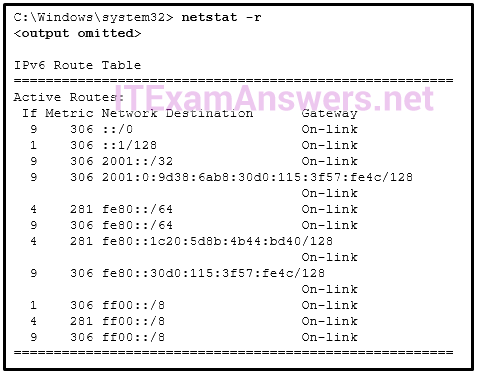
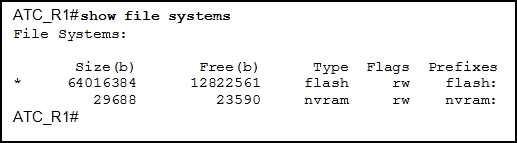
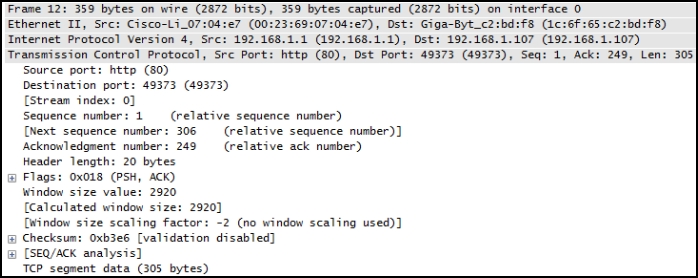
Which information is obtained from this command output?
A nibble consists of “4” bits.
120. Place the options in the following order:
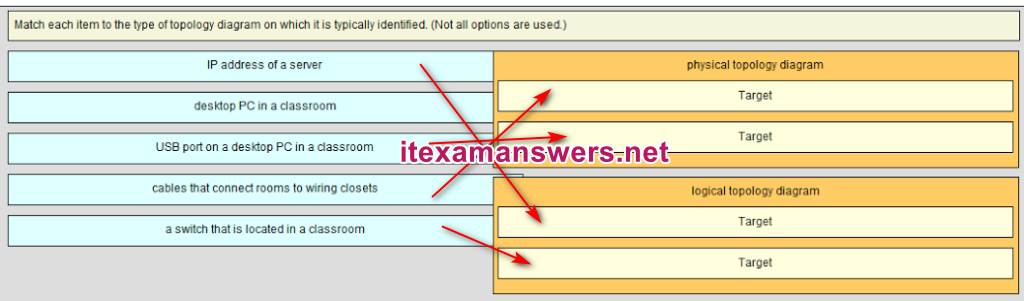
[+] cables connecting rooms to wiring closets
[+] desktop PC in a classroom
[#] IP address of a server
[#] a switch located in a classroom
[+] Order does not matter within this group.
[#] Order does not matter within this group.
121. Why are the paired wires twisted in a CAT5 cable?

124. Refer to the exhibit. Using VLSM, what is the largest and smallest subnet mask required on this network in order to minimize address waste?
133. Which publicly available resources describe protocols, processes, and technologies for the Internet but do not give implementation details?
2. Three bank employees are using the corporate network. The first employee uses a web browser to view a company web page in order to read some announcements. The second employee accesses the corporate database to perform some financial transactions. The third employee participates in an important live audio conference with other corporate managers in branch offices. If QoS is implemented on this network, what will be the priorities from highest to lowest of the different data types?
3. What is a benefit of using cloud computing in networking?
4. What is the function of the shell in an OS?
5. Which connection provides a secure CLI session with encryption to a Cisco switch?
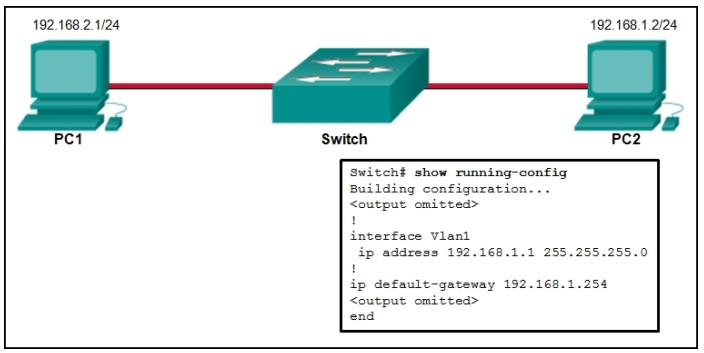
6. A network technician is attempting to configure an interface by entering the following command: SanJose(config)# ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0. The command is rejected by the device. What is the reason for this?
7. An administrator uses the Ctrl-Shift-6 key combination on a switch after issuing the ping command. What is the purpose of using these keystrokes?
8. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is configuring access control to switch SW1. If the administrator uses a console connection to connect to the switch, which password is needed to access user EXEC mode?

9. On which switch interface would an administrator configure an IP address so that the switch can be managed remotely?
10. What protocol is responsible for controlling the size of segments and the rate at which segments are exchanged between a web client and a web server?
11. What is an advantage to using a protocol that is defined by an open standard?
12. What are two benefits of using a layered network model? (Choose two.)
13. Which two OSI model layers have the same functionality as two layers of the TCP/IP model? (Choose two.)
14. Which name is assigned to the transport layer PDU?
15. A network engineer is measuring the transfer of bits across the company backbone for a mission critical database application. The engineer notices that the network throughput appears lower than the bandwidth expected. Which three factors could influence the differences in throughput? (Choose three.)
16. A network administrator is troubleshooting connectivity issues on a server. Using a tester, the administrator notices that the signals generated by the server NIC are distorted and not usable. In which layer of the OSI model is the error categorized?
17. Which type of UTP cable is used to connect a PC to a switch port?
18. A network administrator is measuring the transfer of bits across the company backbone for a mission critical financial application. The administrator notices that the network throughput appears lower than the bandwidth expected. Which three factors could influence the differences in throughput? (Choose three.)
19. What is a characteristic of UTP cabling?
20. What are two characteristics of fiber-optic cable? (Choose two.)
21. What is a characteristic of the LLC sublayer?
22. A network team is comparing physical WAN topologies for connecting remote sites to a headquarters building. Which topology provides high availability and connects some, but not all, remote sites?
23. What method is used to manage contention-based access on a wireless network?
24. What are the three primary functions provided by Layer 2 data encapsulation? (Choose three.)
25. What will a host on an Ethernet network do if it receives a frame with a destination MAC address that does not match its own MAC address?
26. What are two examples of the cut-through switching method? (Choose two.)
27. What are two actions performed by a Cisco switch? (Choose two.)
28. Which frame forwarding method receives the entire frame and performs a CRC check to detect errors before forwarding the frame?
29. Refer to the exhibit. If host A sends an IP packet to host B, what will the destination address be in the frame when it leaves host A?
30. What addresses are mapped by ARP?
31. What information is added during encapsulation at OSI Layer 3?
32. What are two services provided by the OSI network layer? (Choose two.)
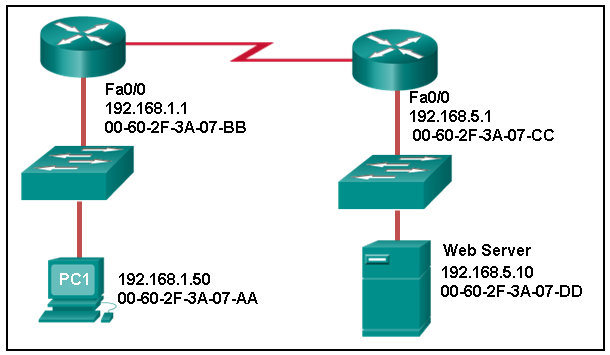
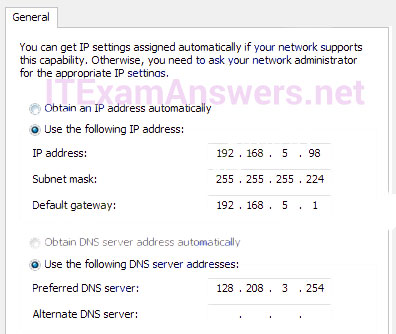
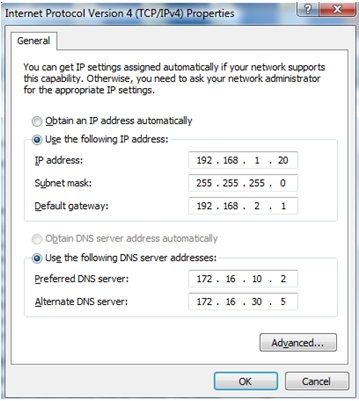
33. Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator for a small advertising company has chosen to use the 192.168.5.96/27 network for internal LAN addressing. As shown in the exhibit, a static IP address is assigned to the company web server. However, the web server cannot access the Internet. The administrator verifies that local workstations with IP addresses that are assigned by a DHCP server can access the Internet, and the web server is able to ping local workstations. Which component is incorrectly configured?
34. Why does a Layer 3 device perform the ANDing process on a destination IP address and subnet mask?
35. What are two functions of NVRAM? (Choose two.)
36. Refer to the exhibit. What will be the result of entering this configuration the next time a network administrator connects a console cable to the router and no additional commands have been entered?

37. What is the dotted decimal representation of the IPv4 address 11001011.00000000.01110001.11010011?
38. What are three characteristics of multicast transmission? (Choose three.)
39. What are the three ranges of IP addresses that are reserved for internal private use? (Choose three.)
40. What purpose does NAT64 serve in IPv6?
41. What is the most compressed representation of the IPv6 address 2001:0000:0000:abcd:0000:0000:0000:0001?
42. Which range of link-local addresses can be assigned to an IPv6-enabled interface?
43. Which three addresses are valid public addresses? (Choose three.)
45. What type of IPv6 address is FE80::1?
46. How many valid host addresses are available on an IPv4 subnet that is configured with a /26 mask?
47. A site administrator has been told that a particular network at the site must accommodate 126 hosts. Which subnet mask would be used that contains the required number of host bits?
48. A network administrator wants to have the same subnet mask for three subnetworks at a small site. The site has the following networks and numbers of devices:
Subnetwork A: IP phones – 10 addresses
Subnetwork B: PCs – 8 addresses
Subnetwork C: Printers – 2 addresses
What single subnet mask would be appropriate to use for the three subnetworks?
49. How many hosts are addressable on a network that has a mask of 255.255.255.248?
50. Which subnet would include the address 192.168.1.96 as a usable host address?
51. What subnet mask is needed if an IPv4 network has 40 devices that need IP addresses and address space is not to be wasted?
52. What are two characteristics shared by TCP and UDP? (Choose two.)
53. Why are port numbers included in the TCP header of a segment?
56. In what two situations would UDP be the preferred transport protocol over TCP? (Choose two.)
57. What important information is added to the TCP/IP transport layer header to ensure communication and connectivity with a remote network device?
58. What is the TCP mechanism used in congestion avoidance?
59. Which scenario describes a function provided by the transport layer?
60. A user opens three browsers on the same PC to access www.cisco.com to search for certification course information. The Cisco web server sends a datagram as a reply to the request from one of the web browsers. Which information is used by the TCP/IP protocol stack in the PC to identify which of the three web browsers should receive the reply?
61. What are two ways that TCP uses the sequence numbers in a segment? (Choose two.)
63. Which three statements characterize UDP? (Choose three.)
64. What is a key characteristic of the peer-to-peer networking model?
65. A technician can ping the IP address of the web server of a remote company but cannot successfully ping the URL address of the same web server. Which software utility can the technician use to diagnose the problem?
66. Which domain name would be an example of a top-level domain?
67. A PC obtains its IP address from a DHCP server. If the PC is taken off the network for repair, what happens to the IP address configuration?
68. When planning for network growth, where in the network should packet captures take place to assess network traffic?
69. A wireless host needs to request an IP address. What protocol would be used to process the request?
70. Which example of malicious code would be classified as a Trojan horse?
71. When applied to a router, which command would help mitigate brute-force password attacks against the router?
72. A network technician suspects that a particular network connection between two Cisco switches is having a duplex mismatch. Which command would the technician use to see the Layer 1 and Layer 2 details of a switch port?
73. Where are Cisco IOS debug output messages sent by default?
74. Match the description with the associated IOS mode. (not all options are used.) Question
Answer
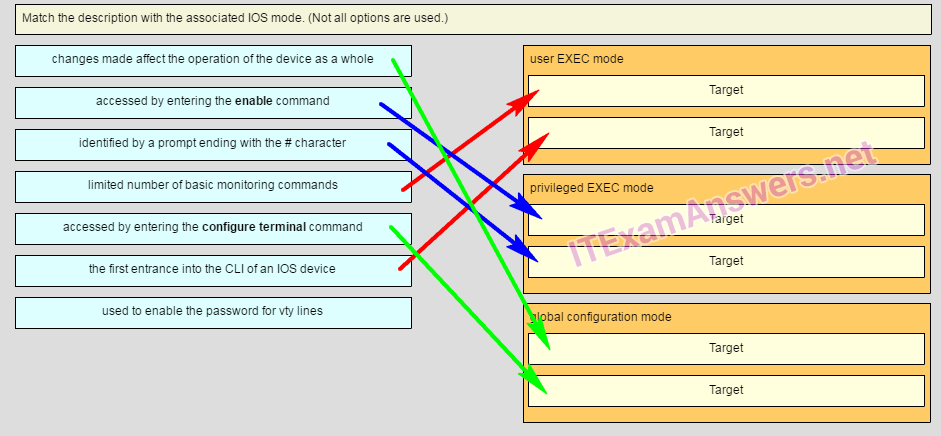

user EXEC mode
limited number of basic monitoring commands
the first entrance intro the CLI of an IOS device
privileged EXEC mode
accessed by entering the enable command
identified by a prompt ending with the # character
global configuration mode
changes made affect the operation of the device as a whole
accessed by entering the configure terminal command
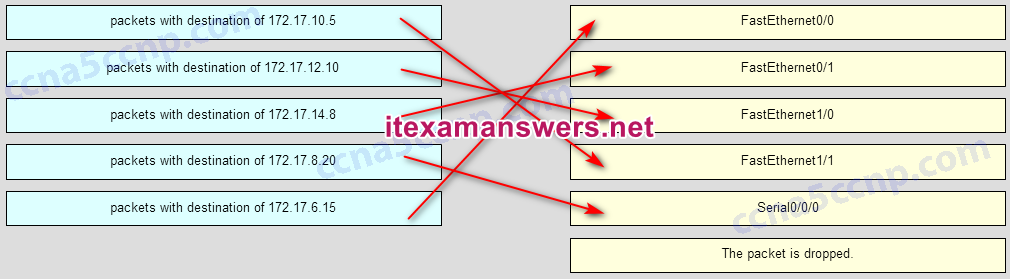
75. Refer to the exhibit. Match the packets with their destination IP address to the exiting interfaces on the router. (Not all options are used.)


Answer


77. A user is unable to reach the web site when typing http://www.cisco.com in a web browser, but can reach the same site by typing http://72.163.4.161. What is the issue?
78. A company is expanding its business to other countries. All branch offices must remain connected to corporate headquarters at all times. Which network technology is required to support this requirement?
79. A home user is looking for an ISP connection that provides high speed digital transmission over regular phone lines. What ISP connection type should be used?
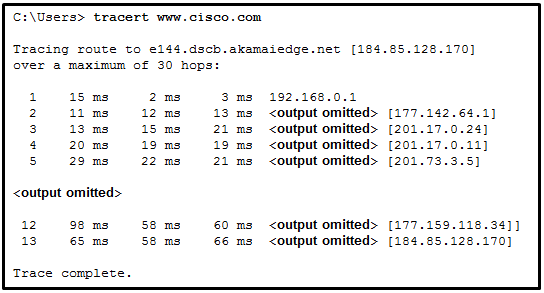
81. What source IP address does a router use by default when the traceroute command is issued?
82. After making configuration changes on a Cisco switch, a network administrator issues a copy running-config startup-config command. What is the result of issuing this command?
83. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is configuring access control to switch SW1. If the administrator has already logged into a Telnet session on the switch, which password is needed to access privileged EXEC mode?

84. Match each item to the type of topology diagram on which it is typically identified. (Not all options are used.)
Question
Answer
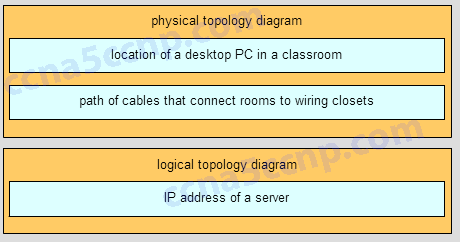
85. Which connection provides a secure CLI session with encryption to a Cisco network device?
86. What function does pressing the Tab key have when entering a command in IOS?
87. What layer is responsible for routing messages through an internetwork in the TCP/IP model?
88. Which statement accurately describes a TCP/IP encapsulation process when a PC is sending data to the network?
89. What unique address is embedded in an Ethernet NIC and used for communication on an Ethernet network?
90. Which procedure is used to reduce the effect of crosstalk in copper cables?
91. During the encapsulation process, what occurs at the data link layer for a PC connected to an Ethernet network?
92. What are two characteristics of Ethernet MAC addresses? (Choose two.)
93. If a device receives an Ethernet frame of 60 bytes, what will it do?
94. Under which two circumstances will a switch flood a frame out of every port except the port that the frame was received on? (Choose two.)
95. Which switching method has the lowest level of latency?
96. Which two commands can be used on a Windows host to display the routing table? (Choose two.)
97. Which two functions are primary functions of a router? (Choose two.)
99. At a minimum, which address is required on IPv6-enabled interfaces?
100. Which service provides dynamic global IPv6 addressing to end devices without using a server that keeps a record of available IPv6 addresses?
101. What is the purpose of the command ping ::1?
102. How many usable IP addresses are available on the 192.168.1.0/27 network?
103. What is the process of dividing a data stream into smaller pieces before transmission?
104. When IPv4 addressing is manually configured on a web server, which property of the IPv4 configuration identifies the network and host portion for an IPv4 address?
105. Which two roles can a computer assume in a peer-to-peer network where a file is being shared between two computers? (Choose two.)
106. Which two protocols operate at the highest layer of the TCP/IP protocol stack? (Choose two.)
107. What is one difference between the client-server and peer-to-peer network models?
108. What is the function of the HTTP GET message?
109. Which networking model is being used when an author uploads one chapter document to a file server of a book publisher?
110. What network service resolves the URL entered on a PC to the IP address of the destination server?
111. A network engineer is analyzing reports from a recently performed network baseline. Which situation would depict a possible latency issue?
112. Which firewall feature is used to ensure that packets coming into a network are legitimate responses to requests initiated from internal hosts?
113. What is one indication that a Windows computer did not receive an IPv4 address from a DHCP server?
114. Which command can an administrator issue on a Cisco router to send debug messages to the vty lines?
115. Fill in the blank.
During data communications, a host may need to send a single message to a specific group of destination hosts simultaneously. This message is in the form of a Multicast message. 116. A medium-sized business is researching available options for connecting to the Internet. The company is looking for a high speed option with dedicated, symmetric access. Which connection type should the company choose?
118. What characteristic of a network enables it to quickly grow to support new users and applications without impacting the performance of the service being delivered to existing users?
119. After several configuration changes are made to a router, the copy running-configuration startup-configuration command is issued. Where will the changes be stored?

122. A technician configures a switch with these commands:SwitchA(config)# interface vlan 1
SwitchA(config-if)# ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
SwitchA(config-if)# no shutdownWhat is the technician configuring?
123. In computer communication, what is the purpose of message encoding?
124. What is a characteristic of multicast messages?
125. A large corporation has modified its network to allow users to access network resources from their personal laptops and smart phones. Which networking trend does this describe?
A dedicated server is not needed when implementing a peer-to-peer network.
Port numbers ranging from 0 to 1023 are considered to be Well Known ports.
136. Fill in the blank.
ISOC, IANA, EIA, and IEEE represent standards organizations which help to promote and maintain an open Internet.
137. Refer to the exhibit. An administrator is trying to configure the switch but receives the error message that is displayed in the exhibit. What is the problem?

139. A network administrator is upgrading a small business network to give high priority to real-time applications traffic. What two types of network services is the network administrator trying to accommodate? (Choose two.)
Question
Answer
141. Which IPv4 address can be pinged to test the internal TCP/IP operation of a host?
ARP
R1# copy running-config tftp
Address or name of remote host [ ]?
When the router prompts for an address or remote host name, what IP address should the administrator enter at the prompt?
173. What two preconfigured settings that affect security are found on most new wireless routers? (Choose two.)
TFTP* is a best-effort, connectionless application layer protocol that is used to transfer files.
176. Which two components are necessary for a wireless client to be installed on a WLAN? (Choose two.)
178. Match the phases to their correct stage in the router bootup process. (Not all options are used.)

179. A host is accessing an FTP server on a remote network. Which three functions are performed by intermediary network devices during this conversation? (Choose three.)

