1. A company uses a cloud-based payroll system. Which cloud computing technology is this company using?
- browser as a service (BaaS)
- infrastructure as a service (IaaS)
- software as a service (SaaS)
- wireless as a service (WaaS)
2. For a data center, what is the difference in the server
virtualization data traffic compared with the traditional client-server
model?
- Data traffic from clients will be routed to multiple virtual servers.
- There are significant data exchanges between virtual servers.
- There is more data traffic flowing from virtual servers to clients.
- More network control traffic is generated between virtual servers and clients.
3. Which component in a traditional infrastructure device
provides Layer 2 and Layer 3 functions to create data paths within a
network?
- data plane
- control plane
- adjacency table
- forwarding information base
4. Which network traffic management technology is a basic element in SDN implementations?
- OpenFlow
- OpenStack
- IEEE 802.1aq
- Interface to the Routing System
5. Which type of hypervisor would most likely be used in a data center?
- Type 2
- Type 1
- Nexus
- Hadoop
Explanation: The
two type of hypervisors are Type 1 and Type 2. Type 1 hypervisors are
usually used on enterprise servers. Enterprise servers rather than
virtualized PCs are more likely to be in a data center.
6. Which is a characteristic of a Type 1 hypervisor?
- installed directly on a server
- best suited for consumers and not for an enterprise environment
- does not require management console software
- installed on an existing operating system
Explanation: Type 1
hypervisors are installed directly on a server and are known as “bare
metal” solutions giving direct access to hardware resources. They also
require a management console and are best suited for enterprise
environments.
7. Which two layers of the OSI model are associated with SDN
network control plane functions that make forwarding decisions? (Choose
two.)
- Layer 1
- Layer 2
- Layer 3
- Layer 4
- Layer 5
Explanation: The SDN control plane uses the Layer 2 ARP table and the Layer 3 routing table to make decisions about forwarding traffic.
8. What pre-populates the FIB on Cisco devices that use CEF to process packets?
- the routing table
- the adjacency table
- the ARP table
- the DSP
Explanation: CEF
uses the FIB and adjacency table to make fast forwarding decisions
without control plane processing. The adjacency table is pre-populated
by the ARP table and the FIB is pre-populated by the routing table.
9. What is a function of the data plane of a network device?
- sending information to the CPU for processing
- building the routing table
- resolving MAC addresses
- forwarding traffic flows
Explanation:
Networking devices operate in two planes; the data plane and the control
plane. The control plane maintains Layer 2 and Layer 3 forwarding
mechanisms using the CPU. The data plane forwards traffic flows.
10. Which statement describes the concept of cloud computing?
- separation of application from hardware
- separation of management plane from control plane
- separation of operating system from hardware
- separation of control plane from data plane
Explanation: Cloud
computing is used to separate the application or service from hardware.
Virtualization separates the operating system from the hardware.
11. Which cloud model provides services for a specific organization or entity?
- a public cloud
- a hybrid cloud
- a private cloud
- a community cloud
Explanation:
Private clouds are used to provide services and applications to a
specific organization and may be set up within the private network of
the organization or managed by an outside organization.
12. What two benefits are gained when an organization adopts cloud computing and virtualization? (Choose two.)
- provides a “pay-as-you-go” model, allowing organizations to treat computing and storage expenses as a utility
- enables rapid responses to increasing data volume requirements
- distributed processing of large data sets in the size of terabytes
- elimination of vulnerabilities to cyber attacks
- increases the dependance on onsite IT resources
Explanation:
Organizations can use virtualization to consolidate the number of
required servers by running many virtual servers on a single physical
server. Cloud computing allows organizations to scale their solutions as
required and to pay only for the resources they require.
13. Which type of Hypervisor is implemented when a user with a laptop running the Mac OS installs a Windows virtual OS instance?
- type 2
- virtual machine
- type 1
- bare metal
Explanation: Type 2
hypervisors, also know as hosted hypervisors, are installed on top of
an existing operating system, such as Mac OS, Windows, or Linux.
14. A small company is considering moving many of its data
center functions to the cloud. What are three advantages of this plan?
(Choose three.)
- The company only needs to pay for the amount of processing and storage capacity that it uses.
- Cloud services are billed at a fixed fee no matter how much processing and storage are used by the company.
- The company does not need to
be concerned about how to handle increasing data storage and processing
demands with in-house data center equipment.
- The company can increase processing and storage capacity as needed and then decrease capacity when it is no longer needed.
- Single-tenant data centers can easily grow to accommodate increasing data storage requirements.
- Cloud services enable the company to own and administer its own servers and storage devices.
