1. An administrator is configuring single-area OSPF on a
router. One of the networks that must be advertised is 64.102.0.0
255.255.255.128. What wildcard mask would the administrator use in the
OSPF network statement?
3. An administrator is configuring single-area OSPF on a router. One of the networks that must be advertised is 128.107.0.0 255.255.255.192. What wildcard mask would the administrator use in the OSPF network statement?

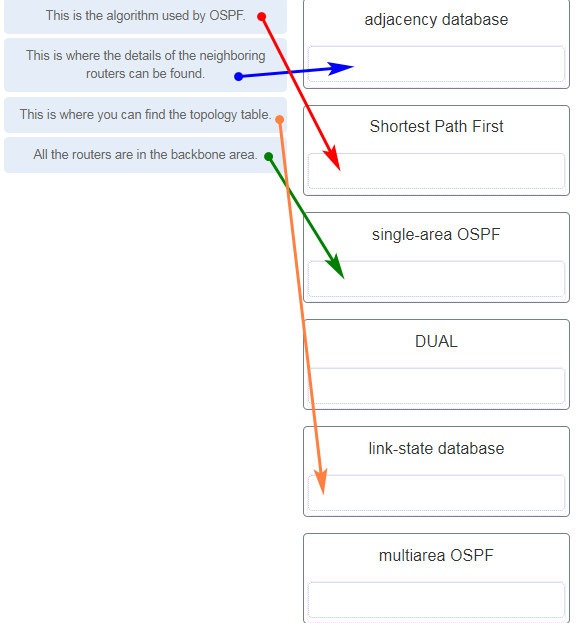
DUAL is the algorithm used by EIGRP. In multiarea OSPF, OSPF is implemented using multiple areas, and all of them must be connected to the backbone area.
34. After modifying the router ID on an OSPF router, what is the preferred method to make the new router ID effective?
Which task has to be performed on Router 1 for it to establish an OSPF adjacency with Router 2?
39. What is a benefit of multiarea OSPF routing?
41. What indicates to a link-state router that a neighbor is unreachable?
44. What is a function of OSPF hello packets?
- 0.0.31.255
- 0.0.0.63
- 0.0.63.255
- 0.0.0.127
- show ipv6 ospf interface serial 0/0/0
- show ip ospf neighbor
- show ip ospf interface fastethernet 0/1
- show ip ospf interface serial 0/0/0
3. An administrator is configuring single-area OSPF on a router. One of the networks that must be advertised is 128.107.0.0 255.255.255.192. What wildcard mask would the administrator use in the OSPF network statement?
- 0.0.63.255
- 0.0.0.63
- 0.0.0.3
- 0.0.0.7
- routers that share the same router ID
- routers whose SPF trees are identical
- routers that have the same link-state information in their LSDBs
- routers that share the same process ID
- the use of multiple areas
- frequent SPF calculations
- autosummarization
- the election of designated routers
- forwarding database
- link-state database
- adjacency database
- routing table
- builds the topology table
- exchanges link-state advertisements
- chooses the best path
- executes the SPF algorithm
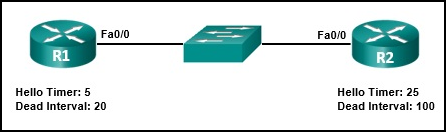
- The dead interval will not change from the default value.
- The dead interval will now be 30 seconds.
- The dead interval will now be 60 seconds.
- The dead interval will now be 15 seconds.

- R1 automatically adjusts its own timers to match the R2 timers.
- The R1 dead timer expires between hello packets from R2.
- The hello timer on R2 expires every ten seconds.
- The neighbor adjacency has formed.
- dead interval
- router priority
- list of neighbors
- router ID
- hello interval
- 0
- 1
- 10
- 255
- database description
- link-state update
- link-state request
- link-state acknowledgment
- when the two adjacent neighbors are interconnected over a point-to-point link
- when all the routers in an OSPF area cannot form adjacencies
- when the routers are interconnected over a common Ethernet network
- when the two adjacent neighbors are in two different networks
- every 5 minutes
- every 10 minutes
- every 30 minutes
- every 60 minutes
- a loopback interface that is configured with the highest IP address on the router
- any IP address that is configured using the router-id command
- the highest active interface IP that is configured on the router
- the highest active interface that participates in the routing process because of a specifically configured network statement
- to uniquely identify the router within the OSPF domain
- to facilitate router participation in the election of the designated router
- to enable the SPF algorithm to determine the lowest cost path to remote networks
- to facilitate the establishment of network convergence
- to facilitate the transition of the OSPF neighbor state to Full