187. Which device should be used for enabling a host to communicate with another host on a different network?
Point-to-point communications where both devices can transmit and receive on the medium at the same time are known as full-duplex
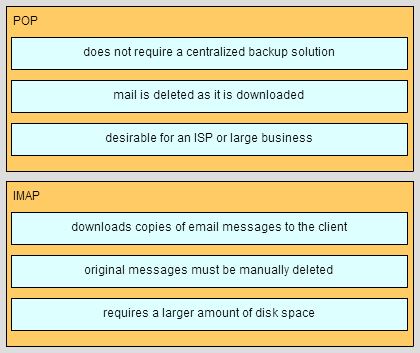
206. Match each characteristic to the appropriate email protocol. (Not all options are used.)
207. A host is accessing a Telnet server on a remote network. Which three functions are performed by intermediary network devices during this conversation? (Choose three.)
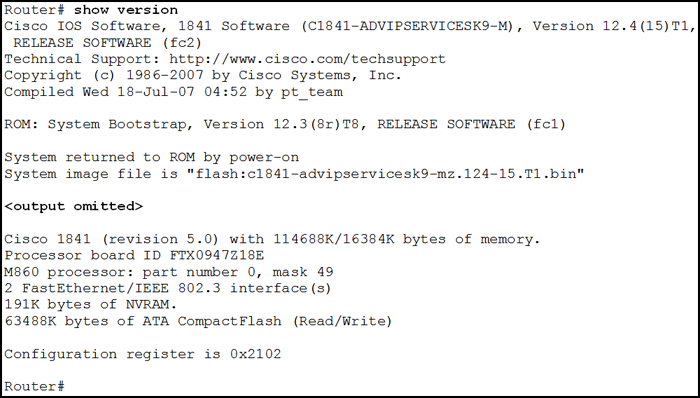
210. During normal operation, from which location do most Cisco switches and routers run the IOS?
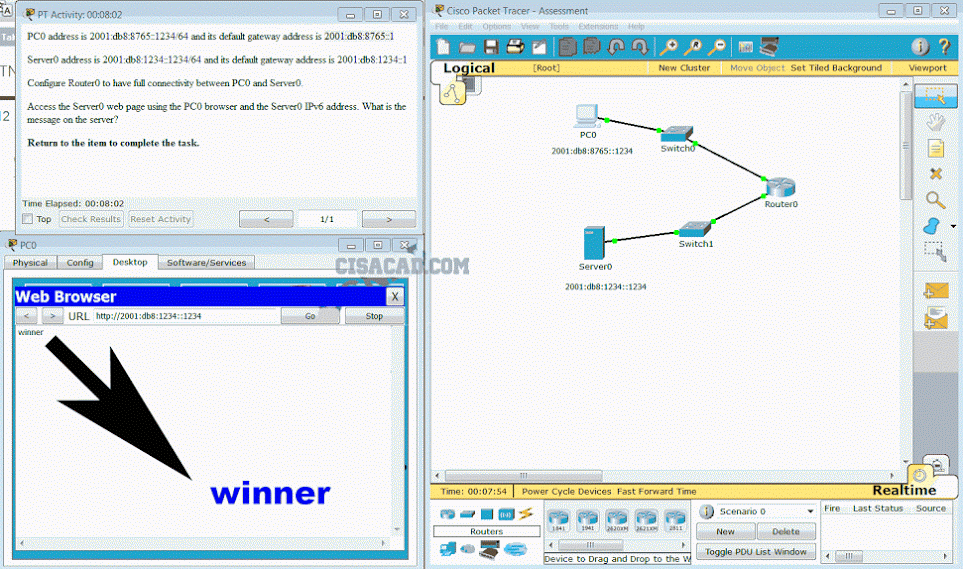
Open the PT activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then fill in the blank.
The Server0 message isb ”winner”
228. Which field in an IPv4 packet header will typically stay the same during its transmission?
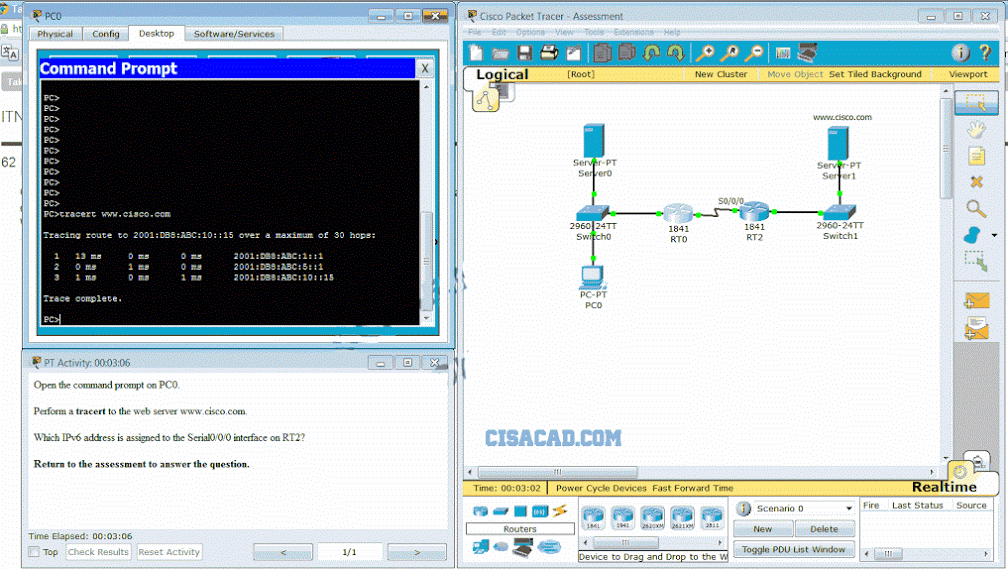
Open the PT Activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then answer the question. Which IPv6 address is assigned to the Serial0/0/0 interface on RT2?
To prevent faulty network devices from carrying dangerous voltage levels, equipment must be grounded *correctly
240. What is a possible hazard that can be caused by network cables in a fire?
255. Refer to the exhibit. The administrator configured the access to the console and the vty lines of a router. Which conclusion can be drawn from this configuration?

Network devices come in two physical configurations. Devices that have expansion slots that provide the flexibility to add new modules have a Modular * configuration.
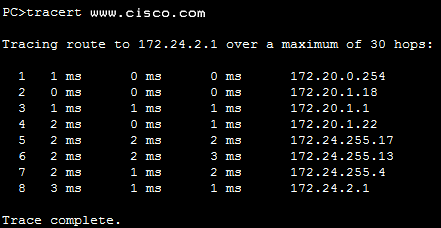
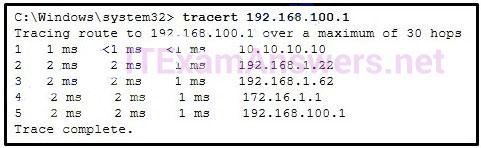
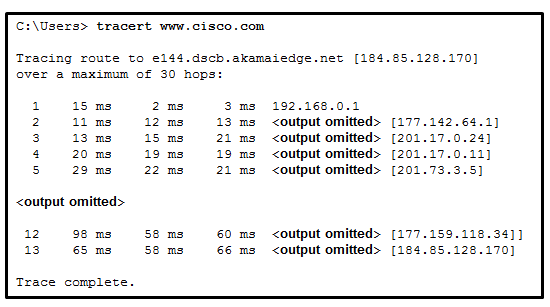
263. Refer to the exhibit. What is the maximum TIL value that is used to reach the destination www.cisco.com?

269. How many bits would need to be borrowed if a network admin were given the IP addressing scheme of 172.16.0.0/16 and needed no more than 16 subnet with equal number of hosts?
It will give 4 options about ping, the correct one is:
The PC2 will be able to ping 192.168.1.1*
271. Which statement best describes the operation of the File Transfer Protocol?
IPv4 multicast addresses are directly mapped to IEEE 802 (Ethernet) MAC addresses using the last ___4___ of the 28 available bits in the IPv4 multicast group address.
279. How could a faulty network device create a source of hazard for a user? (Choose two.)
292. What is an example of a top-level domain?
293. Which protocol requires the establishment of a session between sender and receiver hosts prior to transmitting data?
What three network characteristics are described in this scenario? (Choose three.)
3. A company has a file server that shares a folder named Public. The network security policy specifies that the Public folder is assigned Read-Only rights to anyone who can log into the server while the Edit rights are assigned only to the network admin group. Which component is addressed in the AAA network service framework?
- DoS attack
- identity theft
- spyware
- zero-day attack
- Internet
- intranet
- extranet
- extendednet
- cloud computing
- online collaboration
- bring your own device
- video conferencing
- It is a standards body that develops cabling and wiring standards for networking.
- It is a protocol that establishes how computers within a local network communicate.
- It is an organization that enables individuals and businesses to connect to the Internet.
- It is a networking device that combines the functionality of several different networking devices in one.
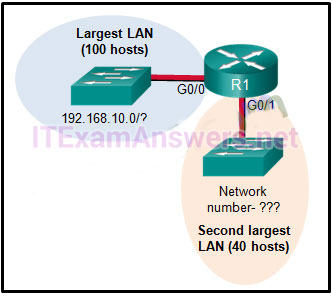
6. An employee at a branch office is creating a quote for a customer. In order to do this, the employee needs to access confidential pricing information from internal servers at the Head Office. What type of network would the employee access?
- an intranet
- the Internet
- an extranet
- a local area network
- New “smart” electrical cabling is used to extend an existing home LAN.
- A home LAN is installed without the use of physical cabling.
- A device connects to an existing home LAN using an adapter and an existing electrical outlet.
- Wireless access points use powerline adapters to distribute data through the home LAN.
- fault tolerance
- scalability
- security
- Quality of Service (QoS)
- reliability
CCNA-1-v7-Modules-1-3-Basic Network Connectivity and Communications Exam Answers 09
- the types of data that need to be prioritized
- the cost of the end devices utilized in the network
- the distance the selected medium can successfully carry a signal
- the number of intermediate devices installed in the network
- the environment where the selected medium is to be installed
- on-line purchasing
- video conferencing
- wiki
- implementing a firewall
- installing a wireless network
- installing antivirus software
- implementing an intrusion detection system
- adding a dedicated intrusion prevention device
- VTY interface
- console interface
- Ethernet interface
- boot IOS mode
- privileged EXEC mode
- router configuration mode
- the AUX interface
- the console port interface
- the switch virtual interface
- the first Ethernet port interface
- It aborts the current command and returns to configuration mode.
- It exits configuration mode and returns to user EXEC mode.
- It moves the cursor to the beginning of the next line.
- It completes the remainder of a partially typed word in a command.
- Issue the reload command without saving the running configuration.
- Delete the vlan.dat file and reboot the device.
- Close and reopen the terminal emulation software.
- Issue the copy startup-config running-config command.
- to restart the ping process
- to interrupt the ping process
- to exit to a different configuration mode
- to allow the user to complete the command
CCNA-1-v7-Modules-1-3-Basic Network Connectivity and Communications Exam Answers 14
- letmein
- secretin
- lineconin
- linevtyin
SwitchA(config)# interface vlan 1 SwitchA(config-if)# ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 SwitchA(config-if)# no shutdownWhat is the technician configuring?
- Telnet access
- SVI
- password encryption
- physical switchport access
- end
- exit
- Ctrl-Z
- Ctrl-C
- RAM provides nonvolatile storage.
- The configuration that is actively running on the device is stored in RAM.
- The contents of RAM are lost during a power cycle.
- RAM is a component in Cisco switches but not in Cisco routers.
- RAM is able to store multiple versions of IOS and configuration files.
- Branch2!
- RM-3-Switch-2A4
- Floor(15)
- HO Floor 17
- SwBranch799
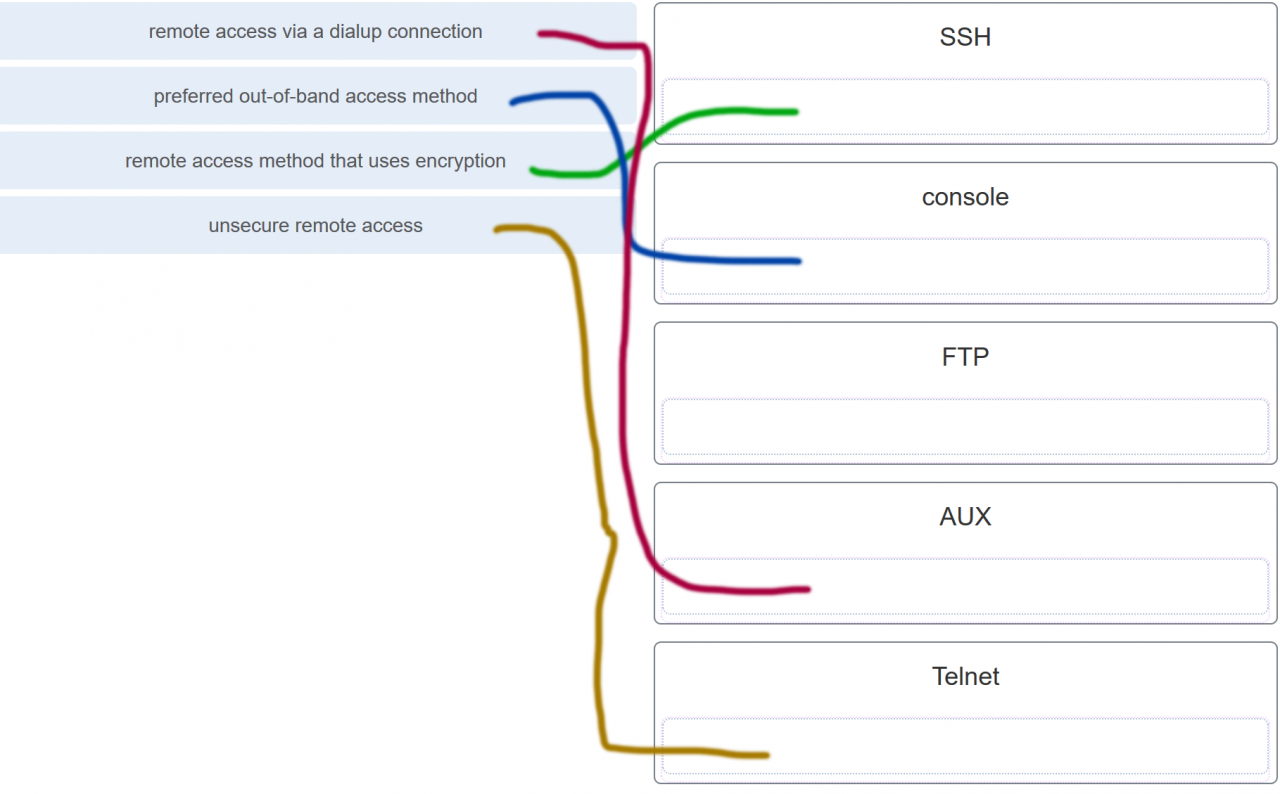
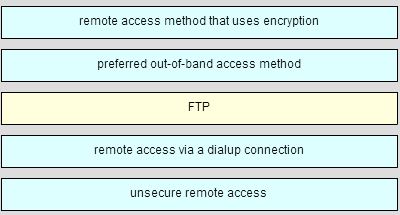
- SSH makes connections over the network, whereas Telnet is for out-of-band access.
- SSH provides security to remote sessions by encrypting messages and using user authentication. Telnet is considered insecure and sends messages in plaintext.
- SSH requires the use of the PuTTY terminal emulation program. Tera Term must be used to connect to devices through the use of Telnet.
- SSH must be configured over an active network connection, whereas Telnet is used to connect to a device from a console connection.
CCNA-1-v7-Modules-1-3-Basic Network Connectivity and Communications Exam Answers 24
- It is designed as a security protocol to protect switch ports.
- It is not associated with any physical interface on a switch.
- It is a special interface that allows connectivity by different types of media.
- It is required to allow connectivity by any device at any location.
- It provides a means to remotely manage a switch.
- It is associated with VLAN1 by default.
- ipconfig
- ping
- traceroute
- show ip interface brief
28. Match the definitions to their respective CLI hot keys and shortcuts. (Not all options are used.)
29. In the show running-config command, which part of the syntax is represented by running-config?
- the command
- a keyword
- a variable
- a prompt
- The new configuration will be stored in flash memory.
- The new configuration will be loaded if the switch is restarted.
- The current IOS file will be replaced with the newly configured file.
- The configuration changes will be removed and the original configuration will be restored.
- (config)# enable password secret
- (config)# enable secret Secret_Password
- (config-line)# password secret
- (config)# service password-encryption
- (config)# enable secret Encrypted_Password
- This command encrypts passwords as they are transmitted across serial WAN links.
- This command prevents someone from viewing the running configuration passwords.
- This command enables a strong encryption algorithm for the enable secret password command.
- This command automatically encrypts passwords in configuration files that are currently stored in NVRAM.
- This command provides an exclusive encrypted password for external service personnel who are required to do router maintenance.
- encapsulation
- flow control
- access method
- response timeout
- Data is sent from the internet layer to the network access layer.
- Packets are sent from the network access layer to the transport layer.
- Segments are sent from the transport layer to the internet layer.
- Frames are sent from the network access layer to the internet layer.
- ARP
- DHCP
- DNS
- FTP
- NAT
- PPP
37. Which name is assigned to the transport layer PDU?
- bits
- data
- frame
- packet
- segment
- DNS server address
- subnet mask
- default gateway
- DHCP server address
- encapsulation
- encoding
- segmentation
- flow control
- internet
- transport
- network access
- session
CCNA-1-v7-Modules-1-3-Basic Network Connectivity and Communications Exam Answers 41
- file
- frame
- packet
- segment

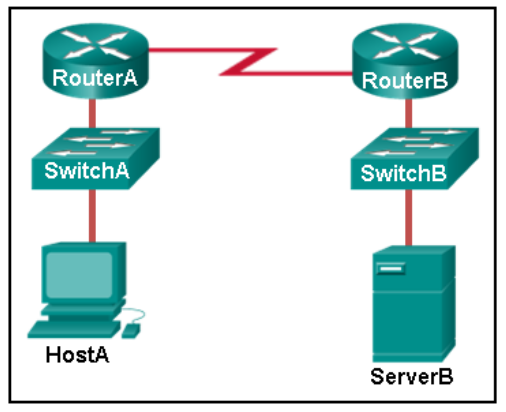
- ServerB will generate a packet with the destination IP address of RouterB.
- ServerB will generate a frame with the destination MAC address of SwitchB.
- ServerB will generate a packet with the destination IP address of RouterA.
- ServerB will generate a frame with the destination MAC address of RouterB.
- ServerB will generate a packet with the destination IP address of HostA.
- ServerB will generate a frame with the destination MAC address of RouterA.
- encapsulation
- flow control
- access method
- response timeout
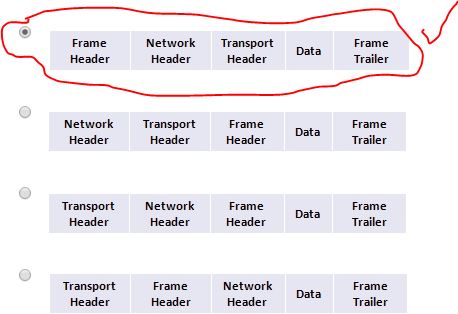
- Ethernet, IP, TCP, HTTP
- HTTP, TCP, IP, Ethernet
- Ethernet, TCP, IP, HTTP
- HTTP, Ethernet, IP, TCP
- data link
- network
- physical
- session
- transport
- physical layer
- data link layer
- network layer
- transport layer
- They are sent to a select group of hosts.
- They are sent to all hosts on a network.
- They must be acknowledged.
- They are sent to a single destination.
- Network protocols define the type of hardware that is used and how it is mounted in racks.
- They define how messages are exchanged between the source and the destination.
- They all function in the network access layer of TCP/IP.
- They are only required for exchange of messages between devices on remote networks.
- Network communications is confined to data transfers between devices from the same vendor.
- A client host and a server running different operating systems can successfully exchange data.
- Internet access can be controlled by a single ISP in each market.
- Competition and innovation are limited to specific types of products.
- a router
- a firewall
- a web server
- a DSL modem
CCNA-1-v7-Modules-1-3-Basic Network Connectivity and Communications Exam Answers 52
- 192.168.5.10
- 192.168.10.5
- 192.168.10.1
- 192.168.5.0
- to enable the switch to send broadcast frames to attached PCs
- to enable the switch to function as a default gateway
- to enable the switch to be managed remotely
- to enable the switch to receive frames from attached PCs

CCNA-1-v7-Modules-1-3-Basic Network Connectivity and Communications Exam Answers 54
- The entire command, configure terminal, must be used.
- The administrator is already in global configuration mode.
- The administrator must first enter privileged EXEC mode before issuing the command.
- The administrator must connect via the console port to access global configuration mode.
- extranet
- cloud
- BYOD
- quality of service
- cloud
- BYOD
- quality of service
- converged network
- peer-to-peer
- cloud
- BYOD
- quality of service
- SOHO network
- BYOD
- quality of service
- converged network
- client/server
- internet
- intranet
- extranet
- SOHO network
- internet
- intranet
- extranet
- powerline networking
- internet
- intranet
- extranet
- quality of service
- internet
- intranet
- extranet
- intranet
- internet
- extranet
- peer-to-peer
- BYOD
- internet
- intranet
- extranet
- network layer
- data link layer
- transport layer
- application layer
- transport layer
- data link layer
- network layer
- application layer
- application layer
- data link layer
- network layer
- transport layer
- network layer
- data link layer
- application layer
- presentation layer
- application layer
- transport layer
- network layer
- presentation layer
- network layer
- application layer
- transport layer
- presentation layer
- data link layer
- application layer
- transport layer
- presentation layer
- transport layer
- application layer
- network layer
- presentation layer
- data link layer
- transport layer
- application layer
- network layer
- transport layer
- network layer
- application layer
- data link layer
- controlling access to media
- transmitting bits across the local media
- performing error detection on received frames
- exchanging frames between nodes over physical network media
- The two strands allow the data to travel for longer distances without degrading.
- They prevent crosstalk from causing interference on the connection.
- They increase the speed at which the data can travel.
- They allow for full-duplex connectivity.
- the distortion of the network signal from fluorescent lighting
- the distortion of the transmitted messages from signals carried in adjacent wires
- the weakening of the network signal over long cable lengths
- the loss of wireless signal over excessive distance from the access point
- requiring proper grounding connections
- twisting opposing circuit wire pairs together
- wrapping the bundle of wires with metallic shielding
- designing a cable infrastructure to avoid crosstalk interference
- avoiding sharp bends during installation

80. A network administrator is measuring the transfer of bits across the company backbone for a mission critical financial application. The administrator notices that the network throughput appears lower than the bandwidth expected. Which three factors could influence the differences in throughput? (Choose three.)
- the amount of traffic that is currently crossing the network
- the sophistication of the encapsulation method applied to the data
- the type of traffic that is crossing the network
- the latency that is created by the number of network devices that the data is crossing
- the bandwidth of the WAN connection to the Internet
- the reliability of the gigabit Ethernet infrastructure of the backbone
- It is not affected by EMI or RFI.
- Each pair of cables is wrapped in metallic foil.
- It combines the technique of cancellation, shielding, and twisting to protect data.
- It typically contains 4 pairs of fiber-optic wires.
- It is more expensive than UTP cabling is.
- create the signals that represent the bits in each frame on to the media
- provide physical addressing to the devices
- determine the path packets take through the network
- control data access to the media
- the magnetic field around the adjacent pairs of wire
- the use of braided wire to shield the adjacent wire pairs
- the reflection of the electrical wave back from the far end of the cable
- the collision caused by two nodes trying to use the media simultaneously

- STP
- UTP
- coax
- fiber
- crosstalk
- bandwidth
- size of the network
- signal modulation technique
- electromagnetic interference

- STP
- UTP
- coax
- fiber
- Blu-ray players
- home theaters
- cordless phones
- microwaves
- incandescent light bulbs
- external hard drives
- It defines the end-to-end delivery addressing scheme.
- It maintains the path between the source and destination devices during the data transmission.
- It manages the access of frames to the network media.
- It provides reliable delivery through link establishment and flow control.
- It ensures that application data will be transmitted according to the prioritization.
- It packages various Layer 3 PDUs into a frame format that is compatible with the network interface.
- to verify the integrity of the received frame
- to verify the physical address in the frame
- to verify the logical address in the frame
- to compute the checksum header for the data field in the frame
- logical address
- physical address
- data
- error detection
- They all include the flow control and logical connection fields.
- Ethernet frame header fields contain Layer 3 source and destination addresses.
- They vary depending on protocols.
- They include information on user applications.
- mesh
- partial mesh
- hub and spoke
- point-to-point
- auto-MDIX
- CEF
- Frame Check Sequence
- minimum frame size
- source MAC address
- deterministic
- half-duplex
- full-duplex
- controlled access
- End devices connect to a central intermediate device, which in turn connects to other central intermediate devices.
- End devices are connected together by a bus and each bus connects to a central intermediate device.
- Each end system is connected to its respective neighbor via an intermediate device.
- All end and intermediate devices are connected in a chain to each other.
- It provides the logical addressing required that identifies the device.
- It provides delimitation of data according to the physical signaling requirements of the medium.
- It places information in the frame allowing multiple Layer 3 protocols to use the same network interface and media.
- It defines software processes that provide services to the physical layer.
- Ethernet utilizes CSMA/CD.
- Media access control provides placement of data frames onto the media.
- Contention-based access is also known as deterministic.
- 802.11 utilizes CSMA/CD.
- Data link layer protocols define the rules for access to different media.
- Networks with controlled access have reduced performance due to data collisions.
- An IP address is added.
- The logical address is added.
- The physical address is added.
- The process port number is added.
- source IP address
- source MAC address
- destination IP address
- destination MAC address
- error-checking information
- access method
- flow control
- message encapsulation
- message encoding
- header
- type field
- MTU size
- data
- trailer
- CRC value
- When a device hears a carrier signal and transmits, a collision cannot occur.
- A jamming signal causes only devices that caused the collision to execute a backoff algorithm.
- All network devices must listen before transmitting.
- Devices involved in a collision get priority to transmit after the backoff period.
- the automatic configuration of an interface for 10/100/1000 Mb/s operation
- the automatic configuration of an interface for a straight-through or a crossover Ethernet cable connection
- the automatic configuration of full-duplex operation over a single Ethernet copper or optical cable
- the ability to turn a switch interface on or off accordingly if an active connection is detected