Explanation: Cloud
computing offers many advantages to the company. Since the cloud data
storage and processing facilities are owned by third-parties, the
company does not need to be concerned about how it will handle
increasing data storage and processing demands with its own data center
equipment. The company can easily increase or decrease processing power
and storage capacity based on need. Also, cloud services are billed by
usage, so the company does not have the costs of supporting its own
expensive data center that is not always used to maximum capacity.
15. How does virtualization help with disaster recovery within a data center?
- support of live migration
- guarantee of power
- improvement of business practices
- supply of consistent air flow
Explanation: Live
migration allows moving of one virtual server to another virtual server
that could be in a different location that is some distance from the
original data center.
16. What technology allows users to access data anywhere and at any time?
- Cloud computing
- virtualization
- micromarketing
- data analytics
Explanation: Cloud
computing allows organizations to eliminate the need for on-site IT
equipment, maintenance, and management. Cloud computing allows
organizations to expand their services or capabilities while avoiding
the increased costs of energy and space.
17. Which action takes place in the assurance element of the IBN model?
- verification and corrective action
- configuring systems
- translation of policies
- integrity checks
Explanation: The assurance element of the IBN model is concerned with end-to-end verification of network-wide behavior.
18. Refer to the exhibit. Which data format is used to represent the data for network automation applications?

Explanation: The common data formats that are used in many applications including network automation and programmability are as follows:
- JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) – In JSON, the
data known as an object is one or more key/value pairs enclosed in
braces { }. Keys must be strings within double quotation marks ” “. Keys
and values are separated by a colon.
- eXtensible Markup Language (XML) – In XML, the data is enclosed within a related set of tags <tag>data</tag>.
- YAML Ain’t Markup Language (YAML) – In YAML, the
data known as an object is one or more key value pairs. Key value pairs
are separated by a colon without the use of quotation marks. YAML uses
indentation to define its structure, without the use of brackets or
commas.
19. What is the function of the key contained in most RESTful APIs?
- It is the top-level object of the API query.
- It is used to authenticate the requesting source.
- It represents the main query components in the API request.
- It is used in the encryption of the message by an API request.
Explanation: Many
RESTful APIs, including public APIs, require a key. The key is used to
identify the source of the request through authentication.
20. Which two configuration management tools are developed using Ruby? (Choose two.)
- Puppet
- Ansible
- SaltStack
- Chef
- RESTCONF
Explanation: Chef
and Puppet are configuration management tools developed using Ruby.
Ansible and SaltStack are configuration management tools developed using
Python. Ruby is typically considered a more difficult language to learn
than Python. RESTCONF is a network management protocol.
21. Which term is used to describe a set of instructions for execution by the configuration management tool Puppet?
- Playbook
- Cookbook
- Manifest
- Pillar
Explanation: The configuration management tool Puppet uses the name Manifest to describe the set of instructions to be executed.
22. Which term is used to describe a set of instructions for execution by the configuration management tool SaltStack?
- Cookbook
- Manifest
- Pillar
- Playbook
Explanation: The configuration management tool SaltStack uses the name Pillar to describe the set of instructions to be executed.
23. Which scenario describes the use of a public API?
- It requires a license.
- It can be used with no restrictions.
- It is used between a company and its business partners.
- It is used only within an organization.
Explanation:
Public, or open, APIs have no restrictions and are available to the
public. Some API providers do require a user to obtain a free key or
token prior to using the API in order to control the volume of API
requests received and processed.
24. What is YAML?
- It is a scripting language.
- It is a data format and superset of JSON.
- It is a compiled programming language.
- It is a web application.
Explanation: Like
JSON, YAML Ain’t Markup Language (YAML) is a data format used by
applications to store and transport data. YAML is considered a superset
of JSON.
25. Which RESTFul operation corresponds to the HTTP GET method?
Explanation: RESTful operations correspond to the following HTTP methods (shown to the left with the RESTful operation on the right):
- POST > Create
- GET > Read
- PUT/PATCH > Update
- DELETE > Delete
26. Which technology virtualizes the network control plane and moves it to a centralized controller?
- SDN
- fog computing
- cloud computing
- IaaS
Explanation:
Networking devices operate in two planes: the data plane and the control
plane. The control plane maintains Layer 2 and Layer 3 forwarding
mechanisms using the CPU. The data plane forwards traffic flows. SDN
virtualizes the control plane and moves it to a centralized network
controller.