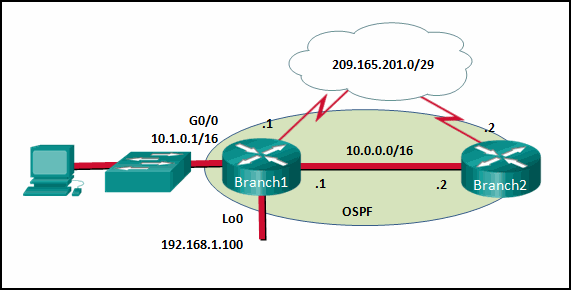
- 10.0.0.1
- 10.1.0.1
- 192.168.1.100
- 209.165.201.1
R1(config)# router ospf 11 R1(config-router)# network 10.10.10.0 0.0.0.255 area 0What does the number 11 represent?
- the OSPF process ID on R1
- the cost of the link to R1
- the autonomous system number to which R1 belongs
- the administrative distance that is manually assigned to R1
- the area number where R1 is located
- router(config-router)# network 172.16.1.0 0.0.255.255 area 0
- router(config-router)# network 172.16.0.0 0.0.15.255 area 0
- router(config-router)# network 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0 area 0
- router(config-router)# network 172.16.1.0 0.0.0.0 area 0

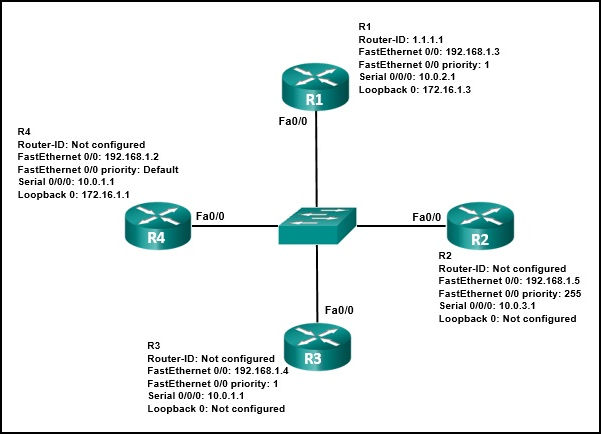
- R3 will be elected BDR.
- The R4 FastEthernet 0/0 priority is 128.
- The R4 router ID is 172.16.1.1.
- R1 will be elected BDR.
- The router ID on R2 is the loopback interface.
- R2 will be elected DR.

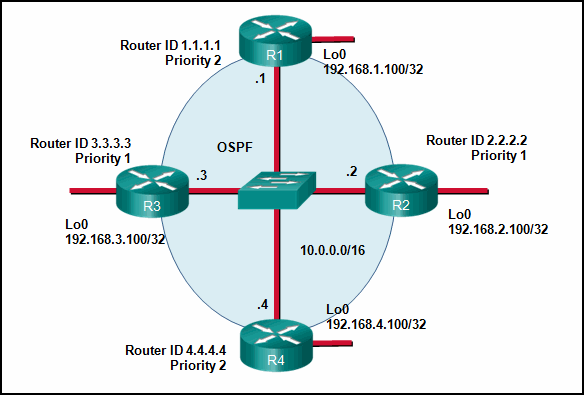
- Router R4 will become the DR and router R1 will become the BDR.
- Router R2 will become the DR and router R3 will become the BDR.
- Router R1 will become the DR and router R2 will become the BDR.
- Router R4 will become the DR and router R3 will become the BDR.
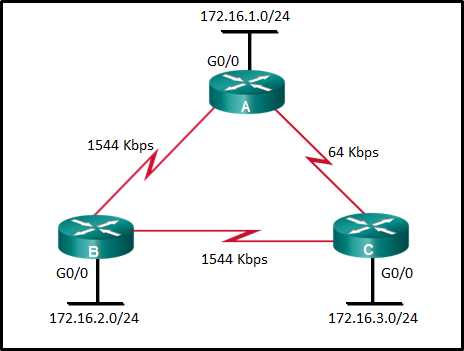
- 100000000
- 10000
- 1
- 100

- 782
- 74
- 128
- 65

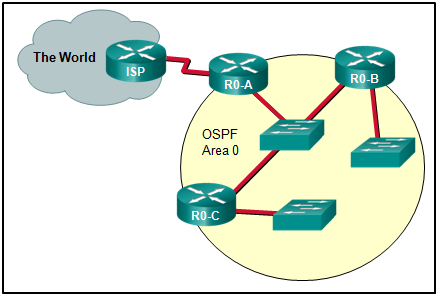
- R0-A
- ISP, R0-A, R0-B, and R0-C
- ISP
- R0-B and R0-C
- ISP and R0-A
- R0-A, R0-B, and R0-C
- ping
- show ip ospf neighbor
- show ip interface brief
- show ip protocols

- R1# show ip ospf interface serial0/0/1
- R1# show ip route ospf
- R1# show ip ospf
- R1# show ip ospf neighbor
- show ip interface brief
- show ip ospf interface
- show ip protocols
- show ip route ospf