- 00-60-2F-3A-07-AA
- 00-60-2F-3A-07-BB
- 00-60-2F-3A-07-CC
- 00-60-2F-3A-07-DD
- port-based buffering
- level 1 cache buffering
- shared memory buffering
- fixed configuration buffering
- store-and-forward switching
- fast-forward switching
- CRC switching
- fragment-free switching
- QOS switching
- cut-through switching
- store-and-forward switching
- fragment-free switching
- fast-forward switching
- to obtain the MAC address of the sending node
- to verify the logical address of the sending node
- to compute the CRC header for the data field
- to determine if errors occurred in the transmission and reception
- cut-through
- store-and-forward
- fragment-free
- fast-forward
- The link between the switches will work at the fastest speed that is supported by both switches.
- The link between switches will work as full-duplex.
- If both switches support different speeds, they will each work at their own fastest speed.
- The auto-MDIX feature will configure the interfaces eliminating the need for a crossover cable.
- The connection will not be possible unless the administrator changes the cable to a crossover cable.
- The duplex capability has to be manually configured because it cannot be negotiated.
- collision detecting
- frame error checking
- faster frame forwarding
- frame forwarding using IPv4 Layer 3 and 4 information
- CRC in the trailer
- source MAC address in the header
- destination MAC address in the header
- protocol type in the header
- cut-through
- fast-forward
- fragment-free
- store-and-forward
- building a routing table that is based on the first IP address in the frame header
- using the source MAC addresses of frames to build and maintain a MAC address table
- forwarding frames with unknown destination IP addresses to the default gateway
- utilizing the MAC address table to forward frames via the destination MAC address
- examining the destination MAC address to add new entries to the MAC address table
- Logical link control is implemented in software.
- Logical link control is specified in the IEEE 802.3 standard.
- The LLC sublayer adds a header and a trailer to the data.
- The data link layer uses LLC to communicate with the upper layers of the protocol suite.
- The LLC sublayer is responsible for the placement and retrieval of frames on and off the media.
- It enables a device to automatically configure an interface to use a straight-through or a crossover cable.
- It enables a device to automatically configure the duplex settings of a segment.
- It enables a device to automatically configure the speed of its interface.
- It enables a switch to dynamically select the forwarding method.
- has a positive impact on bandwidth by dropping most of the invalid frames
- makes a fast forwarding decision based on the source MAC address of the frame
- has a lower latency appropriate for high-performance computing applications
- provides the flexibility to support any mix of Ethernet speeds
- FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF
- 5C-26-0A-4B-19-3E
- 01-00-5E-00-00-03
- 00-26-0F-4B-00-3E

- The woven copper braid should not have been removed.
- The wrong type of connector is being used.
- The untwisted length of each wire is too long.
- The wires are too thick for the connector that is used.

- 1 – rollover, 2 – crossover, 3 – straight-through
- 1 – rollover, 2 – straight-through, 3 – crossover
- 1 – crossover, 2 – straight-through, 3 – rollover
- 1 – crossover, 2 – rollover, 3 – straight-through
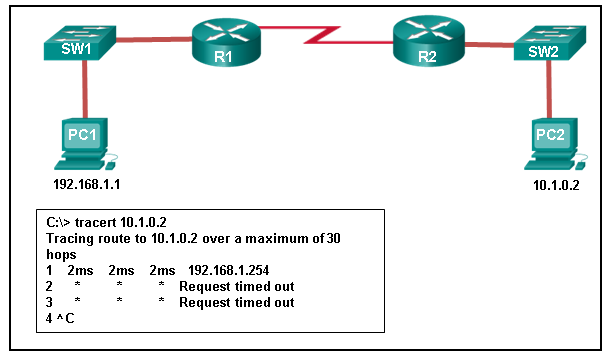
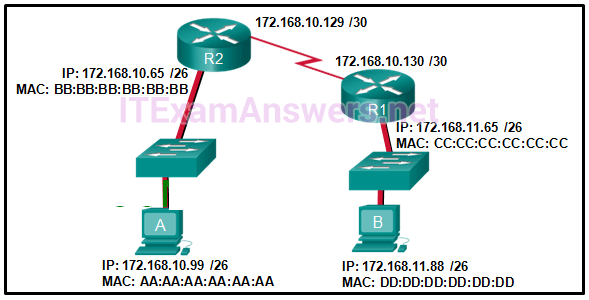
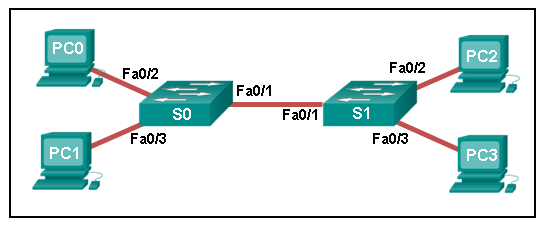
Which port does Switch0 use to send frames to the host with the IPv4 address 10.1.1.5?
- Fa0/1
- Fa0/5
- Fa0/9
- Fa0/11
- loss of signal strength as distance increases
- time for a signal to reach its destination
- leakage of signals from one cable pair to another
- strengthening of a signal by a networking device
- greater distances per cable run
- lower installation cost
- limited susceptibility to EMI/RFI
- durable connections
- greater bandwidth potential
- easily terminated
- modulation
- IEEE
- EIA/TIA
- air
- bandwidth
- IEEE
- EIA/TIA
- air
- bandwidth
- throughput
- latency
- goodput
- throughput
- bandwidth
- latency
- goodput
- latency
- bandwidth
- throughput
- goodput
- latency
- fiber-optic cable
- air
- copper cable
- goodput
- fiber-optic cable
- air
- copper cable
- copper cable
- fiber-optic cable
- air
- goodput
- fiber-optic cable
- goodput
- latency
- throughput
- air
- goodput
- latency
- throughput
- Implements a trailer to detect transmission errors.
- Controls the NIC responsible for sending and receiving data on the physical medium.
- Places information in the frame that identifies which network layer protocol is being used for the frame.
- Adds Layer 2 control information to network protocol data.
- Enables IPv4 and IPv6 to utilize the same network interface and media.
- Enables IPv4 and IPv6 to utilize the same network interface and media.
- Places information in the frame that identifies which network layer protocol is being used for the frame.
- Integrates various physical technologies.
- Implements a process to delimit fields within a Layer 2 frame.
- Controls the NIC responsible for sending and receiving data on the physical medium.
- Provides a mechanism to allow multiple devices to communicate over a shared medium.
- Controls the NIC responsible for sending and receiving data on the physical medium.
- Places information in the frame that identifies which network layer protocol is being used for the frame.
- Adds Layer 2 control information to network protocol data.
- Communicates between the networking software at the upper layers and the device hardware at the lower layers.
- Controls the NIC responsible for sending and receiving data on the physical medium.
- Integrates various physical technologies.
- Communicates between the networking software at the upper layers and the device hardware at the lower layers.
- Adds Layer 2 control information to network protocol data.
- Places information in the frame that identifies which network layer protocol is being used for the frame.
- Adds Layer 2 control information to network protocol data.
- Places information in the frame that identifies which network layer protocol is being used for the frame.
- Performs data encapsulation.
- Controls the NIC responsible for sending and receiving data on the physical medium.
- Integrates various physical technologies.
- Provides synchronization between source and target nodes.
- Integrates various physical technologies.
- Communicates between the networking software at the upper layers and the device hardware at the lower layers.
- Adds Layer 2 control information to network protocol data.
- Enables IPv4 and IPv6 to utilize the same network interface and media.
- Adds Layer 2 control information to network protocol data.
- Enables IPv4 and IPv6 to utilize the same network interface and media.
- Provides data link layer addressing.
- Implements a trailer to detect transmission errors.
- Provides synchronization between source and target nodes.
- Implements a trailer to detect transmission errors.
- Provides synchronization between source and target nodes.
- Places information in the frame that identifies which network layer protocol is being used for the frame.
- Enables IPv4 and IPv6 to utilize the same network interface and media.
- Adds Layer 2 control information to network protocol data.
- Enables IPv4 and IPv6 to utilize the same network interface and media.
- Adds Layer 2 control information to network protocol data.
- Integrates various physical technologies.
- Implements a trailer to detect transmission errors.
- Provides synchronization between source and target nodes.
- Provides a mechanism to allow multiple devices to communicate over a shared medium.
- Controls the NIC responsible for sending and receiving data on the physical medium.
- Places information in the frame that identifies which network layer protocol is being used for the frame.
- Adds Layer 2 control information to network protocol data.
- Enables IPv4 and IPv6 to utilize the same network interface and media.
- The switch refreshes the timer on that entry.
- The switch shares the MAC address table entry with any connected switches.
- The switch does not forward the frame.
- The switch sends the frame to a connected router because the destination MAC address is not local.
- The switch forwards it out all ports except the ingress port.
- The switch shares the MAC address table entry with any connected switches.
- The switch does not forward the frame.
- The switch sends the frame to a connected router because the destination MAC address is not local.
- The host will discard the frame.
- The host sends the frame to the switch to update the MAC address table.
- The host forwards the frame to the router.
- The host forwards the frame to all other hosts.
- The switch forwards it out all ports except the ingress port.
- The switch does not forward the frame.
- The switch sends the frame to a connected router because the destination MAC address is not local.
- The switch shares the MAC address table entry with any connected switches.
- The host will process the frame.
- The host forwards the frame to the router.
- The host sends the frame to the switch to update the MAC address table.
- The host forwards the frame to all other hosts.
- The switch refreshes the timer on that entry.
- The switch adds it to its MAC address table associated with the port number.
- The switch forwards the frame to the associated port.
- The switch sends the frame to a connected router because the destination MAC address is not local.
- The host will process the frame.
- The host returns the frame to the switch.
- The host replies to the switch with its own IP address.
- The host forwards the frame to all other hosts.
- The switch refreshes the timer on that entry.
- The switch shares the MAC address table entry with any connected switches.
- The switch does not forward the frame.
- The switch adds it to its MAC address table associated with the port number.
- The host will discard the frame.
- The host replies to the switch with its own IP address.
- The host forwards the frame to all other hosts.
- The host returns the frame to the switch.
- The switch forwards it out all ports except the ingress port.
- The switch refreshes the timer on that entry.
- The switch does not forward the frame.
- The switch sends the frame to a connected router because the destination MAC address is not local.
- source IP address
- destination IP address
- source data-link address
- destination data-link address
- The packet will be sent to the default gateway first, and then, depending on the response from the gateway, it may be sent to the destination host.
- The packet will be sent directly to the destination host.
- The packet will first be sent to the default gateway, and then from the default gateway it will be sent directly to the destination host.
- The packet will be sent only to the default gateway.
- route the packet out the Gigabit 0/1 interface
- create a new Layer 2 Ethernet frame to be sent to the destination
- look into the ARP cache to determine the destination IP address
- look into the routing table to determine if the destination network is in the routing table
- 126.0.0.1
- 127.0.0.0
- 126.0.0.0
- 127.0.0.1
- The cable is not connected properly to the NIC.
- The computer has an invalid IP address.
- The computer has an incorrect subnet mask.
- The computer has an invalid default gateway address.
- IP encapsulation is modified based on network media.
- IP relies on Layer 2 protocols for transmission error control.
- MAC addresses are used during the IP packet encapsulation.
- IP relies on upper layer services to handle situations of missing or out-of-order packets.
- Because IPv6 has integrated security, there is no need to hide the IPv6 addresses of internal networks.
- Any host or user can get a public IPv6 network address because the number of available IPv6 addresses is extremely large.
- The problems that are induced by NAT applications are solved because the IPv6 header improves packet handling by intermediate routers.
- The end-to-end connectivity problems that are caused by NAT are solved because the number of routes increases with the number of nodes that are connected to the Internet.
- the lower metric value that is associated with the destination network
- the lower gateway IP address to get to the destination network
- the higher metric value that is associated with the destination network
- the higher gateway IP address to get to the destination network
- performing error detection
- routing packets toward the destination
- encapsulating PDUs from the transport layer
- placement of frames on the media
- collision detection
- Hosts that are connected to the switch can use the switch default gateway address to forward packets to a remote destination.
- A switch must have a default gateway to be accessible by Telnet and SSH.
- The default gateway address is used to forward packets originating from the switch to remote networks.
- It provides a next-hop address for all traffic that flows through the switch.
- connectionless
- media dependent
- user data segmentation
- reliable end-to-end delivery
- Time-to-Live
- Sequence Number
- Acknowledgment Number
- Differentiated Services
- smaller-sized header
- little requirement for processing checksums
- smaller-sized source and destination IP addresses
- efficient packet handling
- Protocol
- Identification
- Version
- Differentiated Services
169. What information does the loopback test provide?
- The TCP/IP stack on the device is working correctly.
- The device has end-to-end connectivity.
- DHCP is working correctly.
- The Ethernet cable is working correctly.
- The device has the correct IP address on the network.
- directly-connected routes
- local routes
- remote routes
- C and L source routes
- They have to keep their own local routing table that contains a route to the loopback interface, a local network route, and a remote default route.
- They always direct their packets to the default gateway, which will be responsible for the packet delivery.
- They search in their own local routing table for a route to the network destination address and pass this information to the default gateway.
- They send a query packet to the default gateway asking for the best route.
- Next Header
- Flow Label
- Traffic Class
- Differentiated Services
- ARP is used to discover the IP address of any host on a different network.
- ARP is used to discover the IP address of any host on the local network.
- ARP is used to discover the MAC address of any host on a different network.
- ARP is used to discover the MAC address of any host on the local network.
- The frame has the broadcast address as the destination address.
- The destination address is unknown to the switch.
- The source address in the frame header is the broadcast address.
- The source address in the frame is a multicast address.
- The destination address in the frame is a known unicast address.
- They must be forwarded by all routers on the local network.
- They are received and processed by every device on the local network.
- They are dropped by all switches on the local network.
- They are received and processed only by the target device.
- 0.0.0.0
- 255.255.255.255
- FFFF.FFFF.FFFF
- AAAA.AAAA.AAAA
- the physical address of the destination host
- The ARP cache is cleared.
- The current content of the ARP cache is displayed.
- The detailed information of the ARP cache is displayed.
- The ARP cache is synchronized with the router interface.
- The switch will discard the frame.
- The switch will forward the frame only to port 2.
- The switch will forward the frame to all ports except port 4.
- The switch will forward the frame to all ports.
- The switch will forward the frame only to ports 1 and 3.
- anycast
- broadcast
- echo reply
- echo request
- neighbor solicitation
- neighbor advertisement
- to flood the network with ARP reply broadcasts
- to fill switch MAC address tables with bogus addresses
- to associate IP addresses to the wrong MAC address
- to overwhelm network hosts with ARP requests
- the MAC address of S1
- the MAC address of the G0/0 interface on R1
- the MAC address of the G0/0 interface on R2
- the MAC address of S2
- the MAC address of File_server1
- neighbor table
- ARP cache
- routing table
- MAC address table
- source MAC address
- source IP address
- destination MAC address
- Ethernet type
- destination IP address
185. A new network administrator has been asked to enter a banner message on a Cisco device. What is the fastest way a network administrator could test whether the banner is properly configured?
- Reboot the device.
- Enter CTRL-Z at the privileged mode prompt.
- Exit global configuration mode.
- Power cycle the device.
- Exit privileged EXEC mode and press Enter.

187. Match the phases to the functions during the boot up process of a Cisco router. (Not all options are used.)
188. Match the command with the device mode at which the command is entered. (Not all options are used.)
189. What are two functions of NVRAM? (Choose two.)
- to store the routing table
- to retain contents when power is removed
- to store the startup configuration file
- to contain the running configuration file
- to store the ARP table
- The IOS image is corrupt.
- Cisco IOS is missing from flash memory.
- The configuration file is missing from NVRAM.
- The POST process has detected hardware failure.
- The switch will have a management interface with the address 172.16.100.1.
- The switch can be remotely managed from a host on another network.
- The switch can communicate with other hosts on the 172.16.100.0 network.
- The switch is limited to sending and receiving frames to and from the gateway 172.16.100.1.
- The SSH client on the switch is enabled.
- Communication between the switch and remote users is encrypted.
- The switch requires a username/password combination for remote access.
- The switch requires remote connections via a proprietary client software.