27. What are two functions of hypervisors? (Choose two.)
- to partition the hard drive to run virtual machines
- to manage virtual machines
- to protect the host from malware infection from the virtual machines
- to share the antivirus software across the virtual machines
- to allocate physical system resources to virtual machines
Explanation: The
hypervisor does not protect the hosting OS from malware. Neither does it
allow sharing software across virtual machines. The hard drive of the
supporting computer does not need to be partitioned to run virtual
machines. The hypervisor creates and manages virtual machines on a host
computer and allocates physical system resources to them.
28. What is a difference between the functions of Cloud computing and virtualization?
- Cloud computing requires hypervisor technology whereas virtualization is a fault tolerance technology.
- Cloud computing separates the
application from the hardware whereas virtualization separates the OS
from the underlying hardware.
- Cloud computing provides services on web-based access whereas
virtualization provides services on data access through virtualized
Internet connections.
- Cloud computing utilizes data center technology whereas virtualization is not used in data centers.
Explanation: Cloud
computing separates the application from the hardware. Virtualization
separates the OS from the underlying hardware. Virtualization is a
typical component within cloud computing. Virtualization is also widely
used in data centers. Although the implementation of virtualization
facilitates an easy server fault tolerance setup, it is not a fault
tolerance technology by design. The Internet connection from a data
center or service provider needs redundant physical WAN connections to
ISPs.
29. How is the YAML data format structure different from JSON?
- It uses indentations.
- It uses end tags.
- It uses hierarchical levels of nesting.
- It uses brackets and commas.
Explanation: The structure in YAML is defined by indentations rather than brackets and commas.
30. What is the most widely used API for web services?
- XML-RPC
- SOAP
- JSON-RPC
- REST
Explanation: REST accounts for more than 80% of all API types used for web services, making it the most widely used web service API.
31. What is REST?
- It is a way to store and interchange data in a structured format.
- It is an architecture style for designing web service applications.
- It is a human readable data structure that is used by applications for storing, transforming, and reading data.
- It is a protocol that allows administrators to manage nodes on an IP network.
Explanation: REST is not a protocol or service, but rather a style of software architecture for designing web service applications.
32. What is a difference between the XML and HTML data formats?
- XML does not use predefined tags whereas HTML does use predefined tags.
- XML encloses data within a pair of tags whereas HTML uses a pair of quotation makes to enclose data.
- XML formats data in binary whereas HTML formats data in plain text.
- XML does not require indentation for each key/value pair but HTML does require indentation.
Explanation: XML is
a human readable data structure used to store, transfer, and read data
by applications. Like HTML, XML uses a related set of tags to enclose
data. However, unlike HTML, XML uses no predefined tags or document
structure.
33. To avoid purchasing new hardware, a company wants to take
advantage of idle system resources and consolidate the number of
servers while allowing for multiple operating systems on a single
hardware platform. What service or technology would support this
requirement?
- dedicated servers
- Cisco ACI
- virtualization
- software defined networking
34. Match the term to the RESTful API request
http://www.mapquestapi.com/directions/v2/route?outFormat=json&key=KEY&from=San+Jose,Ca&to=Monterey,Ca
component. (Not all options are used.)
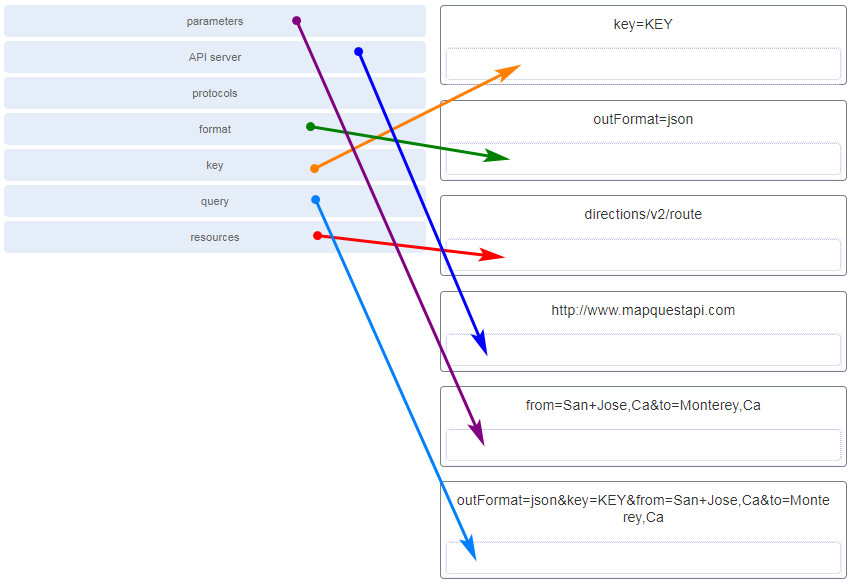 35. Which cloud computing opportunity would provide the use
of network hardware such as routers and switches for a particular
company?