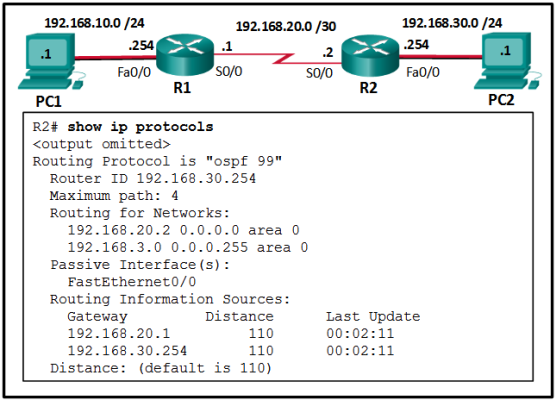
- Interface Fa0/0 has not been activated for OSPFv2 on router R2.
- Interface Fa0/0 is configured as a passive-interface on router R2.
- Interface S0/0 is configured as a passive-interface on router R2.
- Interface s0/0 has not been activated for OSPFv2 on router R2.
- Configure a value using the router-id command.
- Use the highest active interface IP address that is configured on the router.
- Use a loopback interface configured with the highest IP address on the router.
- Use the highest IP address assigned to an active interface participating in the routing process.
- load balancing equal-cost paths
- declaring a neighbor to be inaccessible
- choosing the best route
- executing the SPF algorithm
- 0.0.1.255
- 0.0.7.255
- 0.0.15.255
- 0.0.31.255
- a unique router host name that is configured on the router
- a unique phrase with no more than 16 characters
- a 32-bit number formatted like an IPv4 address
- an 8-bit number with a decimal value between 0 and 255
- a character string with no space
DUAL is the algorithm used by EIGRP. In multiarea OSPF, OSPF is implemented using multiple areas, and all of them must be connected to the backbone area.
34. After modifying the router ID on an OSPF router, what is the preferred method to make the new router ID effective?
- HQ# copy running-config startup-config
- HQ# resume
- HQ# clear ip route *
- HQ# clear ip ospf process
- It allows all 192.168.1.0 networks to be advertised.
- It tells the router which interface to turn on for the OSPF routing process.
- It changes the router ID of the router to 192.168.1.1.
- It enables OSPF on all interfaces on the router.
- to force that specific link to be used in the destination route
- to more accurately reflect the cost of links greater than 100 Mb/s
- to enable the link for OSPF routing
- to increase the speed of the link
Which task has to be performed on Router 1 for it to establish an OSPF adjacency with Router 2?
- Issue the clear ip ospf process command.
- Change the subnet mask of interface FastEthernet 0/0 to 255.255.255.0.
- Remove the passive interface command from interface FastEthernet 0/0.
- Add the network 10.0.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 command to the OSPF process.

39. What is a benefit of multiarea OSPF routing?
- Topology changes in one area do not cause SPF recalculations in other areas.
- Routers in all areas share the same link-state database and have a complete picture of the entire network.
- A backbone area is not required.
- Automatic route summarization occurs by default between areas.

41. What indicates to a link-state router that a neighbor is unreachable?
- if the router no longer receives hello packets
- if the router receives an update with a hop count of 16
- if the router receives an LSP with previously learned information
- if the router no longer receives routing updates
- Exchange
- Init
- ExStart
- Two-way
- Loading
- Down

CCNA 3 v7 Modules 1 – 2: OSPF Concepts and Configuration Exam
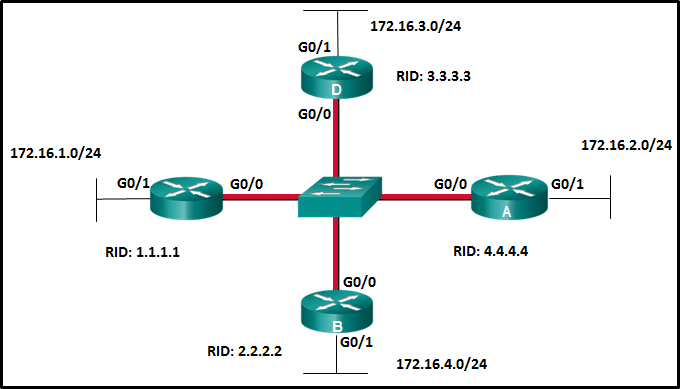
- If the priority of router C is changed to 255, then it will become the DR.
- Router A will become the DR and router D will become the BDR.
- If the DR fails, the new DR will be router B.
- If a new router with a higher priority is added to this network, it will become the DR.
44. What is a function of OSPF hello packets?
- to send specifically requested link-state records
- to discover neighbors and build adjacencies between them
- to ensure database synchronization between routers
- to request specific link-state records from neighbor routers
- hello
- DBD
- LSR
- LSU
- LSAck
- It is a link-state database that represents the network topology.
- Its contents are the result of running the SPF algorithm.
- When converged, all routers in an area have identical topology tables.
- The topology table contains feasible successor routes.
- The table can be viewed via the show ip ospf database command.
- After convergence, the table only contains the lowest cost route entries for all known networks.












0 commentaires:
Enregistrer un commentaire