- 172.24.255.17
- 172.24.1.22
- 172.20.0.254
- 172.24.255.4
- 172.20.1.18
195. Which three commands are used to set up secure access to a router through a connection to the console interface? (Choose three.)
- interface fastethernet 0/0
- line vty 0 4
- line console 0
- enable secret cisco
- login
- password cisco
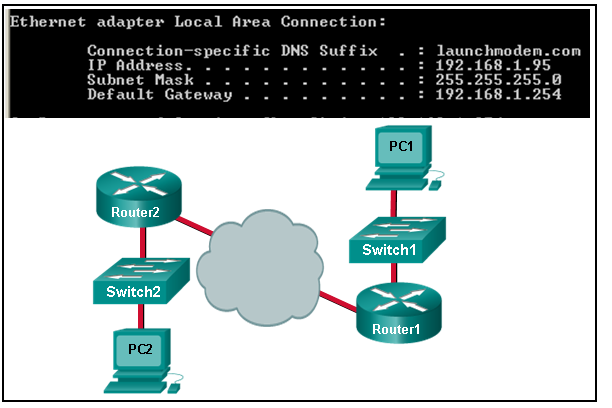
- It is the IP address of the Router1 interface that connects the company to the Internet.
- It is the IP address of the Router1 interface that connects the PC1 LAN to Router1.
- It is the IP address of Switch1 that connects PC1 to other devices on the same LAN.
- It is the IP address of the ISP network device located in the cloud.
- packet forwarding
- microsegmentation
- domain name resolution
- path selection
- flow control
- The contents of ROM will change.
- The contents of RAM will change.
- The contents of NVRAM will change.
- The contents of flash will change.
- The host cannot communicate with other hosts in the local network.
- The switch will not forward packets initiated by the host.
- The host will have to use ARP to determine the correct address of the default gateway.
- The host cannot communicate with hosts in other networks.
- A ping from the host to 127.0.0.1 would not be successful.
- Manually configuring static ARP associations could facilitate ARP poisoning or MAC address spoofing.
- On large networks with low bandwidth, multiple ARP broadcasts could cause data communication delays.
- Network attackers could manipulate MAC address and IP address mappings in ARP messages with the intent of intercepting network traffic.
- Large numbers of ARP request broadcasts could cause the host MAC address table to overflow and prevent the host from communicating on the network.
- Multiple ARP replies result in the switch MAC address table containing entries that match the MAC addresses of hosts that are connected to the relevant switch port.
Which interfaces in each router are active and operational?
- R1: G0/0 and S0/0/0
R2: G0/0 and S0/0/0 - R1: G0/1 and S0/0/1
R2: G0/0 and S0/0/1 - R1: G0/0 and S0/0/0
R2: G0/1 and S0/0/0 - R1: G0/0 and S0/0/1
R2: G0/1 and S0/0/1
- protocol
- destination IPv4 address
- source IPv4 address
- TTL
- differentiated services
- destination IPv4 address
- source IPv4 address
- protocol
- source IPv4 address
- destination IPv4 address
- protocol
- TTL
- header checksum
- source IPv4 address
- protocol
- TTL
RTR1(config)# interface gi0/1 RTR1(config-if)# description Connects to the Marketing LAN RTR1(config-if)# ip address 10.27.15.17 255.255.255.0 RTR1(config-if)# no shutdown RTR1(config-if)# interface gi0/0 RTR1(config-if)# description Connects to the Payroll LAN RTR1(config-if)# ip address 10.27.14.148 255.255.255.0 RTR1(config-if)# no shutdown RTR1(config-if)# interface s0/0/0 RTR1(config-if)# description Connects to the ISP RTR1(config-if)# ip address 10.14.15.254 255.255.255.0 RTR1(config-if)# no shutdown RTR1(config-if)# interface s0/0/1 RTR1(config-if)# description Connects to the Head Office WAN RTR1(config-if)# ip address 203.0.113.39 255.255.255.0 RTR1(config-if)# no shutdown RTR1(config-if)# endRefer to the exhibit. A network administrator is connecting a new host to the Payroll LAN. The host needs to communicate with remote networks. What IP address would be configured as the default gateway on the new host?
- 10.27.14.148
- 10.27.14.1
- 10.14.15.254
- 203.0.113.39
- 10.27.15.17
- destination IPv4 address
- protocol
- TTL
- header checksum
- TTL
- source IPv4 address
- protocol
- header checksum
- version
- source IPv4 address
- protocol
- TTL
- protocol
- version
- differentiated services
- header checksum
- version
- differentiated services
- header checksum
- TTL
- Entries in an ARP table are time-stamped and are purged after the timeout expires.
- A static IP-to-MAC address entry can be entered manually into an ARP table.
- The type field 0x806 appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
- The port-to-MAC address table on a switch has the same entries as the ARP table on the switch.
- A static IP-to-MAC address entry can be entered manually into an ARP table.
- Entries in an ARP table are time-stamped and are purged after the timeout expires.
- The type field 0x806 appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
- The port-to-MAC address table on a switch has the same entries as the ARP table on the switch.
- A static IP-to-MAC address entry can be entered manually into an ARP table.
- The destination MAC address FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
- The source MAC address appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
- The port-to-MAC address table on a switch has the same entries as the ARP table on the switch.
- Local hosts learn the MAC address of the default gateway.
- The destination MAC address FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
- The source MAC address appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
- The port-to-MAC address table on a switch has the same entries as the ARP table on the switch.
Floor(config)# interface gi0/1 Floor(config-if)# description Connects to the Registrar LAN Floor(config-if)# ip address 192.168.235.234 255.255.255.0 Floor(config-if)# no shutdown Floor(config-if)# interface gi0/0 Floor(config-if)# description Connects to the Manager LAN Floor(config-if)# ip address 192.168.234.114 255.255.255.0 Floor(config-if)# no shutdown Floor(config-if)# interface s0/0/0 Floor(config-if)# description Connects to the ISP Floor(config-if)# ip address 10.234.235.254 255.255.255.0 Floor(config-if)# no shutdown Floor(config-if)# interface s0/0/1 Floor(config-if)# description Connects to the Head Office WAN Floor(config-if)# ip address 203.0.113.3 255.255.255.0 Floor(config-if)# no shutdown Floor(config-if)# endRefer to the exhibit. A network administrator is connecting a new host to the Registrar LAN. The host needs to communicate with remote networks. What IP address would be configured as the default gateway on the new host?
- 192.168.235.234
- 192.168.235.1
- 10.234.235.254
- 203.0.113.3
- 192.168.234.114
- The destination MAC address FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
- The source MAC address appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
- The type field 0x806 appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
- ARP replies are broadcast on the network when a host receives an ARP request.
- The source MAC address appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
- The destination MAC address FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
- The type field 0x806 appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
- ARP replies are broadcast on the network when a host receives an ARP request.
- The destination MAC address FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
- The type field 0x806 appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
- Entries in an ARP table are time-stamped and are purged after the timeout expires.
- ARP replies are broadcast on the network when a host receives an ARP request.
- The type field 0x806 appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
- The destination MAC address FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
- Entries in an ARP table are time-stamped and are purged after the timeout expires.
- ARP replies are broadcast on the network when a host receives an ARP request.
- The type field 0x806 appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
- The destination MAC address FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
- Entries in an ARP table are time-stamped and are purged after the timeout expires.
- The port-to-MAC address table on a switch has the same entries as the ARP table on the switch.
Main(config)# interface gi0/1 Main(config-if)# description Connects to the Service LAN Main(config-if)# ip address 172.29.157.156 255.255.255.0 Main(config-if)# no shutdown Main(config-if)# interface gi0/0 Main(config-if)# description Connects to the Engineering LAN Main(config-if)# ip address 172.29.156.36 255.255.255.0 Main(config-if)# no shutdown Main(config-if)# interface s0/0/0 Main(config-if)# description Connects to the ISP Main(config-if)# ip address 10.156.157.254 255.255.255.0 Main(config-if)# no shutdown Main(config-if)# interface s0/0/1 Main(config-if)# description Connects to the Head Office WAN Main(config-if)# ip address 198.51.100.177 255.255.255.0 Main(config-if)# no shutdown Main(config-if)# endRefer to the exhibit. A network administrator is connecting a new host to the Service LAN. The host needs to communicate with remote networks. What IP address would be configured as the default gateway on the new host?
- 172.29.157.156
- 172.29.157.1
- 10.156.157.254
- 198.51.100.177
- 172.29.156.36
BldgA(config)# interface gi0/1 BldgA(config-if)# description Connects to the Medical LAN BldgA(config-if)# ip address 192.168.191.189 255.255.255.0 BldgA(config-if)# no shutdown BldgA(config-if)# interface gi0/0 BldgA(config-if)# description Connects to the Client LAN BldgA(config-if)# ip address 192.168.190.70 255.255.255.0 BldgA(config-if)# no shutdown BldgA(config-if)# interface s0/0/0 BldgA(config-if)# description Connects to the ISP BldgA(config-if)# ip address 10.190.191.254 255.255.255.0 BldgA(config-if)# no shutdown BldgA(config-if)# interface s0/0/1 BldgA(config-if)# description Connects to the Head Office WAN BldgA(config-if)# ip address 198.51.100.213 255.255.255.0 BldgA(config-if)# no shutdown BldgA(config-if)# endRefer to the exhibit. A network administrator is connecting a new host to the Medical LAN. The host needs to communicate with remote networks. What IP address would be configured as the default gateway on the new host?
- 192.168.191.189
- 192.168.191.1
- 10.190.191.254
- 198.51.100.213
- 192.168.190.70
Floor(config)# interface gi0/1 Floor(config-if)# description Connects to the Registrar LAN Floor(config-if)# ip address 192.168.225.223 255.255.255.0 Floor(config-if)# no shutdown Floor(config-if)# interface gi0/0 Floor(config-if)# description Connects to the Manager LAN Floor(config-if)# ip address 192.168.224.103 255.255.255.0 Floor(config-if)# no shutdown Floor(config-if)# interface s0/0/0 Floor(config-if)# description Connects to the ISP Floor(config-if)# ip address 10.224.225.254 255.255.255.0 Floor(config-if)# no shutdown Floor(config-if)# interface s0/0/1 Floor(config-if)# description Connects to the Head Office WAN Floor(config-if)# ip address 203.0.113.246 255.255.255.0 Floor(config-if)# no shutdown Floor(config-if)# endRefer to the exhibit. A network administrator is connecting a new host to the Registrar LAN. The host needs to communicate with remote networks. What IP address would be configured as the default gateway on the new host?
- 192.168.225.223
- 192.168.225.1
- 10.224.225.254
- 203.0.113.246
- 192.168.224.103
Floor(config)# interface gi0/1 Floor(config-if)# description Connects to the Registrar LAN Floor(config-if)# ip address 10.118.63.65 255.255.255.0 Floor(config-if)# no shutdown Floor(config-if)# interface gi0/0 Floor(config-if)# description Connects to the Manager LAN Floor(config-if)# ip address 10.118.62.196 255.255.255.0 Floor(config-if)# no shutdown Floor(config-if)# interface s0/0/0 Floor(config-if)# description Connects to the ISP Floor(config-if)# ip address 10.62.63.254 255.255.255.0 Floor(config-if)# no shutdown Floor(config-if)# interface s0/0/1 Floor(config-if)# description Connects to the Head Office WAN Floor(config-if)# ip address 209.165.200.87 255.255.255.0 Floor(config-if)# no shutdown Floor(config-if)# endRefer to the exhibit. A network administrator is connecting a new host to the Manager LAN. The host needs to communicate with remote networks. What IP address would be configured as the default gateway on the new host?
- 10.118.62.196
- 10.118.62.1
- 10.62.63.254
- 209.165.200.87
- 10.118.63.65
HQ(config)# interface gi0/1 HQ(config-if)# description Connects to the Branch LAN HQ(config-if)# ip address 172.19.99.99 255.255.255.0 HQ(config-if)# no shutdown HQ(config-if)# interface gi0/0 HQ(config-if)# description Connects to the Store LAN HQ(config-if)# ip address 172.19.98.230 255.255.255.0 HQ(config-if)# no shutdown HQ(config-if)# interface s0/0/0 HQ(config-if)# description Connects to the ISP HQ(config-if)# ip address 10.98.99.254 255.255.255.0 HQ(config-if)# no shutdown HQ(config-if)# interface s0/0/1 HQ(config-if)# description Connects to the Head Office WAN HQ(config-if)# ip address 209.165.200.120 255.255.255.0 HQ(config-if)# no shutdown HQ(config-if)# endRefer to the exhibit. A network administrator is connecting a new host to the Store LAN. The host needs to communicate with remote networks. What IP address would be configured as the default gateway on the new host?
- 172.19.98.230
- 172.19.98.1
- 10.98.99.254
- 209.165.200.120
- 172.19.99.99
HQ(config)# interface gi0/1 HQ(config-if)# description Connects to the Branch LAN HQ(config-if)# ip address 172.20.133.132 255.255.255.0 HQ(config-if)# no shutdown HQ(config-if)# interface gi0/0 HQ(config-if)# description Connects to the Store LAN HQ(config-if)# ip address 172.20.132.13 255.255.255.0 HQ(config-if)# no shutdown HQ(config-if)# interface s0/0/0 HQ(config-if)# description Connects to the ISP HQ(config-if)# ip address 10.132.133.254 255.255.255.0 HQ(config-if)# no shutdown HQ(config-if)# interface s0/0/1 HQ(config-if)# description Connects to the Head Office WAN HQ(config-if)# ip address 198.51.100.156 255.255.255.0 HQ(config-if)# no shutdown HQ(config-if)# endRefer to the exhibit. A network administrator is connecting a new host to the Store LAN. The host needs to communicate with remote networks. What IP address would be configured as the default gateway on the new host?
- 172.20.132.13
- 172.20.132.1
- 10.132.133.254
- 198.51.100.156
- 172.20.133.132
Main(config)# interface gi0/1 Main(config-if)# description Connects to the Service LAN Main(config-if)# ip address 192.168.167.166 255.255.255.0 Main(config-if)# no shutdown Main(config-if)# interface gi0/0 Main(config-if)# description Connects to the Engineering LAN Main(config-if)# ip address 192.168.166.46 255.255.255.0 Main(config-if)# no shutdown Main(config-if)# interface s0/0/0 Main(config-if)# description Connects to the ISP Main(config-if)# ip address 10.166.167.254 255.255.255.0 Main(config-if)# no shutdown Main(config-if)# interface s0/0/1 Main(config-if)# description Connects to the Head Office WAN Main(config-if)# ip address 198.51.100.189 255.255.255.0 Main(config-if)# no shutdown Main(config-if)# endRefer to the exhibit. A network administrator is connecting a new host to the Service LAN. The host needs to communicate with remote networks. What IP address would be configured as the default gateway on the new host?
- 192.168.167.166
- 192.168.167.1
- 10.166.167.254
- 198.51.100.189
- 192.168.166.46
BldgA(config)# interface gi0/1 BldgA(config-if)# description Connects to the Medical LAN BldgA(config-if)# ip address 192.168.201.200 255.255.255.0 BldgA(config-if)# no shutdown BldgA(config-if)# interface gi0/0 BldgA(config-if)# description Connects to the Client LAN BldgA(config-if)# ip address 192.168.200.80 255.255.255.0 BldgA(config-if)# no shutdown BldgA(config-if)# interface s0/0/0 BldgA(config-if)# description Connects to the ISP BldgA(config-if)# ip address 10.200.201.254 255.255.255.0 BldgA(config-if)# no shutdown BldgA(config-if)# interface s0/0/1 BldgA(config-if)# description Connects to the Head Office WAN BldgA(config-if)# ip address 203.0.113.222 255.255.255.0 BldgA(config-if)# no shutdown BldgA(config-if)# endRefer to the exhibit. A network administrator is connecting a new host to the Medical LAN. The host needs to communicate with remote networks. What IP address would be configured as the default gateway on the new host?
- 192.168.201.200
- 192.168.201.1
- 10.200.201.254
- 203.0.113.222
- 192.168.200.80
Which interfaces in each router are active and operational?

CCNA 1 v7 Modules 8 – 10 Communicating Between Networks Exam
R2: G0/1 and S0/0/1
R1: G0/1 and S0/0/1
R2: G0/0 and S0/0/1
R1: G0/0 and S0/0/0
R2: G0/1 and S0/0/0
R1: G0/0 and S0/0/0
R2: G0/0 and S0/0/0
231. What is the prefix length notation for the subnet mask 255.255.255.224?
- /25
- /26
- /27
- /28
- 254
- 190
- 192
- 62
- 64
- 255.255.255.0
- 255.255.255.128
- 255.255.255.224
- 255.255.255.240
- 1
- 2
- 4
- 8
- 16
- 64
236. An administrator wants to create four subnetworks from the network address 192.168.1.0/24. What is the network address and subnet mask of the second useable subnet?
- subnetwork 192.168.1.64
subnet mask 255.255.255.192 - subnetwork 192.168.1.32
subnet mask 255.255.255.240 - subnetwork 192.168.1.64
subnet mask 255.255.255.240 - subnetwork 192.168.1.128
subnet mask 255.255.255.192 - subnetwork 192.168.1.8
subnet mask 255.255.255.224
- two
- three
- four
- five
- 30
- 32
- 60
- 62
- 64
- 510
- 512
- 1022
- 1024
- 2046
- 2048
241. What three blocks of addresses are defined by RFC 1918 for private network use? (Choose three.)
- 10.0.0.0/8
- 172.16.0.0/12
- 192.168.0.0/16
- 100.64.0.0/14
- 169.254.0.0/16
- 239.0.0.0/8

- 172.16.16.255
- 172.16.20.255
- 172.16.19.255
- 172.16.23.255
- 172.16.255.255
- 255.255.255.0
- 255.255.255.128
- 255.255.255.224
- 255.255.255.240
- 10.16.10.160/26
- 10.16.10.128/28
- 10.16.10.64/27
- 10.16.10.224/26
- 10.16.10.240/27
- 10.16.10.240/28
- 256
- 254
- 64
- 62
- 32
- 16
- 240.0.0.0 – 254.255.255.255
- 224.0.0.0 – 239.255.255.255
- 169.254.0.0 – 169.254.255.255
- 127.0.0.0 – 127.255.255.255


248. A high school in New York (school A) is using videoconferencing technology to establish student interactions with another high school (school B) in Russia. The videoconferencing is conducted between two end devices through the Internet. The network administrator of school A configures the end device with the IP address 209.165.201.10. The administrator sends a request for the IP address for the end device in school B and the response is 192.168.25.10. Neither school is using a VPN. The administrator knows immediately that this IP will not work. Why?
- This is a loopback address.
- This is a link-local address.
- This is a private IP address.
- There is an IP address conflict.
- 198.133.219.17
- 192.168.1.245
- 10.15.250.5
- 128.107.12.117
- 172.31.1.25
- 64.104.78.227
- limited broadcast
- multicast
- directed broadcast
- unicast
- 192.168.1.16/28
- 192.168.1.64/27
- 192.168.1.128/27
- 192.168.1.96/28
- 192.168.1.192/28
- FEC8:1::FFFF
- FD80::1:1234
- FE80::1:4545:6578:ABC1
- FE0A::100:7788:998F
- FC90:5678:4251:FFFF
3FFE:1044:0000:0000:00AB:0000:0000:0057?
- 3FFE:1044::AB::57
- 3FFE:1044::00AB::0057
- 3FFE:1044:0:0:AB::57
- 3FFE:1044:0:0:00AB::0057
- 3FFE:1044:0000:0000:00AB::57
- 3FFE:1044:0000:0000:00AB::0057
- 16
- 256
- 4096
- 65536
- 2001:db8:0:f00::/52
- 2001:db8:0:8000::/52
- 2001:db8:0:f::/52
- 2001:db8:0:f000::/52
2001:0DB8:BC15:00A0:0000::
2001:0DB8:BC15:00A1:0000::
2001:0DB8:BC15:00A2:0000::
…
2001:0DB8:BC15:00AF:0000::
The prefix-length for the range of addresses is /60 .
257. What type of IPv6 address is FE80::1?
- loopback
- link-local
- multicast
- global unicast
- 0
- 4
- 16
- 256
- the MAC address of the IPv6 enabled interface
- a randomly generated 64-bit hexadecimal address
- an IPv6 address that is provided by a DHCPv6 server
- an IPv4 address that is configured on the interface
- 2001:DB8:BC15
- 2001:DB8:BC15:A
- 2001:DB8:BC15:A:1
- 2001:DB8:BC15:A:12
- the one IPv6 device on the link that has been uniquely configured with this address
- all IPv6 enabled devices on the local link or network
- only IPv6 DHCP servers
- only IPv6 configured routers
263. Which IPv6 prefix is reserved for communication between devices on the same link?
- FC00::/7
- 2001::/32
- FE80::/10
- FDFF::/7
- unique local
- global unicast
- link-local
- anycast
- multicast
- loopback
- link-local
- anycast
- broadcast
- stateful DHCPv6
- SLAAC
- static IPv6 addressing
- stateless DHCPv6
- ARPv6
- DHCPv6
- ICMPv6
- UDP
269. A technician uses the ping 127.0.0.1 command. What is the technician testing?
- the TCP/IP stack on a network host
- connectivity between two adjacent Cisco devices
- connectivity between a PC and the default gateway
- connectivity between two PCs on the same network
- physical connectivity of a particular PC and the network

- PC2
- R1
- SW2
- R2
- SW1
- SNMP
- ICMP
- Telnet
- TCP
- network unreachable
- time exceeded
- protocol unreachable
- port unreachable
- when the value of the Hop Limit field reaches 255
- when the value of the Hop Limit field reaches zero
- when the router receives an ICMP time exceeded message
- when the target host responds with an ICMP echo reply message
- to inform routers about network topology changes
- to ensure the delivery of an IP packet
- to provide feedback of IP packet transmissions
- to monitor the process of a domain name to IP address resolution
- the highest configured IP address on the router
- a loopback IP address
- the IP address of the outbound interface
- the lowest configured IP address on the router

277. A user issues a ping 192.135.250.103 command and receives a response that includes a code of 1. What does this code represent?
- host unreachable
- protocol unreachable
- port unreachable
- network unreachable
- 192.168.1.64/26
- 192.168.1.32/27
- 192.168.1.32/28
- 192.168.1.64/29

CCNA 1 v7 Modules 11 – 13 IP Addressing Exam Answers Full
- 2001:DB8:1:1::1
- 2001:DB8:1:1::A
- 2001:DB8:1:2::2
- 2001:DB8:1:2::1
- 2001:DB8:1:3::1
- 2001:DB8:1:3::2
- 2001:DB8:1:4::1
- all hosts in the same subnet
- a specially defined group of hosts
- the closest neighbor on the same network
- all hosts on the Internet
- one specific host
- a specially defined group of hosts
- all hosts on the Internet
- the closest neighbor on the same network
- address unreachable
- network unreachable
- host unreachable
- protocol unreachable
- a specially defined group of hosts
- one specific host
- all hosts with the same IP address
- the closest neighbor on the same network
- a specially defined group of hosts
- one specific host
- directly connected network devices
- the closest neighbor on the same network
- a specially defined group of hosts
- one specific host
- all hosts with the same IP address
- all hosts on the Internet
- a specially defined group of hosts
- one specific host
- directly connected network devices
- all hosts on the Internet
- a specially defined group of hosts
- all hosts in the same subnet
- directly connected network devices
- the closest neighbor on the same network
- all hosts in the same subnet
- one specific host
- the closest neighbor on the same network
- directly connected network devices
- all hosts in the same subnet
- one specific host
- all hosts on the Internet
- directly connected network devices
- 2001:db8::a0b0:8:1
- 2001:db8::ab8:1:0:1000
- 2001:db80:0:1::80:1
- 2001:db80:::1::80:1
- fe80:9ea:0:2200::fe0:290
- fe80:9:20::b000:290
- fe80:9ea0::2020:0:bf:e0:9290
- fe80:9ea0::2020::bf:e0:9290
- 2002:42:10:c400::909
- 200:420:110:c4b::910:0:90
- 2002:4200::25:1090:0:99
- 2002:42::25:1090:0:99
- 2001:db8::ab8:1:0:1000
- 2001:db8::a0b0:8:1
- 2001:db8:1::ab8:0:1
- 2001:db8:0:1::8:1
- 2002:420:c4:1008:25:190::990
- 2002:42:10:c400::909
- 2002:4200::25:1090:0:99
- 2002:42::25:1090:0:99
- 2001:db8::a0b0:8:1
- 2001:db8:1::ab8:0:1
- 2001:db8::ab8:1:0:1000
- 2001:db8:0:1::8:1
- fe80::220:b3f:f0e0:29
- fe80:9ea:0:2200::fe0:290
- fe80:9ea0::2020:0:bf:e0:9290
- fe80:9ea0::2020::bf:e0:9290
- 2001:db8::a0b0:8:1
- 2001:db8::ab8:1:0:1000
- 2001:db80:0:1::80:1
- 2001:db8:0:1::8:1
- 2002:42:10:c400::909
- 2002:4200::25:1090:0:99
- 2002:420:c4:1008:25:190::990
- 2002:42::25:1090:0:99
- fe80:9ea:0:2200::fe0:290
- fe80:9ea0::2020:0:bf:e0:9290
- fe80::220:b3f:f0e0:29
- fe80::0220:0b3f:f0e0:0029
- beyond scope of the source address
- communication with the destination administratively prohibited
- address unreachable
- no route to destination
- host unreachable
- beyond scope of the source address
- address unreachable
- communication with the destination administratively prohibited
- address unreachable
- communication with the destination administratively prohibited
- beyond scope of the source address
- no route to destination
- network unreachable
- protocol unreachable
- port unreachable
- host unreachable
- port unreachable
- host unreachable
- protocol unreachable
- network unreachable
- network unreachable
- protocol unreachable
- port unreachable
- host unreachable
- port unreachable
- host unreachable
- protocol unreachable
- network unreachable
- beyond scope of the source address
- host unreachable
- protocol unreachable
- network unreachable
- The client sets the window size for the session.
- The client sends an ISN to the server to start the 3-way handshake.
- The client randomly selects a source port number.
- The client sends a synchronization segment to begin the session.
- UDP ACK flag
- TCP 3-way handshake
- UDP sequence number
- TCP port number
- 0 to 255
- 0 to 1023
- 256 – 1023
- 1024 – 49151
- the combination of the source and destination IP address and source and destination Ethernet address
- the combination of a source IP address and port number or a destination IP address and port number
- the combination of the source and destination sequence and acknowledgment numbers
- the combination of the source and destination sequence numbers and port numbers
- 1 segment
- 10 segments
- 100 segments
- 1000 segments
- the amount of data to be transmitted
- the number of services included in the TCP segment
- the amount of data the destination can process at one time
- the amount of data the source is capable of sending at one time
- It just sends the datagrams.
- It queries the server to see if it is ready to receive data.
- It sends a simplified three-way handshake to the server.
- It sends to the server a segment with the SYN flag set to synchronize the conversation.
- Window Size
- Length
- Source Port
- Acknowledgment Number
- Checksum
- Sequence Number
- identifying the proper application for each communication stream
- tracking the individual communication between applications on the source and destination hosts
- providing frame delimiting to identify bits making up a frame
- performing a cyclic redundancy check on the frame for errors
- providing the interface between applications and the underlying network over which messages are transmitted
- port numbers
- sequence numbers
- acknowledgment numbers
- fragment numbers
- timing and synchronization
- destination and source port numbers
- destination and source physical addresses
- destination and source logical network addresses
- Destination devices receive traffic with minimal delay.
- Transmitted data segments are tracked.
- Destination devices reassemble messages and pass them to an application.
- Received data is unacknowledged.
- Unacknowledged data packets are retransmitted.