35. Which cloud computing opportunity would provide the use
of network hardware such as routers and switches for a particular
company?
- software as a service (SaaS)
- wireless as a service (WaaS)
- infrastructure as a service (IaaS)
- browser as a service (BaaS)
Explanation: This item is based on information contained in the presentation.
Routers, switches, and firewalls are infrastructure devices that can be provided in the cloud.
36. What component is considered the brains of the ACI architecture and translates application policies?
- the Application Network Profile endpoints
- the Nexus 9000 switch
- the hypervisor
- the Application Policy Infrastructure Controller
Explanation: The
ACI architecture consists of three core components: the Application
Network Profile, the Application Policy Infrastructure Controller, which
serves as the brains of the ACI architecture, and the Cisco Nexus 9000
switch.
37. Which statement describes the concept of cloud computing?
- separation of management plane from control plane
- separation of control plane from data plane
- separation of application from hardware
- separation of operating system from hardware
Explanation: Cloud
computing is used to separate the application or service from hardware.
Virtualization separates the operating system from the hardware.
38. In which situation would a partner API be appropriate?
- an internet search engine allowing developers to integrate the search engine into their own software applications
- company sales staff accessing internal sales data from their mobile devices
- someone creating an account on an external app or website by using his or her social media credentials
- a vacation service site interacting with hotel databases to display information from all the hotels on its web site
Explanation: Partner API programs incorporate collaboration with other business. They facilitate communication
and integration of software between a company and its business partners.
39. Because of enormous growth in web traffic, a company has
planned to purchase additional servers to help handle the web traffic.
What service or technology would support this requirement?
- virtualization
- data center
- cloud services
- dedicated servers
40. What is the term used to indicate a variation of delay?
- latency
- serialization delay
- speed mismatch
- jitter
41. A network engineer performs a ping test and receives a
value that shows the time it takes for a packet to travel from a source
to a destination device and return. Which term describes the value?
- jitter
- latency
- priority
- bandwidth
42. What role do network devices play in the IntServ QoS model?
- Network devices ensure that resources are available before traffic is allowed to be sent by a host through the network.
- Network devices provide a best-effort approach to forwarding traffic.
- Network devices are configured to service multiple classes of traffic and handle traffic as it may arrive.
- Network devices use QoS on a hop-by-hop basis to provide excellent scalability.
43. Which device would be classified as a trusted endpoint?
- switch
- router
- firewall
- IP phone
44. What is the benefit of deploying Layer 3 QoS marking across an enterprise network?
- Layer 3 marking can carry the QoS information end-to-end.
- Layer 3 marking can carry QoS information on switches that are not IP aware.
- Layer 3 marking can be carried in the 802.1Q fields.
- Layer 3 marking can be used to carry non-IP traffic.
Explanation: Marking traffic at Layer 2 or Layer 3 is very important and will affect how traffic is treated in a network using QoS.
- Layer 2 marking of frames can be performed for non-IP traffic.
- Layer 2 marking of frames is the only QoS option available for switches that are not “IP aware.”
- Layer 3 marking will carry the QoS information end-to-end.
45. What is the function of a QoS trust boundary?
- A trust boundary identifies the location where traffic cannot be remarked.
- A trust boundary only allows traffic to enter if it has previously been marked.
- A trust boundary identifies which devices trust the marking on packets that enter a network.
- A trust boundary only allows traffic from trusted endpoints to enter the network.
Explanation:
Network traffic is classified and marked as close to the source device
as possible. The trust boundary is the location where the QoS markings
on a packet are trusted as they enter an enterprise network.
46. What are two approaches to prevent packet loss due to congestion on an interface? (Choose two.)
- Decrease buffer space.
- Disable queuing mechanisms.
- Drop lower-priority packets.
- Prevent bursts of traffic.
- Increase link capacity.
Explanation: There are three approaches to prevent sensitive traffic from being dropped:
- Increase link capacity to ease or prevent congestion.
- Guarantee enough bandwidth and increase buffer space to accommodate bursts of traffic from fragile flows.
- Prevent congestion by dropping lower-priority packets before congestion occurs.
47. What configuration scenario would offer the most protection to SNMP get and set messages?
- SNMPv2 for in-band management with read-write community strings
- SNMPv1 with out-of-band management in a private subnet
- SNMPv3 configured with the auth security level
- SNMP community strings
Explanation: SNMPv3
supports authentication and encryption with the auth and priv security
levels. SNMPv1 and SNMPv2 do not support authentication or encryption.