321. Which flag in the TCP header is used in response to a received FIN in order to terminate connectivity between two network devices?
- FIN
- ACK
- SYN
- RST
- HTTP
- FTP
- DNS
- SMTP
- UDP datagrams take the same path and arrive in the correct order at the destination.
- Applications that use UDP are always considered unreliable.
- UDP reassembles the received datagrams in the order they were received.
- UDP only passes data to the network when the destination is ready to receive the data.
- registered port
- private port
- dynamic port
- source port
- SMTP
- FTP
- SNMP
- HTTP
- TFTP
- DHCP
- UDP provides basic connectionless transport layer functions.
- UDP provides connection-oriented, fast transport of data at Layer 3.
- UDP relies on application layer protocols for error detection.
- UDP is a low overhead protocol that does not provide sequencing or flow control mechanisms.
- UDP relies on IP for error detection and recovery.
- UDP provides sophisticated flow control mechanisms.
- window
- checksum
- source port
- destination port
- sequence number
- window
- reserved
- checksum
- control bits
- to ensure the fastest possible download speed
- because HTTP is a best-effort protocol
- because transmission errors can be tolerated easily
- because HTTP requires reliable delivery
- applications that need data flow control
- applications that require reliable delivery
- applications that handle reliability themselves
- applications that need the reordering of segments
- applications that can tolerate some data loss, but require little or no delay
- Source port numbers and destination port numbers are not necessary when UDP is the transport layer protocol being used for the communication.
- Source port and destination port numbers are randomly generated.
- If multiple conversations occur that are using the same service, the source port number is used to track the separate conversations.
- Destination port numbers are assigned automatically and cannot be changed.
- when applications need to guarantee that a packet arrives intact, in sequence, and unduplicated
- when a faster delivery mechanism is needed
- when delivery overhead is not an issue
- when applications do not need to guarantee delivery of the data
- when destination port numbers are dynamic
- meeting the reliability requirements of applications, if any
- multiplexing multiple communication streams from many users or applications on the same network
- identifying the applications and services on the client and server that should handle transmitted data
- directing packets towards the destination network
- formatting data into a compatible form for receipt by the destination devices
- conducting error detection of the contents in frames
- The source MAC address is 48 ones (FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF).
- The destination IP address is 255.255.255.255.
- The message comes from a server offering an IP address.
- The message comes from a client seeking an IP address.
- All hosts receive the message, but only a DHCP server replies.
- Only the DHCP server receives the message.
- HTTP
- SMTP
- POP
- IMAP
- DNS
- POP3
- Different SMB message types have a different format.
- Clients establish a long term connection to servers.
- SMB messages cannot authenticate a session.
- SMB uses the FTP protocol for communication.
- to request an HTML page from a web server
- to send error information from a web server to a web client
- to upload content to a web server from a web client
- to retrieve client email from an email server using TCP port 110
- application
- presentation
- session
- transport
- peer-to-peer
- master-slave
- client/server
- point-to-point
- Both models have dedicated servers.
- Both models support devices in server and client roles.
- Both models require the use of TCP/IP-based protocols.
- Both models are used only in the wired network environment.
- peer-to-peer
- client-based
- master-slave
- point-to-point
- Ethernet
- Gnutella
- POP
- SMTP
- wireless networking
- social networking without the Internet
- network printing using a print server
- resource sharing without a dedicated server
- physical
- session
- network
- presentation
- data link
- transport
- application
- A user uses eMule to download a file that is shared by a friend after the file location is determined.
- A workstation initiates an ARP to find the MAC address of a receiving host.
- A user prints a document by using a printer that is attached to a workstation of a coworker.
- A workstation initiates a DNS request when the user types www.cisco.com in the address bar of a web browser.
- internetwork
- session
- presentation
- application
- network access
- Only with SMB can data transfers occur in both directions.
- Only SMB establishes two simultaneous connections with the client, making the data transfer faster.
- SMB is more reliable than FTP because SMB uses TCP and FTP uses UDP.
- SMB clients can establish a long-term connection to the server.
- FTP
- HTTP
- DNS
- SNMP
- DHCP
- SMTP
- DNS
- DHCP
- SMTP
- HTTP
- POP3
- the FQDN of the alias used to identify a service
- the IP address for an FQDN entry
- the domain name mapped to mail exchange servers
- the IP address of an authoritative name server
- ARP
- TCP
- UDP
- FTP
- POP3
- DHCP
- SMTP
- SMB
- IMAP
- HTTPS
- client/server applications
- email applications
- P2P applications
- authentication services
- scalability
- one way data flow
- decentralized resources
- centralized user accounts
- resource sharing without a dedicated server
- A student is using a classroom VoIP phone to call home. The unique identifier burned into the phone is a transport layer address used to contact another network device on the same network.
- A student is playing a short web-based movie with sound. The movie and sound are encoded within the transport layer header.
- A student has two web browser windows open in order to access two web sites. The transport layer ensures the correct web page is delivered to the correct browser window.
- A corporate worker is accessing a web server located on a corporate network. The transport layer formats the screen so the web page appears properly no matter what device is being used to view the web site.
- physical layer
- session layer
- transport layer
- application layer
- presentation layer
- data link layer
- 3001
- 6001
- 4500
- 6000
- 4501
- 6001
- 6000
- 4500
- 6001
- 3001
- 1501
- 1500
- 6001
- 3001
- 3000
- 1500
- 3001
- 4501
- 3000
- 1500
- 3001
- 4501
- 4500
- 1500
- 3001
- 6001
- 4500
- 3000
- 3001
- 6001
- 6000
- 3000
- 4501
- 6001
- 6000
- 3000
- 4501
- 6001
- 1500
- 4500
- 69
- 67
- 53
- 80
- 21
- 69
- 67
- 80
- 22
- 69
- 67
- 80
- 80
- 67
- 53
- 69
- 110
- 67
- 53
- 69
- 23
- 443
- 161
- 110
- 110
- 443
- 161
- 80
- 161
- 443
- 110
- 80
- 25
- 443
- 161
- 110
- 443
- 161
- 110
- 80
- security center
- port scanner
- antimalware
- antivirus
- firewall
- RouterA(config)# login block-for 10 attempts 2 within 30
- RouterA(config)# login block-for 30 attempts 2 within 10
- RouterA(config)# login block-for 2 attempts 30 within 10
- RouterA(config)# login block-for 30 attempts 10 within 2
- to require users to prove who they are
- to determine which resources a user can access
- to keep track of the actions of a user
- to provide challenge and response questions
- access attack
- reconnaissance attack
- denial of service attack
- worm attack

382. Match the type of information security threat to the scenario. (Not all options are used.)

383. Which example of malicious code would be classified as a Trojan horse?
- malware that was written to look like a video game
- malware that requires manual user intervention to spread between systems
- malware that attaches itself to a legitimate program and spreads to other programs when launched
- malware that can automatically spread from one system to another by exploiting a vulnerability in the target
- Viruses self-replicate but worms do not.
- Worms self-replicate but viruses do not.
- Worms require a host file but viruses do not.
- Viruses hide in legitimate programs but worms do not.
- denial-of-service
- man-in-the-middle attack
- extraction of security parameters
- username enumeration
- reconnaissance
- DoS
- dictionary
- man-in-the-middle

388. What is the purpose of the network security authentication function?
- to require users to prove who they are
- to determine which resources a user can access
- to keep track of the actions of a user
- to provide challenge and response questions
- stateful packet inspection
- URL filtering
- application filtering
- packet filtering
- exec-timeout 30
- service password-encryption
- banner motd $Max failed logins = 5$
- login block-for 60 attempts 5 within 60

392. What feature of SSH makes it more secure than Telnet for a device management connection?
- confidentiality with IPsec
- stronger password requirement
- random one-time port connection
- login information and data encryption
- SSH is easier to use.
- SSH operates faster than Telnet.
- SSH provides secure communications to access hosts.
- SSH supports authentication for a connection request.
- detecting and blocking of attacks in real time
- connecting global threat information to Cisco network security devices
- authenticating and validating traffic
- filtering of nefarious websites
- attack based
- risk based
- structured
- layered
- configuring a router with a complete MAC address database to ensure that all frames can be forwarded to the correct destination
- configuring a switch with proper security to ensure that all traffic forwarded through an interface is filtered
- designing a network to use multiple virtual devices to ensure that all traffic uses the best path through the internetwork
- designing a network to use multiple paths between switches to ensure there is no single point of failure
- voice
- video
- instant messaging
- FTP
- SNMP
- to identify the source and destination of local network traffic
- to capture the Internet connection bandwidth requirement
- to document and analyze network traffic requirements on each network segment
- to establish a baseline for security analysis after the network is upgraded

- Connectivity to the remote device was successful.
- A router along the path did not have a route to the destination.
- A ping packet is being blocked by a security device along the path.
- The connection timed out while waiting for a reply from the remote device.
- Issue the ping command from within interface configuration mode.
- Issue the ping command without specifying a destination IP address.
- Issue the ping command without extended commands.
- Issue the ping command after shutting down un-needed interfaces.
- a change in the bandwidth according to the show interfaces output
- a next-hop timeout from a traceroute
- an increase in host-to-host ping response times
- a change in the amount of RAM according to the show version output
- ‘!’ indicates that the ping was unsuccessful and that the device may have issues finding a DNS server.
- ‘U’ may indicate that a router along the path did not contain a route to the destination address and that the ping was unsuccessful.
- ‘.’ indicates that the ping was successful but the response time was longer than normal.
- A combination of ‘.’ and ‘!’ indicates that a router along the path did not have a route to the destination address and responded with an ICMP unreachable message.
- The NIC in the PC is bad.
- The TCP/IP protocol is not enabled.
- The router that is attached to the same network as the workstation is down.
- Nothing can be determined for sure at this point.
- It forces the trace to use IPv6.
- It limits the trace to only 6 hops.
- It sets a 6 milliseconds timeout for each replay.
- It sends 6 probes within each TTL time period.
- to determine the active TCP connections on a PC
- to check information about a DNS name in the DNS server
- to identify where a packet was lost or delayed on a network
- to display the IP address, default gateway, and DNS server address for a PC
- The network administrator suspects a virus because the ping command did not work.
- The network administrator wants to verify Layer 2 connectivity.
- The network administrator wants to verify the IP address configured on router R2.
- The network administrator wants to determine if connectivity can be established from a non-directly connected network.
- show version
- show ip route
- show interfaces
- show cdp neighbors detail
- the routing protocol version that is enabled
- the value of the configuration register
- the operational status of serial interfaces
- the administrative distance used to reach networks
- debug all
- logging synchronous
- show running-config
- terminal monitor
- terminal monitor
- logging console
- logging buffered
- logging synchronous
- Verify full system functionality.
- Test the theory to determine cause.
- Establish a theory of probable causes.
- Establish a plan of action to resolve the issue.
- netstat
- tracert
- nslookup
- ipconfig
- The PC cannot contact a DHCP server.
- The DNS server address is misconfigured.
- The default gateway address is not configured.
- The PC is configured to obtain an IP address automatically.
- The enterprise network is misconfigured for dynamic routing.

- traceroute
- show cdp neighbors
- Telnet
- an extended ping

- Connectivity between H1 and H3 is fine.
- H3 is not connected properly to the network.
- Something is causing interference between H1 and R1.
- Performance between the networks is within expected parameters.
- Something is causing a time delay between the networks.
- DHCP
- Telnet
- DNS
- traceroute
- show arp
- show interfaces
- show ip route
- show protocols
- Fast Ethernet interfaces
- console ports
- serial interfaces
- vty ports
- loopback interfaces
- Set the user privilege levels.
- Generate the asymmetric RSA keys.
- Configure the correct IP domain name.
- Configure role-based CLI access.
- Create a valid local username and password database.
- Manually enable SSH after the RSA keys are generated.
- Change system passwords every 30 days.
- Ensure that all systems have the most current virus definitions.
- Ensure that AAA is configured in the network.
- Download security updates from the operating system vendor and patch all vulnerable systems.
- Tracert shows each hop, while ping shows a destination reply only.
- Tracert uses IP addresses; ping does not.
- Both ping and tracert can show results in a graphical display.
- Ping shows whether the transmission is successful; tracert does not.
- FTP
- HTTP
- SSH
- Telnet

CCNA 1 v7 Modules 16 – 17 Building and Securing a Small Network Exam
- service password-encryption
- transport input ssh
- enable secret class
- ip domain-name cisco.com
- It is strong because it uses a passphrase.
- It is weak because it is often the default password on new devices.
- It is weak since it uses easily found personal information.
- It is weak since it is a word that is easily found in the dictionary.
- It is strong because it uses a minimum of 10 numbers, letters and special characters.
- It is weak because it is often the default password on new devices.
- It is weak since it uses easily found personal information.
- It is weak since it is a word that is easily found in the dictionary.
- It is strong because it contains 10 numbers and special characters.
- It is weak because it is often the default password on new devices.
- It is weak since it uses easily found personal information.
- It is strong because it uses a minimum of 10 numbers, letters and special characters.
- It is strong because it uses a minimum of 10 numbers, letters and special characters.
- It is weak since it is a word that is easily found in the dictionary.
- It is strong because it uses a passphrase.
- It is strong because it contains 10 numbers and special characters.
- It is weak because it uses a series of numbers or letters.
- It is strong because it uses a passphrase.
- It is weak since it is a word that is easily found in the dictionary.
- It is strong because it uses a minimum of 10 numbers, letters and special characters.
- It is weak because it is often the default password on new devices.
- It is strong because it uses a passphrase.
- It is strong because it uses a minimum of 10 numbers, letters and special characters.
- It is strong because it contains 10 numbers and special characters.
- It is weak because it uses easily found personal information.
- It is strong because it uses a passphrase.
- It is weak since it is a word that is easily found in the dictionary.
- It is strong because it uses a minimum of 10 numbers, letters and special characters.
- It is weak because it is a commonly used password.
- It is weak since it is a word that is easily found in the dictionary.
- It is strong because it uses a passphrase.
- It is strong because it uses a minimum of 10 numbers, letters and special characters.
- It is weak since it uses easily found personal information.
- It is strong because it uses a passphrase.
- It is strong because it uses a minimum of 10 numbers, letters and special characters.
- It is strong because it contains 10 numbers and special characters.
- It is weak because it uses easily found personal information.
- It is strong because it uses a passphrase.
- It is weak since it is a word that is easily found in the dictionary.
- It is strong because it uses a minimum of 10 numbers, letters and special characters.
* minimum of 8 characters, preferably 10.
* use complex combinations of numbers, special characters, and upper and lower case letters.
* avoid repetition, common dictionary words, letter or number sequences.
* avoid names of children, relatives, pets, birthdays, or any easily identifiable personal information.
* can be created by misspelling words or replacing vowels with numbers or special characters.
434. A network technician is troubleshooting an issue and needs to verify the IP addresses of all interfaces on a router. What is the best command to use to accomplish the task?
- show ip interface brief
- nslookup
- ipconfig getifaddr en0
- show ip route
- show interfaces
- ipconfig getifaddr en0
- copy running-config startup-config
- show ip nat translations
- ipconfig
- copy running-config startup-config
- show interfaces
- show ip nat translations
- copy running-config startup-config
- show interfaces
- show ip nat translations
- show ip route
- ipconfig getifaddr en0
- copy running-config startup-config
- show interfaces
- show ip nat translations
- show ipv6 interface
- show interfaces
- show ip nat translations
- show ip route
- ipconfig
- copy running-config startup-config
- show interfaces
- show ip nat translations
- show running-config
- show interfaces
- copy running-config startup-config
- show ip nat translations
- nslookup
- show ipv6 route
- show ipv6 interface
- copy startup-config running-config
- show running-config
- show ipv6 route
- show ipv6 interface
- copy startup-config running-config
- Internet
- intranet
- extranet*
- extendednet
- DSL*
- dial-up
- satellite
- cell modem
- cable modem

- The entire command, configure terminal, must be used.
- The administrator is already in global configuration mode.
- The administrator must first enter privileged EXEC mode before issuing the command.*
- The administrator must connect via the console port to access global configuration mode.
- Ctrl-Shift-X
- Ctrl-Shift-6*
- Ctrl-Z
- Ctrl-C

- letmein
- secretin
- lineconin
- linevtyin*
- This command encrypts passwords as they are transmitted across serial WAN links.
- This command prevents someone from viewing the running configuration passwords.*
- This command enables a strong encryption algorithm for the enable secret password command.
- This command automatically encrypts passwords in configuration files that are currently stored in NVRAM.
- This command provides an exclusive encrypted password for external service personnel who are required to do router maintenance.
- The SVI provides a physical interface for remote access to the switch.
- The SVI provides a faster method for switching traffic between ports on the switch.
- The SVI adds Layer 4 connectivity between VLANs.
- The SVI provides a virtual interface for remote access to the switch.*
- duplex
- unicast
- multicast
- broadcast*
- POP
- BOOTP
- ICMP*
- IP*
- PPP
- segment*
- packet
- frame
- bits
- It is tagged with information guaranteeing reliable delivery.
- It is segmented into smaller individual pieces.
- It is encapsulated into a TCP segment.
- It is encapsulated in a Layer 2 frame.*
- fiber
- radio waves*
- microwave
- UTP
- crosstalk*
- bandwidth
- size of the network
- signal modulation technique
- electromagnetic interference *
- internet
- physical
- LLC*
- transport
- MAC*
- network access
- bus
- hierarchical
- mesh*
- ring
- star
- access method*
- flow control
- message encapsulation
- message encoding
- Layer 3
- data link*
- physical
- Layer 4
- a single IP multicast address that is used by all destinations in a group*
- an IP address that is unique for each destination in the group
- a group address that shares the last 23 bits with the source IPv4 address
- a 48 bit address that is determined by the number of members in the multicast group
- drop the frame
- process the frame as it is*
- send an error message to the sending device
- add random data bytes to make the frame 1518 bytes long and then forward it
- source MAC address
- source IP address
- destination MAC address*
- Ethernet type
- destination IP address
- It initiates an ARP request.
- It broadcasts the frame out of all ports on the switch.
- It notifies the sending host that the frame cannot be delivered.
- It forwards the frame out of all ports except for the port at which the frame was received.*
- If a host is ready to send a packet to a local destination device and it has the IP address but not the MAC address of the destination, it generates an ARP broadcast.*
- An ARP request is sent to all devices on the Ethernet LAN and contains the IP address of the destination host and its multicast MAC address.
- When a host is encapsulating a packet into a frame, it refers to the MAC address table to determine the mapping of IP addresses to MAC addresses.
- If no device responds to the ARP request, then the originating node will broadcast the data packet to all devices on the network segment.
- If a device receiving an ARP request has the destination IPv4 address, it responds with an ARP reply.*
- DNS*
- WINS
- HTTP
- DHCP*
- SMTP
- connectionless*
- media dependent
- user data segmentation
- reliable end-to-end delivery

- ::1/128
- fe80::30d0:115:3f57:fe4c/128*
- fe80::/64
- 2001:0:9d38:6ab8:30d0:115:3f57:fe4c/128
- 2001:DB8:0:AB00::1234*
- 2001:DB8:0:AB::1234
- 2001:DB8::AB00::1234
- 2001:DB8:0:AB:0:1234
- link-local*
- unique local
- site local
- global unicast
- all IPv6 enabled devices across the network
- all IPv6 enabled devices on the local link
- all IPv6 DHCP servers
- all IPv6 configured routers on the local link*
- to inform routers about network topology changes
- to ensure the delivery of an IP packet
- to provide feedback of IP packet transmissions*
- to monitor the process of a domain name to IP address resolution
- It sends four Echo Request messages.
- It utilizes the ICMP Source Quench messages.
- It is primarily used to test connectivity between two hosts.
- It identifies the routers in the path from a source host to a destination host.*
- 256
- 254
- 64
- 62*
- 32
- 16

- 172.16.16.255
- 172.16.20.255
- 172.16.19.255*
- 172.16.23.255
- 172.16.255.255
- 2001:db8:0:f00::/52
- 2001:db8:0:8000::/52
- 2001:db8:0:f::/52
- 2001:db8:0:f000::/52*
- The data flow is being tracked based on the destination port number utilized by each application.
- The data flow is being tracked based on the source port number utilized by each application.*
- The data flow is being tracked based on the source IP address used by the PC of the technician.
- The data flow is being tracked based on the destination IP address used by the PC of the technician.
- flow control*
- encryption of data
- path determination
- connection establishment *
- error recovery*
- bit transmission
- data representation
- A delivery failure message is sent to the source host.
- The part of the television transmission that was lost is re-sent.
- The entire transmission is re-sent.
- The transmission continues without the missing portion.*
- internet
- network
- presentation*
- session*
- transport
- client*
- master
- server
- slave
- transient
- local server address
- subnet mask*
- default gateway address*
- physical address of the recipient
- physical address of the sender
- during times of peak utilization*
- during off-peak hours
- during employee holidays and weekends
- during randomly selected times
- discovery and mapping of systems*
- unauthorized manipulation of data
- disabling network systems or services
- denying access to resources by legitimate users
- This command encrypts passwords as they are transmitted across serial WAN links.
- This command automatically encrypts passwords in configuration files that are currently stored in NVRAM.
- This command provides an exclusive encrypted password for external service personnel who are required to do router maintenance.
- This command enables a strong encryption algorithm for the enable secret password command.
- This command prevents someone from viewing the running configuration passwords.*
- login block-for 150 attempts 4 within 90
- All login attempts will be blocked for 150 seconds if there are 4 failed attempts within 90 seconds.*
- All login attempts will be blocked for 90 seconds if there are 4 failed attempts within 150 seconds.
- All login attempts will be blocked for 1.5 hours if there are 4 failed attempts within 150 seconds.
- All login attempts will be blocked for 4 hours if there are 90 failed attempts within 150 seconds.
- ROM is nonvolatile and stores the running IOS.
- FLASH is nonvolatile and contains a limited portion of the IOS.
- RAM is volatile and stores the IP routing table.*
- NVRAM is nonvolatile and stores a full version of the IOS.
- ROM is nonvolatile and contains basic diagnostic software.*
- The NIC in the PC is bad.
- The TCP/IP protocol is not enabled.
- The router that is attached to the same network as the workstation is down.
- Nothing can be determined for sure at this point.*
- Ctrl+Shift+6*
- Ctrl+Esc
- Ctrl+x
- Ctrl+c


Place the options in the following order.
— not scored —
locale and load the Cisco IOS software -> phase 2
locate and load the startup configuration file -> phase 3
perform the POST and load the bootstrap program -> phase 1
48. What three blocks of addresses are defined by RFC 1918 for private network use? (Choose three.)
- 10.0.0.0/8*172.16.0.0/12*
- 192.168.0.0/16*
- 100.64.0.0/14
- 169.254.0.0/16
- 239.0.0.0/8
- 10.1.1.128/28
10.1.1.144/28
10.1.1.160/29* - 10.1.1.128/28
10.1.1.144/28
10.1.1.160/2810.1.1.128/28
10.1.1.140/28
10.1.1.158/26 - 10.1.1.128/26
10.1.1.144/26
10.1.1.160/26 - 10.1.1.128/26
10.1.1.140/26
10.1.1.158/28
Question

Answer

Place the options in the following order.
— not scored —
CLI -> users interact with the operating system by typing commands
GUI -> enables the user to interact with the operating system by pointing and clicking
kernel -> the part of the OS that interacts directly with the device hardware
shell -> the part of the operating system that interfaces with applications and the user
51. Match the requirements of a reliable network with the supporting network architecture. (Not all options are used.)
Question

Answer

Place the options in the following order.
Protect the network from unauthorized access. -> security
Provide redundant links and devices. -> fault tolerance
— not scored —
Expand the network without degrading the service for existing users. -> scalability
— not scored —
52. Match the functions with the corresponding OSI layer. (Not all options are used.)
Question

Answer

Place the options in the following order.
Application layer
HTTP and FTP
end user program functionality
Presentation layer
compression
common format
Session layer
dialog maintenance
53. What subnet mask is required to support 512 subnets on networks 172.28.0.0/16?
- 255.255.240.0
- 255.255.255.224
- 255.255.255.240
- 255.255.255.128*
- 255.255.252.0
- 210
- 60
- 109
- 107*
- 146
Older Version
55. What is an advantage of storing configuration files to a USB flash drive instead of to a TFTP server?- The files can be saved without using terminal emulation software.
- The transfer of the files does not rely on network connectivity.*
- The USB flash drive is more secure.
- The configuration files can be stored to a flash drive that uses any file system format.