Using a default community string is not secure because the default
string of “public” is well known and would allow anyone with SNMP
systems to read device MIBs.
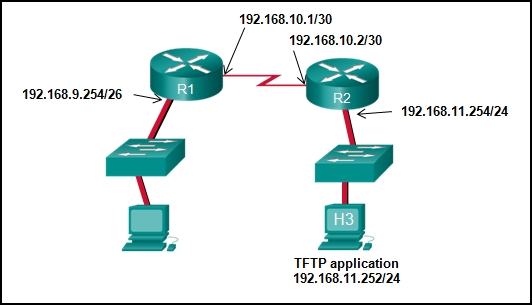
48. Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator enters these commands into the R1 router:
R1# copy running-config tftp
Address or name of remote host [ ]?
When the router prompts for an address or remote host name, what IP address should the administrator enter at the prompt?
- 192.168.9.254
- 192.168.10.2
- 192.168.11.252
- 192.168.11.254
- 192.168.10.1
Explanation: The
requested address is the address of the TFTP server. A TFTP server is an
application that can run on a multitude of network devices including a
router, server, or even a networked PC.
49. The command ntp server 10.1.1.1 is issued on a router. What impact does this command have?
- determines which server to send system log files to
- synchronizes the system clock with the time source with IP address 10.1.1.1
- identifies the server on which to store backup configurations
- ensures that all logging will have a time stamp associated with it
Explanation: The ntp server ip-address global configuration command configures the NTP server for IOS devices.
50. As the network administrator you have been asked to
implement EtherChannel on the corporate network. What does this
configuration consist of?
- providing redundant links that dynamically block or forward traffic
- grouping two devices to share a virtual IP address
- grouping multiple physical ports to increase bandwidth between two switches
- providing redundant devices to allow traffic to flow in the event of device failure
Explanation:
EtherChannel is utilized on a network to increase speed capabilities by
grouping multiple physical ports into one or more logical EtherChannel
links between two switches. STP is used to provide redundant links that
dynamically block or forward traffic between switches. FHRPs are used to
group physical devices to provide traffic flow in the event of failure.
51. What is a definition of a two-tier LAN network design?
- access and core layers collapsed into one tier, and the distribution layer on a separate tier
- distribution and core layers collapsed into one tier, and the access layer on a separate tier
- access, distribution, and core layers collapsed into one tier, with a separate backbone layer
- access and distribution layers collapsed into one tier, and the core layer on a separate tier
Explanation:
Maintaining three separate network tiers is not always required or
cost-efficient. All network designs require an access layer, but a
two-tier design can collapse the distribution and core layers into one
layer to serve the needs of a small location with few users.
52. What are two reasons to create a network baseline? (Choose two.)
- to select a routing protocol
- to determine what kind of equipment to implement
- to design a network according to a proper model
- to identify future abnormal network behavior
- to evaluate security vulnerabilities in the network
- to determine if the network can deliver the required policies
Explanation: A
network baseline is created to provide a comparison point, at the time
that the network is performing optimally, to whatever changes are
implemented in the infrastructure. A baseline helps to keep track of the
performance, to track the traffic patterns, and to monitor network
behavior.
53. A computer can access devices on the same network but
cannot access devices on other networks. What is the probable cause of
this problem?
- The computer has an incorrect subnet mask.
- The computer has an invalid default gateway address.
- The cable is not connected properly to the NIC.
- The computer has an invalid IP address.
Explanation: The
default gateway is the address of the device a host uses to access the
Internet or another network. If the default gateway is missing or
incorrect, that host will not be able to communicate outside the local
network. Because the host can access other hosts on the local network,
the network cable and the other parts of the IP configuration are
working.
54. In which step of gathering symptoms does the network
engineer determine if the problem is at the core, distribution, or
access layer of the network?
- Gather information.
- Narrow the scope.
- Document the symptoms.
- Determine ownership.
- Determine the symptoms.
Explanation: In the
“narrow the scope” step of gathering symptoms, a network engineer will
determine if the network problem is at the core, distribution, or access
layer of the network. Once this step is complete and the layer is
identified, the network engineer can determine which pieces of equipment
are the most likely cause.
55. A network administrator is deploying QoS with the ability
to provide a special queue for voice traffic so that voice traffic is
forwarded before network traffic in other queues. Which queuing method
would be the best choice?
Explanation: Low
latency queuing (LLQ) allows delay-sensitive data, such as voice
traffic, to be defined in a strict priority queue (PQ) and to always be
sent first before any packets in any other queue are forwarded.
56. What are two characteristics of voice traffic? (Choose two.)
- Voice traffic latency should not exceed 150 ms.
- Voice traffic is unpredictable and inconsistent.
- Voice traffic requires at least 384 kbs of bandwidth.
- Voice traffic consumes lots of network resources.
- Dropped voice packets are not retransmitted.
Explanation: Voice
traffic does not consume a lot of network resources, such as bandwidth.
However, it is very sensitive to delay and dropped packets cannot be
retransmitted. For good voice quality, the amount of latency should
always be less than 150 milliseconds.
57. Which type of network traffic cannot be managed using congestion avoidance tools?
Explanation:
Queuing and compression techniques can help to reduce and prevent UDP
packet loss, but there is no congestion avoidance for User Datagram
Protocol (UDP) based traffic.
58. When QoS is implemented in a converged network, which two
factors can be controlled to improve network performance for real-time
traffic? (Choose two.)
- delay
- packet addressing
- jitter
- packet routing
- link speed
Explanation: Delay
is the latency between a sending and receiving device. Jitter is the
variation in the delay of the received packets. Both delay and jitter
need to be controlled in order to support real-time voice and video
traffic.
59. An administrator wants to replace the configuration file
on a Cisco router by loading a new configuration file from a TFTP
server. What two things does the administrator need to know before
performing this task? (Choose two.)
- name of the configuration file that is currently stored on the router
- configuration register value
- name of the configuration file that is stored on the TFTP server
- router IP address
- TFTP server IP address
Explanation: In
order to identify the exact location of the desired configuration file,
the IP address of the TFTP server and the name of the configuration file
are essential information. Because the file is a new configuration, the
name of the current configuration file is not necessary.
60. Refer to the exhibit. Which of the three Cisco IOS images shown will load into RAM?
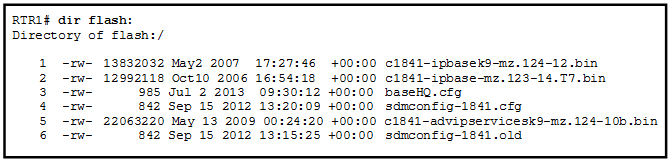
- The router selects an image depending on the boot system command in the configuration.
- The router selects an image depending on the value of the configuration register.
- The router selects the third Cisco IOS image because it is the most recent IOS image.
- The router selects the third Cisco IOS image because it contains the advipservicesk9 image.
- The router selects the second Cisco IOS image because it is the smallest IOS image.
Explanation: When performing an upgrade or testing different IOS versions, the boot system command is used to select which image is used to boot the Cisco device.
61. Refer to the exhibit. What two types of devices are connected to R1? (Choose two.)
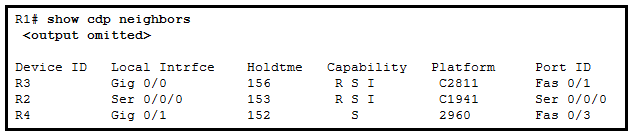
- switch
- hub
- router
- repeater
- Source Route Bridge
Explanation: The
capabilities of the devices displayed by the output show them to be a
Cisco 2811 series router, Cisco 1941 series router, and a Cisco 2960
switch.
62. What are three functions provided by the syslog service? (Choose three.)
- to select the type of logging information that is captured
- to periodically poll agents for data
- to provide statistics on packets that are flowing through a Cisco device
- to provide traffic analysis
- to gather logging information for monitoring and troubleshooting
- to specify the destinations of captured messages
Explanation: There are three primary functions provided by the syslog service:
- gathering logging information
- selection of the type of information to be logged
- selection of the destination of the logged information
63. What is the function of the MIB element as part of a network management system?
- to collect data from SNMP agents
- to send and retrieve network management information
- to change configurations on SNMP agents
- to store data about a device
Explanation: The
Management Information Base (MIB) resides on a networking device and
stores operational data about the device. The SNMP manager can collect
information from SNMP agents. The SNMP agent provides access to the
information.
64. What network design would contain the scope of disruptions on a network should a failure occur?
- the reduction in the number of redundant devices and connections in the network core
- the installation of only enterprise class equipment throughout the network
- the deployment of distribution layer switches in pairs and the division of access layer switch connections between them
- the configuration of all access layer devices to share a single gateway
Explanation: One
way to contain the impact of a failure on the network is to implement
redundancy. One way this is accomplished is by deploying redundant
distribution layer switches and dividing the access layer switch
connections between the redundant distribution layer switches. This
creates what is called a switch block. Failures in a switch block are
contained to that block and do not bring down the whole network.