- The command does not exist.
- One or more required keywords or arguments were omitted.
- Not enough characters were entered for the interpreter to recognize the command.*
- The administrator does not have the required level of access to use this command.
- regenerating data signals*
- acting as a client or a server
- providing a channel over which messages travel
- applying security settings to control the flow of data *
- notifying other devices when errors occur*
- serving as the source or destination of the messages
- It can rapidly adapt to the loss of data transmission facilities. *
- It efficiently utilizes the network infrastructure to transfer data. *
- Data packets can travel multiple paths through the network simultaneously.*
- It allows for billing of network use by the amount of time a connection is established.
- It requires that a data circuit between the source and destination be established before data can be transferred.
- DSL
- dialup
- satellite
- leased line*
- cable modem
- It is a standards body that develops cabling and wiring standards for networking.
- It is a protocol that establishes how computers within a local network communicate.
- It is an organization that enables individuals and businesses to connect to the Internet.*
- It is a networking device that combines the functionality of several different networking devices in one.

CCNA 1 Practice Final Answer 001 (v5.02, 2015)
- Connect to the Ethernet port on the PC.
- Change connection settings to even parity.
- Move the cable to the router console port.*
- Use a crossover cable instead of a rollover cable.
- a console connection
- an AUX connection
- a Telnet connection
- an SSH connection*

CCNA 1 Practice Final Answer 003 (v5.02, 2015)
- The banner message is too long.
- The delimiting character appears in the banner message.*
- The symbol “!” signals the end of a banner message.
- Message-of-the-day banners will only appear when a user logs in through the console port.
- The host cannot communicate with other hosts in the local network.
- The switch will not forward packets initiated by the host.
- The host will have to use ARP to determine the correct address of the default gateway.
- The host cannot communicate with hosts in other networks.*
- A ping from the host to 127.0.0.1 would not be successful.
- The end-user device only has an Ethernet NIC.
- The end-user device requires a dedicated connection because of performance requirements.
- The end-user device needs mobility when connecting to the network.*
- The end-user device area has a high concentration of RFI.
- presentation layer
- network layer
- physical layer*
- data link layer

CCNA 1 Practice Final Answer 005 (v5.02, 2015)
- physical
- network
- data link*
- transport
- application
- controlled access
- deterministic
- full-duplex
- half-duplex*
- to determine the physical address of the sending device
- to verify the network layer protocol information
- to compare the interface media type between the sending and receiving ends
- to check the frame for possible transmission errors*
- to verify that the frame destination matches the MAC address of the receiving device
- Layer 3 address to a Layer 2 address*
- Layer 3 address to a Layer 4 address
- Layer 4 address to a Layer 2 address
- Layer 2 address to a Layer 4 address
- building a routing table that is based on the first IP address in the frame header
- using the source MAC addresses of frames to build and maintain a MAC address table*
- forwarding frames with unknown destination IP addresses to the default gateway
- utilizing the MAC address table to forward frames via the destination MAC address*
- examining the destination MAC address to add new entries to the MAC address table
- packet switching*
- microsegmentation
- domain name resolution
- path selection*
- flow control
- The IOS image is corrupt.
- Cisco IOS is missing from flash memory.
- The configuration file is missing from NVRAM.*
- The POST process has detected hardware failure.
- Perform the POST routine.
- Search for a backup IOS in ROM.
- Load the bootstrap program from ROM.
- Load the running-config file from RAM.
- Locate and load the startup-config file from NVRAM.*
- to identify missing segments at the destination*
- to reassemble the segments at the remote location*
- to specify the order in which the segments travel from source to destination
- to limit the number of segments that can be sent out of an interface at one time
- to determine if the packet changed during transit
- This is a loopback address.
- This is a link-local address.
- This is a private IP address.*
- There is an IP address conflict.
- ARP
- DHCP
- DNS
- NAT*
- 2001:0DB8::ABCD::1234
- ABCD:160D::4GAB:FFAB
- 2001:DB8:0:1111::200*
- 2001::ABCD::
- FEC0::/10?
- FDEE::/7?
- FEBF::/10*
- FF00::/8?
- broadcast address
- global routing prefix*
- subnet mask
- subnet ID *
- interface ID*
- 3
- 4*
- 6
- 8
- 14
- 16
- 192.168.99.0/26
192.168.99.64/27* - 192.168.99.0/27
192.168.99.32/26 - 192.168.99.0/27
192.168.99.32/28 - 192.168.99.0/28
192.168.99.16/28 - 192.168.99.0/28
192.168.99.64/26
- 1024
- 2048
- 4096*
- 8192
- 65536
- DNS server*
- WINS server
- HTTP server
- default gateway*
- Netbios
- Layer 7 devices
- Layer 4 devices
- Layer 2 devices*
- Layer 3 devices
- line*
- router
- global
- interface
- privileged EXEC

CCNA 1 Practice Final Answer 007 (v5.02, 2015)
- Connectivity to the remote device was successful.
- A router along the path did not have a route to the destination.*
- A ping packet is being blocked by a security device along the path.
- The connection timed out while waiting for a reply from the remote device.
- indicates the point of failure in the connection
- shows the IP address of the next hop router for each route*
- lists the IP addresses of all hops the traffic will pass through to reach the destination network
- shows the incoming and outgoing interfaces the traffic will go through in order to reach the destination network
- The workstation NIC has malfunctioned.
- The subnet mask was configured incorrectly.
- The DNS server IP address needs to be configured.
- The workstation is unable to obtain an IP address from a DHCP server.*
- ipconfig /all
- arp -a
- ipconfig /displaydns*
- nslookup
- The command should have been copy startup-config tftp.
- The configuration should have been copied to the running configuration instead.*
- The configuration changes were copied into RAM and require a reboot to take effect.
- A TFTP server can only be used to restore the Cisco IOS, not the router configuration.

CCNA 1 Practice Final Answer 008 (v5.02, 2015)
- It identifies the wireless LAN.
- It allows the access point to inform clients of its presence.
- It translates IP addresses into easy-to-remember domain names.
- It encrypts data between the wireless client and the access point.*
- It translates an internal address or group of addresses into an outside, public address.
- EAP
- PSK
- WEP*
- WPA

CCNA 1 Practice Final Answer 009 (v5.02, 2015)
- network mode
- SSID*
- radio band
- wide channel
- standard channel
- SSID broadcast*
Which interface configuration mode command puts a Layer 3 switch interface into Layer 3 mode? no switchport
96. Fill in the blank.
A nibble consists of 4 bits.
97. Match each item to the type of topology diagram on which it is typically identified. (Not all options are used.)

98. Match the situation with the appropriate use of network media.

99. Match the subnetwork to a host address that would be included within the subnetwork. (Not all options are used.)

100. Open the PT activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then fill in the blank.
The Server0 message is winner.?
101. Which two statements are correct in a comparison of IPv4 and IPv6 packet headers? (Choose two.)
- The Source Address field name from IPv4 is kept in IPv6.*
- The Version field from IPv4 is not kept in IPv6.
- The Destination Address field is new in IPv6.
- The Header Checksum field name from IPv4 is kept in IPv6.
- The Time-to-Live field from IPv4 has been replaced by the Hop Limit field in IPv6.*
- to allow the receiving host to assemble the packet in the proper order
- to enable a receiving host to forward the data to the appropriate application*
- to determine which Layer 3 protocol should be used to encapsulate the data
- to identify which switch ports should receive or forward the segment
- to indicate the correct router interface that should be used to forward a segment

What is the secret keyword that is displayed on the web page?
- cisco
- switch
- frame
- packet*
- router
- voice*
- file transfer
- instant messaging
- video*
In dotted decimal notation, the IP address “172.25.0.126” is the last host address for the network 172.25.0.64/26.
106. What are two characteristics of a scalable network? (Choose two.)
- is not as reliable as a small network
- grows in size without impacting existing users*
- easily overloaded with increased traffic
- suitable for modular devices that allow for expansion*
- offers limited number of applications

Subnet 192.168.1.32/27 will have a valid host range from 192.168.1.33 – 192.168.1.62 with the broadcast address as 192.168.1.63
Subnet 192.168.1.64/27 will have a valid host range from 192.168.1.65 – 192.168.1.94 with the broadcast address as 192.168.1.95
Subnet 192.168.1.96/27 will have a valid host range from 192.168.1.97 – 192.168.1.126 with the broadcast address as 192.168.1.127
108. What information is added during encapsulation at OSI Layer 3?
- source and destination port number
- source and destination MAC
- source and destination IP address*
- source and destination application protocol

- A packet with the destination IP address of RouterA.
- A frame with the destination MAC address of SwitchA.
- A frame with the destination MAC address of RouterA.*
- A packet with the destination IP address of RouterB.
- A packet with the destination IP address of ServerB.*
- A frame with the destination MAC address of ServerB.
- It will remove the frame from the media.
- It will discard the frame.*
- It will forward the frame to the next host.
- It will strip off the data-link frame to check the destination IP address.
- 1,500
- 5
- 6,001*
- 1,501
- 6,000
- error detection*
- port identification
- addressing*
- path determination
- IP address resolution
- frame delimiting*
The minimum Ethernet frame size is “64” bytes. Anything smaller than that should be considered a “runt frame.”
114. What three statements describe features or functions of media access control? (Choose three.)
- Ethernet utilizes CSMA/CD.*
- 802.11 utilizes CSMA/CD.
- It uses contention-based access also known as deterministic access.
- Data link layer protocols define the rules for access to different media.*
- Controlled media access involves collision handling.
- It is responsible for detecting transmission errors in transmitted data.*

Which information is obtained from this command output?
- 10.20.20.3, non-authoritative answer*
- 10.20.20.4, non-authoritative answer
- 10.20.20.3, authoritative answer
- 10.20.20.4, authoritative answer
- greater bandwidth potential*
- limited susceptibility to EMI/RFI*
- durable connections
- easily terminated
- greater distances per cable run*
- lower installation cost
- point-to-point
- mesh
- partial mesh*
- hub and spoke
- It assures that clients are connected to the correct WLAN.
- It describes the smallest building block of the WLAN.
- It provides the mechanism for media access.*
- It allows a host to move between cells without loss of signal.
A nibble consists of “4” bits.
120. Place the options in the following order:


[+] cables connecting rooms to wiring closets
[+] desktop PC in a classroom
[#] IP address of a server
[#] a switch located in a classroom
[+] Order does not matter within this group.
[#] Order does not matter within this group.
121. Why are the paired wires twisted in a CAT5 cable?
- to improve the mechanical strength
- to provide eletromagnetic noise cancellation*
- to facilitate cable termination in the connector
- to extend the signaling length

- The administrator will be presented with the R1> prompt.*
- The administrator will be required to enter Cisco789.
- The administrator will be required to enter Cisco234.
- The administrator will be required to enter Cisco123.


124. Refer to the exhibit. Using VLSM, what is the largest and smallest subnet mask required on this network in order to minimize address waste?

- 255.255.254.0 and 255.255.255.252*
- 255.255.255.128 and 255.255.255.224
- 255.255.254.0 and 255.255.255.224
- 255.255.255.0 and 255.255.255.252
- synchronizing sequence numbers between source and destination in preparation for data transfer*
- determining the IP address of the destination host in preparation for data transfer
- sending echo requests from the source to the destination host to establish the presence of the destination
- requesting the destination to transfer a binary file to the source
- EAP
- PSK
- WEP*
- WPA
- NVRAM must be erased before the new IOS can be installed.
- The old IOS should be backed up to NVRAM so that it is not lost during a power failure.
- The new IOS might require more RAM to function properly.*
- The old IOS must be removed first.
- Fiber-optic cabling does not conduct electricity.*
- Fiber-optic cabling has high signal loss.
- Fiber-optic cabling is primarily used as backbone cabling.*
- Multimode fiber-optic cabling carries signals from multiple sending devices.
- Fiber-optic cabling uses LEDs for single-mode cables and laser technology for multimode cables.
- DHCPDISCOVER
- DHCPOFFER
- DHCPREQUEST
- DHCPACK*
- DHCPNACK
- www
- .com*
- http
- index
- to show all of the cached DNS entries*
- to show the local DNS server parameters
- to show the result of last name resolution request
- to show the DNS configuration for the workstation
2001:0DB8:BC15:00A0:0000:: 2001:0DB8:BC15:00A1:0000:: 2001:0DB8:BC15:00A2:0000:: … 2001:0DB8:BC15:00AF:0000::The prefix-length for the range of addresses is __60__
133. Which publicly available resources describe protocols, processes, and technologies for the Internet but do not give implementation details?
- protocol models
- Request for Comments*
- IRTF research papers
- IEEE standards
- The device has the correct IP address on the network.
- The Ethernet cable is working correctly.
- The device has end-to-end connectivity.
- DHCP is working correctly.
- The TCP/IP stack on the device is working correctly.*
- adjacency tables*
- ARP tables
- routing tables
- forwarding information base (FIB)*
- MAC-address tables
- 192.168.1.64/26*
- 192.168.1.32/27
- 192.168.1.32/28
- 192.168.1.64/29
- exec-timeout 30
- banner motd $Max failed logins = 5$
- login block-for 60 attempts 5 within 60*
- service password-encryption
- An FTP client uses a source port number of 21 and a randomly generated destination port number during the establishment of control traffic with an FTP Server.
- An FTP client uses a source port number of 20 and a randomly generated destination port number during the establishment of data traffic with an FTP Server.*
- An FTP server uses a source port number of 20 and a randomly generated destination port number during the establishment of control traffic with an FTP client.
- An FTP server uses a source port number of 21 and a randomly generated destination port number during the establishment of control traffic with an FTP client.
Version 6.0:
1. What is a characteristic of a fault tolerant network?- a network that protects confidential information from unauthorized access
- a network that can expand quickly to support new users and applications without impacting the performance of the service delivered to existing users
- a network that supports a mechanism for managing congestion and ensuring reliable delivery of content to all users
- a network that recovers quickly when a failure occurs and depends on redundancy to limit the impact of a failure*
2. Three bank employees are using the corporate network. The first employee uses a web browser to view a company web page in order to read some announcements. The second employee accesses the corporate database to perform some financial transactions. The third employee participates in an important live audio conference with other corporate managers in branch offices. If QoS is implemented on this network, what will be the priorities from highest to lowest of the different data types?
- financial transactions, audio conference, web page
- audio conference, financial transactions, web page*
- audio conference, web page, financial transactions
- financial transactions, web page, audio conference
3. What is a benefit of using cloud computing in networking?
- End users have the freedom to use personal tools to access information and communicate across a business network.
- Network capabilities are extended without requiring investment in new infrastructure, personnel, or software.*
- Technology is integrated into every-day appliances allowing them to interconnect with other devices, making them more ‘smart’ or automated.
- Home networking uses existing electrical wiring to connect devices to the network wherever there is an electrical outlet, saving the cost of installing data cables.
4. What is the function of the shell in an OS?
- It interacts with the device hardware.
- It interfaces between the users and the kernel.*
- It provides dedicated firewall services.
- It provides the intrusion protection services for the device.
5. Which connection provides a secure CLI session with encryption to a Cisco switch?
- a console connection
- an AUX connection
- a Telnet connection
- an SSH connection*
6. A network technician is attempting to configure an interface by entering the following command: SanJose(config)# ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0. The command is rejected by the device. What is the reason for this?
- The command is being entered from the wrong mode of operation.*
- The command syntax is wrong.
- The subnet mask information is incorrect.
- The interface is shutdown and must be enabled before the switch will accept the IP address.
7. An administrator uses the Ctrl-Shift-6 key combination on a switch after issuing the ping command. What is the purpose of using these keystrokes?
- to restart the ping process
- to interrupt the ping process*
- to exit to a different configuration mode
- to allow the user to complete the command
8. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is configuring access control to switch SW1. If the administrator uses a console connection to connect to the switch, which password is needed to access user EXEC mode?

- letmein
- secretin
- linevtyin
- lineconin*
9. On which switch interface would an administrator configure an IP address so that the switch can be managed remotely?
- FastEthernet0/1
- VLAN 1*
- vty 0
- console 0
10. What protocol is responsible for controlling the size of segments and the rate at which segments are exchanged between a web client and a web server?
- TCP*
- IP
- HTTP
- Ethernet
11. What is an advantage to using a protocol that is defined by an open standard?
- A company can monopolize the market.
- The protocol can only be run on equipment from a specific vendor.
- An open standard protocol is not controlled or regulated by standards organizations.
- It encourages competition and promotes choices.*
12. What are two benefits of using a layered network model? (Choose two.)
- It assists in protocol design. *
- It speeds up packet delivery.
- It prevents designers from creating their own model.
- It prevents technology in one layer from affecting other layers.*
- It ensures a device at one layer can function at the next higher layer.
13. Which two OSI model layers have the same functionality as two layers of the TCP/IP model? (Choose two.)
- data link
- network*
- physical
- session
- transport*
14. Which name is assigned to the transport layer PDU?
- bits
- data
- frame
- packet
- segment*
15. A network engineer is measuring the transfer of bits across the company backbone for a mission critical database application. The engineer notices that the network throughput appears lower than the bandwidth expected. Which three factors could influence the differences in throughput? (Choose three.)
- the amount of traffic that is currently crossing the network*
- the sophistication of the encapsulation method applied to the data
- the type of traffic that is crossing the network*
- the latency that is created by the number of network devices that the data is crossing*
- the bandwidth of the WAN connection to the Internet
- the reliability of the gigabit Ethernet infrastructure of the backbone
16. A network administrator is troubleshooting connectivity issues on a server. Using a tester, the administrator notices that the signals generated by the server NIC are distorted and not usable. In which layer of the OSI model is the error categorized?
- presentation layer
- network layer
- physical layer*
- data link layer
17. Which type of UTP cable is used to connect a PC to a switch port?
- console
- rollover
- crossover
- straight-through**
18. A network administrator is measuring the transfer of bits across the company backbone for a mission critical financial application. The administrator notices that the network throughput appears lower than the bandwidth expected. Which three factors could influence the differences in throughput? (Choose three.)
- the amount of traffic that is currently crossing the network*
- the sophistication of the encapsulation method applied to the data
- the type of traffic that is crossing the network *
- the latency that is created by the number of network devices that the data is crossing*
- the bandwidth of the WAN connection to the Internet
- the reliability of the gigabit Ethernet infrastructure of the backbone
19. What is a characteristic of UTP cabling?
- cancellation*
- cladding
- immunity to electrical hazards
- woven copper braid or metallic foil
20. What are two characteristics of fiber-optic cable? (Choose two.)
- It is not affected by EMI or RFI.*
- Each pair of cables is wrapped in metallic foil.
- It combines the technique of cancellation, shielding, and twisting to protect data.
- It typically contains 4 pairs of fiber-optic wires.
- It is more expensive than UTP cabling is.*
21. What is a characteristic of the LLC sublayer?
- It provides the logical addressing required that identifies the device.
- It provides delimitation of data according to the physical signaling requirements of the medium.
- It places information in the frame allowing multiple Layer 3 protocols to use the same network interface and media.*
- It defines software processes that provide services to the physical layer.
22. A network team is comparing physical WAN topologies for connecting remote sites to a headquarters building. Which topology provides high availability and connects some, but not all, remote sites?
- mesh
- partial mesh*
- hub and spoke
- point-to-point
23. What method is used to manage contention-based access on a wireless network?
- CSMA/CD
- priority ordering
- CSMA/CA*
- token passing
24. What are the three primary functions provided by Layer 2 data encapsulation? (Choose three.)
- error correction through a collision detection method
- session control using port numbers
- data link layer addressing*
- placement and removal of frames from the media
- detection of errors through CRC calculations *
- delimiting groups of bits into frames*
- conversion of bits into data signals
25. What will a host on an Ethernet network do if it receives a frame with a destination MAC address that does not match its own MAC address?
- It will discard the frame.*
- It will forward the frame to the next host.
- It will remove the frame from the media.
- It will strip off the data-link frame to check the destination IP address.
26. What are two examples of the cut-through switching method? (Choose two.)
- store-and-forward switching
- fast-forward switching*
- CRC switching
- fragment-free switching*
- QOS switching
27. What are two actions performed by a Cisco switch? (Choose two.)
- building a routing table that is based on the first IP address in the frame header
- using the source MAC addresses of frames to build and maintain a MAC address table*
- forwarding frames with unknown destination IP addresses to the default gateway
- utilizing the MAC address table to forward frames via the destination MAC address*
- examining the destination MAC address to add new entries to the MAC address table
28. Which frame forwarding method receives the entire frame and performs a CRC check to detect errors before forwarding the frame?
- cut-through switching
- store-and-forward switching*
- fragment-free switching
- fast-forward switching
29. Refer to the exhibit. If host A sends an IP packet to host B, what will the destination address be in the frame when it leaves host A?

- DD:DD:DD:DD:DD:DD
- 172.168.10.99
- CC:CC:CC:CC:CC:CC
- 172.168.10.65
- BB:BB:BB:BB:BB:BB*
- AA:AA:AA:AA:AA:AA
30. What addresses are mapped by ARP?
- destination MAC address to a destination IPv4 address*
- destination IPv4 address to the source MAC address
- destination IPv4 address to the destination host name
- destination MAC address to the source IPv4 address
31. What information is added during encapsulation at OSI Layer 3?
- source and destination MAC
- source and destination application protocol
- source and destination port number
- source and destination IP address*
32. What are two services provided by the OSI network layer? (Choose two.)
- performing error detection
- routing packets toward the destination *
- encapsulating PDUs from the transport layer*
- placement of frames on the media
- collision detection
33. Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator for a small advertising company has chosen to use the 192.168.5.96/27 network for internal LAN addressing. As shown in the exhibit, a static IP address is assigned to the company web server. However, the web server cannot access the Internet. The administrator verifies that local workstations with IP addresses that are assigned by a DHCP server can access the Internet, and the web server is able to ping local workstations. Which component is incorrectly configured?

- subnet mask
- DNS address
- host IP address
- default gateway address*
34. Why does a Layer 3 device perform the ANDing process on a destination IP address and subnet mask?
- to identify the broadcast address of the destination network
- to identify the host address of the destination host
- to identify faulty frames
- to identify the network address of the destination network*
35. What are two functions of NVRAM? (Choose two.)
- to store the routing table
- to retain contents when power is removed *
- to store the startup configuration file*
- to contain the running configuration file
- to store the ARP table
36. Refer to the exhibit. What will be the result of entering this configuration the next time a network administrator connects a console cable to the router and no additional commands have been entered?