65. Which action should be taken when planning for redundancy on a hierarchical network design?
- add alternate physical paths for data to traverse the network
- continually purchase backup equipment for the network
- implement STP portfast between the switches on the network
- immediately replace a non-functioning module, service or device on a network
Explanation: One
method of implementing redundancy is path redundancy, installing
alternate physical paths for data to traverse the network. Redundant
links in a switched network supports high availability and can be used
for load balancing, reducing congestion on the network.
66. What are two benefits of extending access layer connectivity to users through a wireless medium? (Choose two.)
- increased flexibility
- increased network management options
- decreased number of critical points of failure
- reduced costs
- increased bandwidth availability
Explanation:
Wireless connectivity at the access layer provides increased
flexibility, reduced costs, and the ability to grow and adapt to
changing business requirements. Utilizing wireless routers and access
points can provide an increase in the number of central points of
failure. Wireless routers and access points will not provide an increase
in bandwidth availability.
67. What is a basic function of the Cisco Borderless Architecture access layer?
- aggregates Layer 2 broadcast domains
- provides access to the user
- aggregates Layer 3 routing boundaries
- provides fault isolation
Explanation: A
function of the Cisco Borderless Architecture access layer is providing
network access to the users. Layer 2 broadcast domain aggregation, Layer
3 routing boundaries aggregation, and high availability are
distribution layer functions. The core layer provides fault isolation
and high-speed backbone connectivity.
68. Which characteristic would most influence a network design engineer to select a multilayer switch over a Layer 2 switch?
- ability to have multiple forwarding paths through the switched network based on VLAN number(s)
- ability to build a routing table
- ability to provide power to directly-attached devices and the switch itself
- ability to aggregate multiple ports for maximum data throughput
Explanation:
Multilayer switches, also known as Layer 3 switches, can route and build
a routing table. This capability is required in a multi-VLAN network
and would influence the network designer to select a multilayer switch.
The other options are features also available on Layer 2 switches, so
they would not influence the decision to select a multilayer switch.
69. Refer to the exhibit. Why are routers R1 and R2 not able to establish an OSPF adjacency?
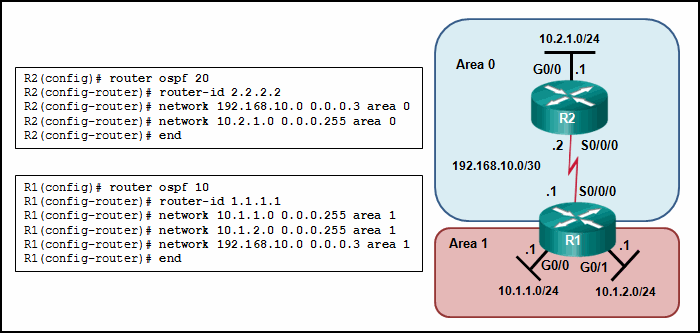
- The serial interfaces are not in the same area.
- The process numbers are not the same in both routers.
- A backbone router cannot establish an adjacency with an ABR router.
- The router ID values are not the same in both routers.
Explanation: On
router R1, the network 192.168.10.0/30 is defined in the wrong area
(area 1). It has to be defined in area 0 in order to establish adjacency
with router R2, which has the network 192.168.10.0/30 defined in area
0.
70. When is the most appropriate time to measure network operations to establish a network performance baseline?
- whenever high network use is detected, so that how the network performs under stress can be monitored
- during quiet vacation periods, so that the level of non-data traffic can be determined
- at the same time each day across a set period of average working days, so that typical traffic patterns can be established
- at random times during a 10 week period, so that abnormal traffic levels can be detected
Explanation: The
purpose of establishing a network performance baseline is to provide a
reference of normal or average network use to enable data traffic
anomalies to be detected and then investigated. Network operations that
are not average, or are not normal, cannot be used to establish a
network performance baseline.
71. Refer to the exhibit. A user has configured a NIC on the
PC as shown but finds that the PC is unable to access the Internet. What
is the problem?
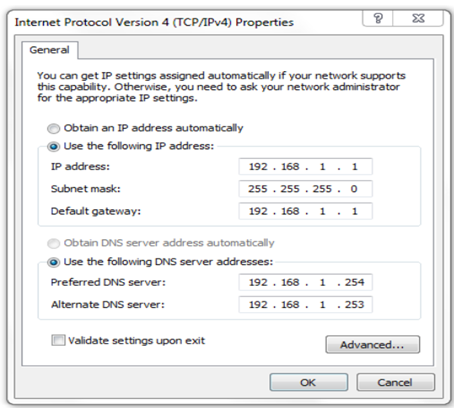
- The preferred DNS address is incorrect.