- The administrator will be required to enter Cisco123.
- The administrator will be required to enter Cisco234.
- The administrator will be required to enter Cisco789.
- The administrator will be presented with the R1> prompt.*
37. What is the dotted decimal representation of the IPv4 address 11001011.00000000.01110001.11010011?
- 192.0.2.199
- 198.51.100.201
- 203.0.113.211*
- 209.165.201.223
38. What are three characteristics of multicast transmission? (Choose three.)
- The source address of a multicast transmission is in the range of 224.0.0.0 to 224.0.0.255.
- A single packet can be sent to a group of hosts. *
- Multicast transmission can be used by routers to exchange routing information. *
- Routers will not forward multicast addresses in the range of 224.0.0.0 to 224.0.0.255.*
- Computers use multicast transmission to request IPv4 addresses.
- Multicast messages map lower layer addresses to upper layer addresses.
39. What are the three ranges of IP addresses that are reserved for internal private use? (Choose three.)
- 10.0.0.0/8*
- 64.100.0.0/14
- 127.16.0.0/12
- 172.16.0.0/12*
- 192.31.7.0/24
- 192.168.0.0/16*
40. What purpose does NAT64 serve in IPv6?
- It converts IPv6 packets into IPv4 packets.*
- It translates private IPv6 addresses into public IPv6 addresses.
- It enables companies to use IPv6 unique local addresses in the network.
- It converts regular IPv6 addresses into 64-bit addresses that can be used on the Internet.
- It converts the 48-bit MAC address into a 64-bit host address that can be used for automatic host addressing.
41. What is the most compressed representation of the IPv6 address 2001:0000:0000:abcd:0000:0000:0000:0001?
- 2001:0:abcd::1
- 2001:0:0:abcd::1*
- 2001::abcd::1
- 2001:0000:abcd::1
- 2001::abcd:0:1
42. Which range of link-local addresses can be assigned to an IPv6-enabled interface?
- FEC0::/10
- FDEE::/7
- FE80::/10*
- FF00::/8
43. Which three addresses are valid public addresses? (Choose three.)
- 198.133.219.17*
- 192.168.1.245
- 10.15.250.5
- 128.107.12.117*
- 192.15.301.240
- 64.104.78.227 *

- There is connectivity between this device and the device at 192.168.100.1.*
- The connectivity between these two hosts allows for videoconferencing calls.
- There are 4 hops b**etween this device and the device at 192.168.100.1.*
- The average transmission time between the two hosts is 2 milliseconds.
- This host does not have a default gateway configured.
45. What type of IPv6 address is FE80::1?
- loopback
- link-local*
- multicast
- global unicast
46. How many valid host addresses are available on an IPv4 subnet that is configured with a /26 mask?
- 254
- 190
- 192
- 62*
- 64
47. A site administrator has been told that a particular network at the site must accommodate 126 hosts. Which subnet mask would be used that contains the required number of host bits?
- 255.255.255.0
- 255.255.255.128*
- 255.255.255.224
- 255.255.255.240
48. A network administrator wants to have the same subnet mask for three subnetworks at a small site. The site has the following networks and numbers of devices:
Subnetwork A: IP phones – 10 addresses
Subnetwork B: PCs – 8 addresses
Subnetwork C: Printers – 2 addresses
What single subnet mask would be appropriate to use for the three subnetworks?
- 255.255.255.0
- 255.255.255.240*
- 255.255.255.248
- 255.255.255.252
49. How many hosts are addressable on a network that has a mask of 255.255.255.248?
- 2
- 6*
- 8
- 14
- 16
- 254
50. Which subnet would include the address 192.168.1.96 as a usable host address?
- 192.168.1.64/26*
- 192.168.1.32/27
- 192.168.1.32/28
- 192.168.1.64/29
51. What subnet mask is needed if an IPv4 network has 40 devices that need IP addresses and address space is not to be wasted?
- 255.255.255.0
- 255.255.255.128
- 255.255.255.192*
- 255.255.255.224
- 255.255.255.240
52. What are two characteristics shared by TCP and UDP? (Choose two.)
- default window size
- connectionless communication
- port numbering*
- 3-way handshake
- ability to to carry digitized voice
- use of checksum*
53. Why are port numbers included in the TCP header of a segment?
- to indicate the correct router interface that should be used to forward a segment
- to identify which switch ports should receive or forward the segment
- to determine which Layer 3 protocol should be used to encapsulate the data
- to enable a receiving host to forward the data to the appropriate application*
- to allow the receiving host to assemble the packet in the proper order

- 192.168.10.0
- 192.168.10.128*
- 192.168.10.192
- 192.168.10.224
- 192.168.10.240
- Each subnet is the same size.
- The size of each subnet may be different, depending on requirements.*
- Subnets may only be subnetted one additional time.
- Bits are returned, rather than borrowed, to create additional subnets.
56. In what two situations would UDP be the preferred transport protocol over TCP? (Choose two.)
- when applications need to guarantee that a packet arrives intact, in sequence, and unduplicated
- when a faster delivery mechanism is needed*
- when delivery overhead is not an issue
- when applications do not need to guarantee delivery of the data*
- when destination port numbers are dynamic
57. What important information is added to the TCP/IP transport layer header to ensure communication and connectivity with a remote network device?
- timing and synchronization
- destination and source port numbers*
- destination and source physical addresses
- destination and source logical network addresses
58. What is the TCP mechanism used in congestion avoidance?
- three-way handshake
- socket pair
- two-way handshake
- sliding window*
59. Which scenario describes a function provided by the transport layer?
- A student is using a classroom VoIP phone to call home. The unique identifier burned into the phone is a transport layer address used to contact another network device on the same network.
- A student is playing a short web-based movie with sound. The movie and sound are encoded within the transport layer header.
- A student has two web browser windows open in order to access two web sites. The transport layer ensures the correct web page is delivered to the correct browser window.*
- A corporate worker is accessing a web server located on a corporate network. The transport layer formats the screen so the web page appears properly no matter what device is being used to view the web site.
60. A user opens three browsers on the same PC to access www.cisco.com to search for certification course information. The Cisco web server sends a datagram as a reply to the request from one of the web browsers. Which information is used by the TCP/IP protocol stack in the PC to identify which of the three web browsers should receive the reply?
- the destination IP address
- the destination port number*
- the source IP address
- the source port number
61. What are two ways that TCP uses the sequence numbers in a segment? (Choose two.)
- to identify missing segments at the destination *
- to reassemble the segments at the remote location*
- to specify the order in which the segments travel from source to destination
- to limit the number of segments that can be sent out of an interface at one time
- to determine if the packet changed during transit
- compression*
- addressing
- encryption*
- session control
- authentication
63. Which three statements characterize UDP? (Choose three.)
- UDP provides basic connectionless transport layer functions.*
- UDP provides connection-oriented, fast transport of data at Layer 3.
- UDP relies on application layer protocols for error detection. *
- UDP is a low overhead protocol that does not provide sequencing or flow control mechanisms.*
- UDP relies on IP for error detection and recovery.
- UDP provides sophisticated flow control mechanisms.
64. What is a key characteristic of the peer-to-peer networking model?
- wireless networking
- social networking without the Internet
- network printing using a print server
- resource sharing without a dedicated server*
65. A technician can ping the IP address of the web server of a remote company but cannot successfully ping the URL address of the same web server. Which software utility can the technician use to diagnose the problem?
- tracert
- ipconfig
- netstat
- nslookup*
66. Which domain name would be an example of a top-level domain?
- www.cisco.com
- cisco.com
- .com*
- root.cisco.com
67. A PC obtains its IP address from a DHCP server. If the PC is taken off the network for repair, what happens to the IP address configuration?
- The configuration is permanent and nothing changes.
- The address lease is automatically renewed until the PC is returned.
- The address is returned to the pool for reuse when the lease expires.*
- The configuration is held by the server to be reissued when the PC is returned.
68. When planning for network growth, where in the network should packet captures take place to assess network traffic?
- on as many different network segments as possible*
- only at the edge of the network
- between hosts and the default gateway
- only on the busiest network segment
69. A wireless host needs to request an IP address. What protocol would be used to process the request?
- FTP
- HTTP
- DHCP*
- ICMP
- SNMP
70. Which example of malicious code would be classified as a Trojan horse?
- malware that was written to look like a video game*
- malware that requires manual user intervention to spread between systems
- malware that attaches itself to a legitimate program and spreads to other programs when launched
- malware that can automatically spread from one system to another by exploiting a vulnerability in the target
71. When applied to a router, which command would help mitigate brute-force password attacks against the router?
- exec-timeout 30
- service password-encryption
- banner motd $Max failed logins = 5$
- login block-for 60 attempts 5 within 60*
72. A network technician suspects that a particular network connection between two Cisco switches is having a duplex mismatch. Which command would the technician use to see the Layer 1 and Layer 2 details of a switch port?
- show mac-address-table
- show ip interface brief
- show interfaces*
- show running-config
73. Where are Cisco IOS debug output messages sent by default?
- Syslog server
- console line*
- memory buffers
- vty lines
74. Match the description with the associated IOS mode. (not all options are used.) Question

Answer


user EXEC mode
limited number of basic monitoring commands
the first entrance intro the CLI of an IOS device
privileged EXEC mode
accessed by entering the enable command
identified by a prompt ending with the # character
global configuration mode
changes made affect the operation of the device as a whole
accessed by entering the configure terminal command
75. Refer to the exhibit. Match the packets with their destination IP address to the exiting interfaces on the router. (Not all options are used.)


Answer


- FastEthernet0/0 -> packets with destination of 172.17.6.15
- FastEthernet0/1 -> packets with destination of 172.17.14.8
- FastEthernet1/0 -> packets with destination of 172.17.12.10
- FastEthernet1/1 -> packets with destination of 172.17.10.5
- Serial0/0/0 -> packets with destination of 172.17.8.20

- Connectivity to the remote device was successful.
- A router along the path did not have a route to the destination.*
- A ping packet is being blocked by a security device along the path.
- The connection timed out while waiting for a reply from the remote device.
77. A user is unable to reach the web site when typing http://www.cisco.com in a web browser, but can reach the same site by typing http://72.163.4.161. What is the issue?
- default gateway
- DHCP
- TCP/IP protocol stack
- DNS *
78. A company is expanding its business to other countries. All branch offices must remain connected to corporate headquarters at all times. Which network technology is required to support this requirement?
- LAN
- MAN
- WAN*
- WLAN
79. A home user is looking for an ISP connection that provides high speed digital transmission over regular phone lines. What ISP connection type should be used?
- DSL*
- dial-up
- satellite
- cell modem
- cable modem
- by limiting the impact of a network failure
- by allowing quick recovery from network failures
- by providing mechanisms to manage congested network traffic*
- by providing the ability for the network to grow to accommodate new users
81. What source IP address does a router use by default when the traceroute command is issued?
- the highest configured IP address on the router
- the lowest configured IP address on the router
- a loopback IP address
- the IP address of the outbound interface*
82. After making configuration changes on a Cisco switch, a network administrator issues a copy running-config startup-config command. What is the result of issuing this command?
- The new configuration will be stored in flash memory.
- The new configuration will be loaded if the switch is restarted.*
- The current IOS file will be replaced with the newly configured file.
- The configuration changes will be removed and the original configuration will be restored.
83. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is configuring access control to switch SW1. If the administrator has already logged into a Telnet session on the switch, which password is needed to access privileged EXEC mode?

- letmein
- secretin*
- lineconin
- linevtyin
84. Match each item to the type of topology diagram on which it is typically identified. (Not all options are used.)
Question

Answer

- physical topology diagram
location of a desktop PC in a classroom
path of cables that connect rooms to wiring closets - logical topology diagram
IP address of a server
85. Which connection provides a secure CLI session with encryption to a Cisco network device?
- a console connection
- an AUX connection
- a Telnet connection
- an SSH connection*
86. What function does pressing the Tab key have when entering a command in IOS?
- It aborts the current command and returns to configuration mode.
- It exits configuration mode and returns to user EXEC mode.
- It moves the cursor to the beginning of the next line.
- It completes the remainder of a partially typed word in a command.*
87. What layer is responsible for routing messages through an internetwork in the TCP/IP model?
- internet*
- transport
- network access
- session
88. Which statement accurately describes a TCP/IP encapsulation process when a PC is sending data to the network?
- Data is sent from the internet layer to the network access layer.
- Packets are sent from the network access layer to the transport layer.
- Segments are sent from the transport layer to the internet layer.*
- Frames are sent from the network access layer to the internet layer.
89. What unique address is embedded in an Ethernet NIC and used for communication on an Ethernet network?
- host address
- IP address
- MAC address*
- network address
- k layer
90. Which procedure is used to reduce the effect of crosstalk in copper cables?
- requiring proper grounding connections
- twisting opposing circuit wire pairs together*
- wrapping the bundle of wires with metallic shielding
- designing a cable infrastructure to avoid crosstalk interference
- avoiding sharp bends during installation
91. During the encapsulation process, what occurs at the data link layer for a PC connected to an Ethernet network?
- An IP address is added.
- The logical address is added.
- The physical address is added.*
- The process port number is added.
92. What are two characteristics of Ethernet MAC addresses? (Choose two.)
- They are globally unique.*
- They are routable on the Internet.
- They are expressed as 12 hexadecimal digits.*
- MAC addresses use a flexible hierarchical structure.
- MAC addresses must be unique for both Ethernet and serial interfaces on a device.
93. If a device receives an Ethernet frame of 60 bytes, what will it do?
- drop the frame*
- process the frame as it is
- send an error message to the sending device
- add random data bytes to make it 64 bytes long and then forward it
94. Under which two circumstances will a switch flood a frame out of every port except the port that the frame was received on? (Choose two.)
- The frame has the broadcast address as the destination address. *
- The destination address is unknown to the switch.*
- The source address in the frame header is the broadcast address.
- The source address in the frame is a multicast address.
- The destination address in the frame is a known unicast address.
95. Which switching method has the lowest level of latency?
- cut-through
- store-and-forward
- fragment-free
- fast-forward*
96. Which two commands can be used on a Windows host to display the routing table? (Choose two.)
- netstat -s
- route print*
- show ip route
- netstat -r*
- tracert
97. Which two functions are primary functions of a router? (Choose two.)
- packet forwarding*
- microsegmentation
- domain name resolution
- path selection*
- flow control
- 10111010
- 11010101
- 11001010*
- 11011010
99. At a minimum, which address is required on IPv6-enabled interfaces?
- link-local*
- unique local
- site local
- global unicast
100. Which service provides dynamic global IPv6 addressing to end devices without using a server that keeps a record of available IPv6 addresses?
- stateful DHCPv6
- SLAAC*
- static IPv6 addressing
- stateless DHCPv6
101. What is the purpose of the command ping ::1?
- It tests the internal configuration of an IPv6 host.*
- It tests the broadcast capability of all hosts on the subnet.
- It tests the multicast connectivity to all hosts on the subnet.
- It tests the reachability of the default gateway for the network.
102. How many usable IP addresses are available on the 192.168.1.0/27 network?
- 256
- 254
- 62
- 30*
- 16
- 32
103. What is the process of dividing a data stream into smaller pieces before transmission?
- segmentation*
- encapsulation
- encoding
- flow control
104. When IPv4 addressing is manually configured on a web server, which property of the IPv4 configuration identifies the network and host portion for an IPv4 address?
- DNS server address
- subnet mask*
- default gateway
- DHCP server address
105. Which two roles can a computer assume in a peer-to-peer network where a file is being shared between two computers? (Choose two.)
- client*
- master
- server*
- slave
- transient
106. Which two protocols operate at the highest layer of the TCP/IP protocol stack? (Choose two.)
- DNS*
- Ethernet
- IP
- POP*
- TCP
- UDP
107. What is one difference between the client-server and peer-to-peer network models?
- Only in the client-server model can file transfers occur.
- Every device in a peer-to-peer network can function as a client or a server.*
- A peer-to-peer network transfers data faster than a transfer using a client-server network.
- A data transfer that uses a device serving in a client role requires that a dedicated server be present.
108. What is the function of the HTTP GET message?
- to request an HTML page from a web server*
- to send error information from a web server to a web client
- to upload content to a web server from a web client
- to retrieve client email from an email server using TCP port 110
109. Which networking model is being used when an author uploads one chapter document to a file server of a book publisher?
- peer-to-peer
- master-slave
- client/server*
- point-to-point
110. What network service resolves the URL entered on a PC to the IP address of the destination server?
- DNS*
- DHCP
- FTP
- SNMP
111. A network engineer is analyzing reports from a recently performed network baseline. Which situation would depict a possible latency issue?
- a change in the bandwidth according to the show interfaces output
- a next-hop timeout from a traceroute
- an increase in host-to-host ping response times*
- a change in the amount of RAM according to the show version output
112. Which firewall feature is used to ensure that packets coming into a network are legitimate responses to requests initiated from internal hosts?
- stateful packet inspection*
- URL filtering
- application filtering
- packet filtering
113. What is one indication that a Windows computer did not receive an IPv4 address from a DHCP server?
- The computer cannot ping 127.0.0.1.
- Windows displays a DHCP timeout message.
- The computer receives an IP address that starts with 169.254*
- The computer cannot ping other devices on the same network with IP addresses in the 169.254.0.0/16 range.
114. Which command can an administrator issue on a Cisco router to send debug messages to the vty lines?
- terminal monitor*
- logging console
- logging buffered
- logging synchronous
115. Fill in the blank.
During data communications, a host may need to send a single message to a specific group of destination hosts simultaneously. This message is in the form of a Multicast message. 116. A medium-sized business is researching available options for connecting to the Internet. The company is looking for a high speed option with dedicated, symmetric access. Which connection type should the company choose?
- DSL
- dialup
- satellite
- leased line*
- cable modem
- to provide high speed connectivity to all end devices
- to make sure that all types of data packets will be treated equally
- to achieve fault tolerance and high availability of data network infrastructure devices
- to reduce the cost of deploying and maintaining the communication infrastructure*
118. What characteristic of a network enables it to quickly grow to support new users and applications without impacting the performance of the service being delivered to existing users?
- reliability
- scalability*
- quality of service
- accessibility
119. After several configuration changes are made to a router, the copy running-configuration startup-configuration command is issued. Where will the changes be stored?
- flash
- ROM
- NVRAM*
- RAM
- the configuration register
- a TFTP server

- The banner message is too long.
- The delimiting character appears in the banner message.*
- The symbol “!” signals the end of a banner message.
- Message-of-the-day banners will only appear when a user logs in through the console port.
- It is designed as a security protocol to protect switch ports.
- It is not associated with any physical interface on a switch.*
- It is a special interface that allows connectivity by different types of media.
- It is required to allow connectivity by any device at any location.
- It provides a means to remotely manage a switch. *
- It is associated with VLAN1 by default.*
122. A technician configures a switch with these commands:SwitchA(config)# interface vlan 1
SwitchA(config-if)# ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
SwitchA(config-if)# no shutdownWhat is the technician configuring?
- Telnet access
- SVI*
- password encryption
- physical switchport access
123. In computer communication, what is the purpose of message encoding?
- to convert information to the appropriate form for transmission*
- to interpret information
- to break large messages into smaller frames
- to negotiate correct timing for successful communication
124. What is a characteristic of multicast messages?
- They are sent to a select group of hosts.*
- They must be acknowledged.
- They are sent to a single destination.
- They are sent to all hosts on a network.
125. A large corporation has modified its network to allow users to access network resources from their personal laptops and smart phones. Which networking trend does this describe?
- bring your own device*
- video conferencing
- online collaboration
- cloud computing
A dedicated server is not needed when implementing a peer-to-peer network.
- true*
- false
- Internet
- intranet
- extranet*
- extendednet
- 255.255.240.0
- 255.255.255.224
- 255.255.255.240
- 255.255.255.128*
- 255.255.252.0
- 210
- 60
- 109
- 107*
- 146
Version 5:
130. What is a function of the data link layer?- provides the formatting of data
- provides for the exchange of data over a common local media*
- provides end-to-end delivery of data between hosts
- provides delivery of data between two applications
- wiki
- weblog
- instant messaging*
- regenerating data signals*
- acting as a client or a server
- providing a channel over which messages travel
- applying security settings to control the flow of data *
- notifying other devices when errors occur*
- serving as the source or destination of the messages

- flash memory*
- NVRAM?
- RAM
- ROM
- a TFTP server?

- PC1 can send a ping to 192.168.1.1?.
- PC1 can send a ping to 192.168.1.254?.
- PC2 can send a ping to 192.168.1.1.*
- PC2 can send a ping to 192.168.1.254?.
Port numbers ranging from 0 to 1023 are considered to be Well Known ports.
136. Fill in the blank.
ISOC, IANA, EIA, and IEEE represent standards organizations which help to promote and maintain an open Internet.
137. Refer to the exhibit. An administrator is trying to configure the switch but receives the error message that is displayed in the exhibit. What is the problem?

- The entire command, configure terminal, must be used.
- The administrator is already in global configuration mode.
- The administrator must first enter privileged EXEC mode before issuing the command.*
- The administrator must connect via the console port to access global configuration mode.
- LAN
- MAN
- WAN*
- WLAN
139. A network administrator is upgrading a small business network to give high priority to real-time applications traffic. What two types of network services is the network administrator trying to accommodate? (Choose two.)
- SNMP
- instant messaging
- voice*
- FTP
- video*
Question

Answer
CCNA 1 v6.0 Final Exam Answers 2019-2020
- Copper Cables
horizontal cabling structure
desktop PCs in an enterprise office - Fiber Optic
backbone cabling in an enterprise
long-haul networks - Wireless
guest access in a coffee shop
waiting rooms in a hospital
141. Which IPv4 address can be pinged to test the internal TCP/IP operation of a host?
- 0.0.0.0
- 0.0.0.1
- 127.0.0.1*
- 192.168.1.1
- 255.255.255.255
ARP
- DHCP*
- DNS*
- FTP*
- NAT
- PPP
- ARP
- BOOTP
- ICMP*
- IP*
- PPP
- Request for Comments*
- IRTF research papers
- protocol models
- IEEE standards
- IP address
- default gateway address
- MAC address*
- logical address
- ARP, multicast
- DNS, unicast
- DNS, broadcast
- ARP, broadcast*
- PING, multicast
- PING, broadcast
- The host cannot communicate with other hosts in the local network.
- The switch will not forward packets initiated by the host.
- The host will have to use ARP to determine the correct address of the default gateway.
- The host cannot communicate with hosts in other networks.*
- A ping from the host to 127.0.0.1 would not be successful.
- It accepts frames from the physical media.
- It encapsulates upper layer data into frames.
- It defines the media access method performed by the hardware interface.
- It encodes frames into electrical, optical, or radio wave signals.*
- Fiber-optic cabling does not conduct electricity.*
- Fiber-optic cabling has high signal loss.
- Fiber-optic cabling is primarily used as backbone cabling.*
- Multimode fiber-optic cabling carries signals from multiple sending devices.
- Fiber-optic cabling uses LEDs for single-mode cab?les and laser technology for multimode cables.
- logical address
- physical address
- data
- error detection*

- just PC0 and PC1 MAC addresses*
- just the PC0 MAC address
- PC0, PC1, and PC2 MAC addresses
- just the PC1 MAC address
- just the PC2 MAC address
- A Layer 3 switch supports VLANs, but a Layer 2 switch does not.
- An IP address can be assigned to a physical port of a Layer 3 switch. However, this is not supported in Layer 2 switches.*
- A Layer 3 switch maintains an IP address table instead of a MAC address table.
- A Layer 3 switch learns the MAC addresses that are associated with each of its ports. However, a Layer 2 switch does not.
- to encapsulate data that is used to communicate across a network
- to select the paths that are used to direct traffic to destination networks*
- to convert a URL name into an IP address
- to provide secure Internet file transfer
- to forward traffic on the basis of MAC addresses
- ARP
- DNS
- NAT*
- SMB
- DHCP
- HTTP

- It is the IP address of the Router1 interface that connects the company to the Internet.
- It is the IP address of the Router1 interface that connects the PC1 LAN to Router1.*
- It is the IP address of Switch1 that connects PC1 to other devices on the same LAN.
- It is the IP address of the ISP network device located in the cloud.
- packet switching*
- microsegmentation
- domain name resolution
- path selection*
- flow control
- ROM is nonvolatile and contains basic diagnostic software.*
- FLASH is nonvolatile and contains a limited portion of the IOS.
- ROM is nonvolatile and stores the running IOS.
- RAM is volatile and stores the IP routing table.*
- NVRAM is nonvolatile and stores other system files.
- NVRAM, RAM, TFTP
- NVRAM, TFTP, setup mode*
- setup mode, NVRAM, TFTP
- TFTP, ROM, NVRAM
- flash, ROM, setup mode
- A delivery failure message is sent to the source host.
- The part of the VoIP transmission that was lost is re-sent.
- The entire transmission is re-sent.
- The transmission continues without the missing portion.*
- 10.172.168.1*
- 172.32.5.2
- 192.167.10.10
- 172.20.4.4 *
- 192.168.5.254*
- 224.6.6.6
- 4
- 8
- 16*
- 32
- to assign the router to the all-nodes multicast group
- to enable the router as an IPv6 router*
- to permit only unicast packets on the router
- to prevent the router from joining the all-routers multicast group
- FEC0::/10?
- FDFF::/7?
- FEBF::/10?
- FF00::/8*
- to inform routers about network topology changes
- to ensure the delivery of an IP packet
- to provide feedback of IP packet transmissions*
- to monitor the process of a domain name to IP address resolution

- The DNS server addresses are incorrect.
- The default gateway address in incorrect.*
- The wrong subnet mask was assigned to the workstation.
- The workstation is not in the same network as the DNS servers.
- random static addresses to improve security
- addresses from different subnets for redundancy
- predictable static IP addresses for easier identification*
- dynamic addresses to reduce the probability of duplicate addresses

- Site 1
- Site 2*
- Site 3
- Site 4
- /62
- /64*
- /66
- /68*
- /70
- DHCPDISCOVER*
- DHCPOFFER
- DHCPREQUEST*
- DHCPACK
- DHCPNACK
- to require users to prove who they are
- to determine which resources a user can access
- to keep track of the actions of a user*
- to provide challenge and response questions
R1# copy running-config tftp
Address or name of remote host [ ]?
When the router prompts for an address or remote host name, what IP address should the administrator enter at the prompt?

- 192.168.9.254
- 192.168.10.1
- 192.168.10.2
- 192.168.11.252*
- 192.168.11.254

173. What two preconfigured settings that affect security are found on most new wireless routers? (Choose two.)
- broadcast SSID*
- MAC filtering enabled
- WEP encryption enabled
- PSK authentication required
- default administrator password*
- EAP
- PSK
- WEP
- WPA*
TFTP* is a best-effort, connectionless application layer protocol that is used to transfer files.
176. Which two components are necessary for a wireless client to be installed on a WLAN? (Choose two.)
- media
- wireless NIC*
- custom adapter
- crossover cable
- wireless bridge
- wireless client software*
2001:0DB8:BC15:00A0:0000:: 2001:0DB8:BC15:00A1:0000:: 2001:0DB8:BC15:00A2:0000:: … 2001:0DB8:BC15:00AF:0000::The prefix-length for the range of addresses is /60*
178. Match the phases to their correct stage in the router bootup process. (Not all options are used.)

179. A host is accessing an FTP server on a remote network. Which three functions are performed by intermediary network devices during this conversation? (Choose three.)
- regenerating data signals*
- acting as a client or a server
- providing a channel over which messages travel
- applying security settings to control the flow of data*
- notifying other devices when errors occur*
- serving as the source or destination of the messages
- when a cellular telephone provides the service
- when a high-speed connection is provided over a cable TV network
- when a satellite dish is used
- when a regular telephone line is used*
- audio conference, database, HTTP*
- database, HTTP, audio conference
- audio conference, HTTP, database
- database, audio conference, HTTP
- RAM*
- flash
- NVRAM
- disk drive
- Ctrl-Shift-X
- Ctrl-Shift-6*
- Ctrl-Z
- Ctrl-C
- HR Switch(config)#?
- Switch(config)#?*
- HRSwitch(config)#?
- HR(config)#?
- Switch#
- the TCP/IP stack on a network host*
- connectivity between two adjacent Cisco devices
- connectivity between a PC and the default gateway
- connectivity between two PCs on the same network
- physical connectivity of a particular PC and the network

187. Which device should be used for enabling a host to communicate with another host on a different network?
- switch
- hub
- router*
- host
- the amount of traffic that is currently crossing the network*
- the sophistication of the encapsulation method applied to the data
- the type of traffic that is crossing the network*
- the latency that is created by the number of network devices that the data is crossing*
- the bandwidth of the WAN connection to the Internet
- the reliability of the gigabit Ethernet infrastructure of the backbone
- It is not affected by EMI or RFI.*
- Each pair of cables is wrapped in metallic foil.
- It combines the technique of cancellation, shielding and twisting to protect data.
- It has a maximum speed of 100 Mbps.
- It is the most expensive type of LAN cabling*
- It is straightforward to troubleshoot.*
- End devices are connected together by a bus.
- It is easy to add and remove end devices.*
- All end devices are connected in a chain to each other.
- Each end system is connected to its respective neighbor.
- to determine the physical address of the sending device
- to verify the network layer protocol information
- to compare the interface media type between the sending and receiving ends
- to check the frame for possible transmission errors*
- to verify that the frame destination matches the MAC address of the receiving device
- It initiates an ARP request.
- It broadcasts the frame out of all ports on the switch.
- It notifies the sending host that the frame cannot be delivered.
- It forwards the frame out of all ports except for the port at which the frame was received.*
- the lower metric value that is associated with the destination network*
- the lower gateway IP address to get to the destination network
- the higher metric value that is associated with the destination network
- the higher gateway IP address to get to the destination network
- stores routing tables
- allows software to be updated without replacing pluggable chips on the motherboard
- maintains instructions for POST diagnostics*
- holds ARP cache
- stores bootstrap program*
- A console port is used for remote management of the router.
- A console port is not used for packet forwarding.*
- Serial and DSL interfaces are types of management ports.
- Each Cisco router has a LED indicator to provide information about the status of the management ports.
- A delivery failure message is sent to the source host.
- The part of the radio transmission that was lost is re-sent.
- The entire transmission is re-sent.
- The transmission continues without the missing portion.*
- private addresses
- public addresses*
- multicast addresses
- experimental addresses

- 11
- 12
- 13*
- 14
- 192.168.1.16/28
- 192.168.1.64/27*
- 192.168.1.128/27
- 192.168.1.96/28*
- 192.168.1.192/28
- /23
- /24
- /25*
- /26
- Transmission Control Protocol
- Real-Time Transport Protocol*
- Secure File Transfer Protocol
- Video over Internet Protocol
- to determine the active TCP connections on a PC
- to check information about a DNS name in the DNS server
- to identify where a packet was lost or delayed on a network*
- to display the IP address, default gateway, and DNS server address for a PC

- The asterisk shows which file system was used to boot the system.
- The asterisk designates which file system is the default file system.*
- An asterisk indicates that the file system is bootable.
- An asterisk designates that the file system has at least one file that uses that file system.
- EAP
- PSK
- WEP
- WPA*
Point-to-point communications where both devices can transmit and receive on the medium at the same time are known as full-duplex
206. Match each characteristic to the appropriate email protocol. (Not all options are used.)

207. A host is accessing a Telnet server on a remote network. Which three functions are performed by intermediary network devices during this conversation? (Choose three.)
- regenerating data signals*
- acting as a client or a server
- providing a channel over which messages travel
- applying security settings to control the flow of data*
- notifying other devices when errors occur*
- serving as the source or destination of the messages

- area A
- area B
- area C*
- area D
- audio conference, financial transactions, web page*
- financial transactions, web page, audio conference
- audio conference, web page, financial transactions
- financial transactions, audio conference, web page
210. During normal operation, from which location do most Cisco switches and routers run the IOS?
- RAM*
- flash
- NVRAM
- disk drive
- The configuration will be copied to flash.
- The configuration will load when the router is restarted.*
- The new configuration file will replace the IOS file.
- The changes will be lost when the router restarts.
- The TCP/IP stack on the device is working correctly.*
- The device has end-to-end connectivity.
- DHCP is working correctly.
- The Ethernet cable is working correctly.
- The device has the correct IP address on the network.
- The switch places the new CRC value in the FCS field and forwards the frame.
- The switch notifies the source of the bad frame.
- The switch drops the frame.*
- The switch floods the frame to all ports except the port through which the frame arrived to notify the hosts of the error.
- 0.0.0.0
- 255.255.255.255
- FFFF.FFFF.FFFF*
- 127.0.0.1
- 01-00-5E-00-AA-23
- the automatic configuration of an interface for 10/100/1000 Mb/s operation
- the automatic configuration of an interface for a straight-through or a crossover Ethernet cable connection*
- the automatic configuration of full-duplex operation over a single Ethernet copper or optical cable
- the ability to turn a switch interface on or off accordingly if an active connection is detected
- adjacency tables*
- MAC-address tables
- routing tables
- ARP tables
- forwarding information base (FIB)*
- It receives the packet and forwards it directly to the destination host.
- It de-encapsulates the packet, selects the appropriate path, and encapsulates the packet to forward it toward the destination host*
- It de-encapsulates the packet and forwards it toward the destination host.
- It selects the path and forwards it toward the destination host.

- The directly connected networks have to be created manually to be displayed in the routing table.
- The routing table will only display information about these networks when the router receives a packet.
- The no shutdown command was not issued on these interfaces.*
- The gateway of last resort was not configured.
- A delivery failure message is sent to the source host.
- The part of the television transmission that was lost is re-sent.
- The entire transmission is re-sent.
- The transmission continues without the missing portion.*
- TCP and UDP port numbers are used by application layer protocols.*
- TCP uses port numbers to provide reliable transportation of IP packets.
- UDP uses windowing and acknowledgments for reliable transfer of data.
- TCP uses windowing and sequencing to provide reliable transfer of data.*
- TCP is a connection-oriented protocol. UDP is a connectionless protocol.*
- Datagrams that arrive in a different order than that in which they were sent are not placed in order.*
- A session must be established before datagrams can be exchanged.
- A three-way handshake takes place before the transmission of data begins.
- Application servers have to use port numbers above 1024 in order to be UDP capable.
- MAC address
- IP address*
- kernel
- shell
- subnet mask*
- It eliminates most address configuration errors.*
- It ensures that addresses are only applied to devices that require a permanent address.
- It guarantees that every device that needs an address will get one.
- It provides an address only to devices that are authorized to be connected to the network.
- It reduces the burden on network support staff.*
- 2001:DB8:BC15::0
- 2001:DB8:BC15:A::0*
- 2001:DB8:BC15:A:1::1
- 2001:DB8:BC15:A:12::0
- to require users to prove who they are*
- to determine which resources a user can access
- to keep track of the actions of a user
- to provide challenge and response questions
- EAP
- PSK
- WEP
- WPA*

Open the PT activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then fill in the blank.
The Server0 message isb ”winner”
228. Which field in an IPv4 packet header will typically stay the same during its transmission?
- Packet Length
- Destination Address*
- Flag
- Time-to-Live

Open the PT Activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then answer the question. Which IPv6 address is assigned to the Serial0/0/0 interface on RT2?
- 2001:db8:abc:1::1
- 2001:db8:abc:5::1*
- 2001:db8:abc:5::2
- 2001:db8:abc:10::15
- Manually configure next-hop Layer 2 addresses.
- Issue the no shutdown command on routed ports.
- CEF is enabled by default, so no configuration is necessary.*
- Manually map Layer 2 addresses to Layer 3 addresses to populate the forwarding information base (FIB).
- to populate the forwarding information base (FIB)
- to maintain Layer 2 next-hop addresses*
- to allow the separation of Layer 2 and Layer 3 decision making
- to update the forwarding information base (FIB)
- It manages the data transport between the processes running on each host.
- In the encapsulation process, it adds source and destination port numbers to the IP header.
- When a packet arrives at the destination host, its IP header is checked by the network layer to determine where the packet has to be routed.
- Its protocols specify the packet structure and processing used to carry the data from one host to another.*
- Both users must be using the same Internet Service Provider.
- ISPs use Network Address Translation to change a user IP address into an address that can be used on the Internet.*
- ISPs use Domain Name Service to change a user IP address into a public IP address that can be used on the Internet.
- Both users must be on the same network.
- to ensure the fastest possible download speed
- because HTTP is a best-effort protocol
- because transmission errors can be tolerated easily
- because HTTP requires reliable delivery*
- 2001:DB8:0:AB00::1234*
- 2001:DB8:0:AB::1234
- 2001:DB8::AB00::1234
- 2001:DB8:0:AB:0:1234
- TTL field
- CRC field
- Hop Limit field*
- Time Exceeded field
- port filtering
- stateful packet inspection*
- URL filtering
- application filtering
- trace 10.1.1.5
- traceroute 10.1.1.5
- tracert 10.1.1.5*
- ping 10.1.1.5
To prevent faulty network devices from carrying dangerous voltage levels, equipment must be grounded *correctly
240. What is a possible hazard that can be caused by network cables in a fire?
- The cable insulation could be flammable.*
- Users could be exposed to excessive voltage.
- Network cables could be exposed to water.
- The network cable could explode.
- a multimeter
- an Optical Time Domain Reflectometer
- a cable tester*
- an ohmmeter
- capacitance
- wire map*
- inductance
- flexibility

- just PC0 and PC1 MAC addresses*
- just the PC0 MAC address
- PC0, PC1, and PC2 MAC addresses
- just the PC1 MAC address
- just the PC2 MAC address
- data encapsulation
- detection of missing packets*
- communication session control
- path determination for data packets
- an ARP table
- a routing table*
- the destination PC physical address
- a switching table
- an inband router interface
- a console port
- a serial WAN interface
- an AUX port*
- user executive mode
- global configuration mode
- any line configuration mode*
- privileged EXEC mode
- TCP and UDP port numbers are used by application layer protocols.*
- TCP uses port numbers to provide reliable transportation of IP packets.
- UDP uses windowing and acknowledgments for reliable transfer of data.
- TCP uses windowing and sequencing to provide reliable transfer of data.*
- TCP is a connection-oriented protocol. UDP is a connectionless protocol.*

- 2
- 21
- 250
- 306*
- 2921
- IPv6 traffic-forwarding is enabled on the interface.
- A link-local IPv6 address is automatically configured on the interface.*
- A global unicast IPv6 address is dynamically configured on the interface.
- Any IPv4 addresses that are assigned to the interface are replaced with an IPv6 address.

- 172.16.16.255
- 172.16.20.255
- 172.16.19.255*
- 172.16.23.255
- 172.16.255.255
- 10.1.1.128/28
10.1.1.144/28
10.1.1.160/29* - 10.1.1.128/28
10.1.1.144/28
10.1.1.160/28 - 10.1.1.128/28
10.1.1.140/28
10.1.1.158/26 - 10.1.1.128/26
10.1.1.144/26
10.1.1.160/26 - 10.1.1.128/26
10.1.1.140/26
10.1.1.158/28
- 2
- 3
- 4*
- 5
- 6

255. Refer to the exhibit. The administrator configured the access to the console and the vty lines of a router. Which conclusion can be drawn from this configuration?

- Unauthorized individuals can connect to the router via Telnet without entering a password.
- Because the IOS includes the login command on the vty lines by default, access to the device via Telnet will require authentication.*
- Access to the vty lines will not be allowed via Telnet by anyone.
- Because the login command was omitted, the password cisco command is not applied to the vty lines.
- It will remove encryption from all passwords.
- It will reverse only the vty and console password encryptions.
- It will not reverse any encryption.*
- It will reverse only the enable password encryption.
- The new configuration will be stored in flash memory.
- The new configuration will be loaded if the switch is restarted.*
- The current IOS file will be replaced with the newly configured file.
- The configuration changes will be removed and the original configuration will be restored.
- If a host is ready to send a packet to a local destination device and it has the IP address but not the MAC address of the destination, it generates an ARP broadcast.*
- An ARP request is sent to all devices on the Ethernet LAN and contains the IP address of the destination host and its multicast MAC address.
- When a host is encapsulating a packet into a frame, it refers to the MAC address table to determine the mapping of IP addresses to MAC addresses.
- If no device responds to the ARP request, then the originating node will broadcast the data packet to all devices on the network segment.
- If a device receiving an ARP request has the destination IPv4 address, it responds with an ARP reply.*
- Data sent with a service that uses TCP is received in the order the data was sent.
- A port is considered to be open when it has an active server application that is assigned to it.*
- An individual server can have two services that are assigned to the same port number.
- An individual server cannot have multiple services running at the same time.
- Server security can be improved by closing ports that are associated with unused services.*
- 234.17.10.9
- 234.16.12.10
- 236.17.12.6
- 236.17.12.10*
- ipconfig /all
- arp -a
- ipconfig /displaydns*
- nslookup
Network devices come in two physical configurations. Devices that have expansion slots that provide the flexibility to add new modules have a Modular * configuration.
263. Refer to the exhibit. What is the maximum TIL value that is used to reach the destination www.cisco.com?

- 11
- 12
- 13*
- 14
- When a device that is configured to use DHCP boots, the client broadcasts a DHCPDISCOVER message to identify any available DHCP servers on the network.*
- A client must wait for lease expiration before it sends another DHCPREOUEST message.
- The DHCPDISCOVER message contains the IP address and sub net masK to be assigned, the IP address of the DNS server, and the IP address of the default gateway.
- If the client receives several DHCPOFFER messages from different servers, it sends a unicast DHCPREOUEST message to the server from which it chooses to obtain the IP information.
- EAP
- PSK
- WEP*
- WPA
- the amount of traffic*
- the type of data encapsulation in use
- the type of traffic*
- the number and type of network devices that the data is crossing*
- the bandwidth of the connection to the ISP
- the reliability of the network backbone
- DHCPDISCOVER
- DHCPOFFER*
- DHCPPREQUEST
- DHCPACK
- DHCPNACK

- letmein
- secretin
- lineconin*
- linevtyin
269. How many bits would need to be borrowed if a network admin were given the IP addressing scheme of 172.16.0.0/16 and needed no more than 16 subnet with equal number of hosts?
- 10
- 12
- 2
- 4*
- 8

It will give 4 options about ping, the correct one is:
The PC2 will be able to ping 192.168.1.1*
271. Which statement best describes the operation of the File Transfer Protocol?
- An FTP client uses a source port number of 21 and a randomly generated destination port number during the establishment of control traffic with an FTP Server.
- An FTP client uses a source port number of 20 and a randomly generated destination port number during the establishment of data traffic with an FTP Server.
- An FTP server uses a source port number of 20 and a randomly generated destination port number during the establishment of control traffic with an FTP client.*
- An FTP server uses a source port number of 21 and a randomly generated destination port number during the establishment of control traffic with an FTP client.
- The acknowledgment number field is modified by adding 1 to the randomly chosen initial sequence number in response to the client.*
- The acknowledgment number is set to 11 to signify an acknowledgment packet and synchronization packet back to the client.
- The acknowledgment number field uses a random source port number in response to the client.
- The acknowledgment number is set to 1 to signify an acknowledgment packet back to the client.
- to identify host address and destination host;
- to identify network address of destination host;*
- to identify faulty frames;
- to identify broadcast address of destination network;
- no password at all;*
- password of the lines are in clear;
- login password;
- ?
- message encapsulation
- flow control
- message encoding
- access method*
- to conserve IPv6 addresses
- to avoid wasting IPv6 addresses
- to conserve IPv6 prefixes
- to create a hierarchical Layer 3 network design*
- It is the measure of the bits transferred across the media under perfect conditions.
- It is the measure of the bits transferred across the media over a given period of time.*
- It indicates the capacity of a particular medium to carry data.
- It is the guaranteed data transfer rate offered by an ISP.
IPv4 multicast addresses are directly mapped to IEEE 802 (Ethernet) MAC addresses using the last ___4___ of the 28 available bits in the IPv4 multicast group address.
279. How could a faulty network device create a source of hazard for a user? (Choose two.)
- It could stop functioning.*
- It could apply dangerous voltage to other pieces of equipment.
- It could explode.*
- It could produce an unsafe electromagnetic field.
- It could apply dangerous voltage to itself.
- preventing duplication of addresses*
- providing and controlling access*
- documenting the network
- monitoring security and performance
- conserving addresses*
- implementing new services
- 24
- 90
- 05
- 2170112*
- VoIP*
- DNS*
- HTTP
- FTP
- POP3
New Questions (v6.0):
283. What action does a DHCPv4 client take if it receives more than one DHCPOFFER from multiple DHCP servers?- It sends a DHCPREQUEST that identifies which lease offer the client is accepting.*
- It sends a DHCPNAK and begins the DHCP process over again.
- It discards both offers and sends a new DHCPDISCOVER.
- It accepts both DHCPOFFER messages and sends a DHCPACK.
- Class B
- Class D
- Class A*
- Class C
- Class E
- 16
- 14
- 8
- 254
- 6*
- 2
- radio waves*
- fiber
- microwave
- UTP
- EUI-64
- static
- SLAAC*
- stateful DHCPv6
- DNS servers can cache recent queries to reduce DNS query traffic.*
- DNS servers are programmed to drop requests for name translations that are not within their zone.
- All DNS servers must maintain mappings for the entire DNS structure.
- DNS relies on a hub-and-spoke topology with centralized servers.
- 2001:DB8:BC15
- 2001:DB8:BC15:A*
- 2001:DB8:BC15:A:1
- 2001:DB8:BC15:A:12
- Layer 2 next hops
- MAC address to IPv4 address mappings*
- IP address to interface mappings
- the IP addresses of all neighboring routers
- terminal monitor*
- logging console
- logging buffered
- logging synchronous
292. What is an example of a top-level domain?
- root.cisco.com
- http://www.cisco.com
- .com*
- cisco.com
293. Which protocol requires the establishment of a session between sender and receiver hosts prior to transmitting data?
- UDP
- TCP*
- IP
- ICMP
- TCP
- IP
- UDP
- POP
- DNS
- Ethernet
- It sends to the server a segment with the SYN flag set to synchronize the conversation.
- It just sends the datagrams.*
- It queries the server to see if it is ready to receive data.
- It sends a simplified three-way handshake to the server.
- They are sent to all hosts on a network.
- They must be acknowledged.
- They are sent to a select group of hosts.*
- They are sent to a single destination.
- FTP
- HTTP
- DNS *
- SMTP
- master-slave
- client-based
- peer-to-peer *
- point-to-point
Introduction to Networks (Version 7.00) – Final Exam Answers Full
1. An employee of a large corporation remotely logs into the company using the appropriate username and password. The employee is attending an important video conference with a customer concerning a large sale. It is important for the video quality to be excellent during the meeting. The employee is unaware that after a successful login, the connection to the company ISP failed. The secondary connection, however, activated within seconds. The disruption was not noticed by the employee or other employees.What three network characteristics are described in this scenario? (Choose three.)
- security
- quality of service
- scalability
- powerline networking
- integrity
- fault tolerance
- does not require a dedicated end-to-end connection *
- operates independently of the network media*
- retransmits packets if errors occur
- re-assembles out of order packets into the correct order at the receiver end
- guarantees delivery of packets
3. A company has a file server that shares a folder named Public. The network security policy specifies that the Public folder is assigned Read-Only rights to anyone who can log into the server while the Edit rights are assigned only to the network admin group. Which component is addressed in the AAA network service framework?
- automation
- accounting
- authentication
- authorization












thank you
RépondreSupprimer