- The default gateway address is incorrect.
- The settings were not validated upon exit.
- There should not be an alternate DNS server.
Explanation: In
order for a computer to communicate outside its network, it must have a
valid default gateway configured.This address cannot be the same as the
IP address of the computer.
72. Refer to the exhibit. A network engineer configured an
ACL preventing Telnet and HTTP access to the HQ web server from guest
users in the Branch LAN. The address of the web server is 192.168.1.10
and all guest users are assigned addresses in the 192.168.10.0/24
network. After implementing the ACL, no one can access any of the HQ
servers. What is the problem?
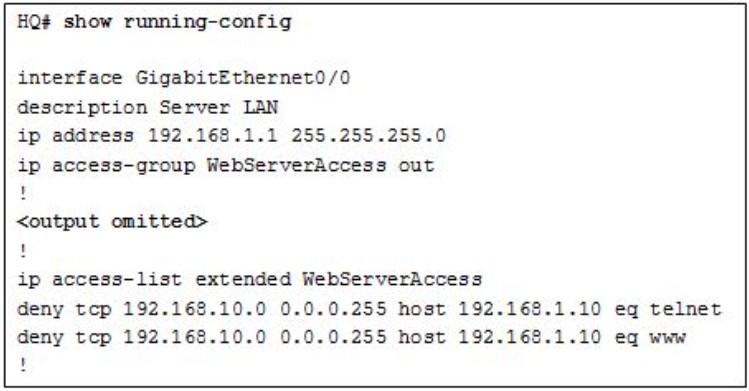
- Inbound ACLs must be routed before they are processed.
- The ACL is implicitly denying access to all the servers.
- Named ACLs require the use of port numbers.
- The ACL is applied to the interface using the wrong direction.
Explanation: Both named and numbered ACLs have an implicit deny ACE at the end of the list. This implicit deny blocks all traffic.
73. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator has
configured OSPFv2 on the two Cisco routers as shown. PC1 is unable to
connect to PC2. What should the administrator do first when
troubleshooting the OSPFv2 implementation?
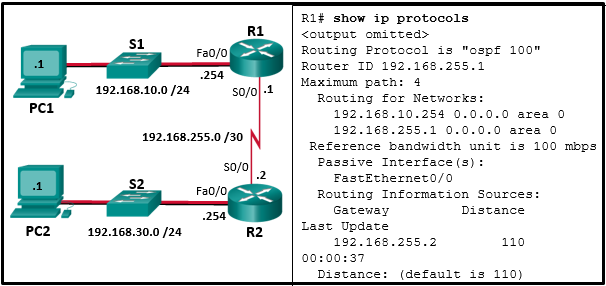
- Disconnect the serial link between router R1 and R2.
- Turn off OSPFv2.
- Implement the network 192.168.255.0 0.0.0.3 area 0 command on router R1.
- Test Layer 3 connectivity between the directly connected routers.
Explanation: A
prerequisite for OSPFv2 neighbor relationships to form between two
routers is Layer 3 connectivity. A successful ping confirms that a
router interface is active and may be able to form an OSPF neighbor
adjacency.
74. What type of traffic is described as requiring latency to be no more than 150 milliseconds (ms)?
75. A network manager wants to add a time to log messages so
that there is record of when the message was generated. What command
should the administrator use on a Cisco router?
- show cdp interface
- ntp server 10.10.14.9
- service timestamps log datetime
- clock timezone PST -7
76. Match the functions to the corresponding layers. (Not all options are used.)
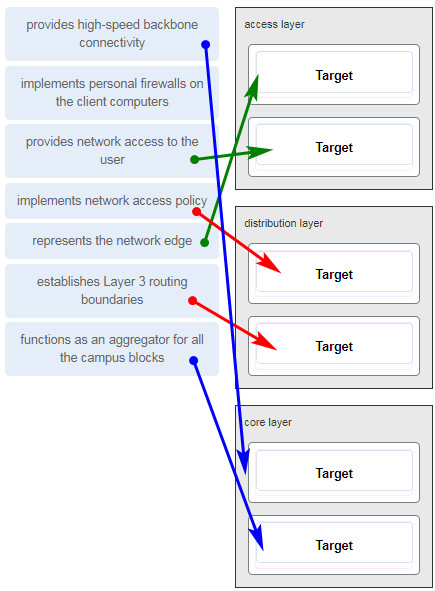 77. Match the borderless switched network guideline description to the principle. (Not all options are used.)
77. Match the borderless switched network guideline description to the principle. (Not all options are used.)
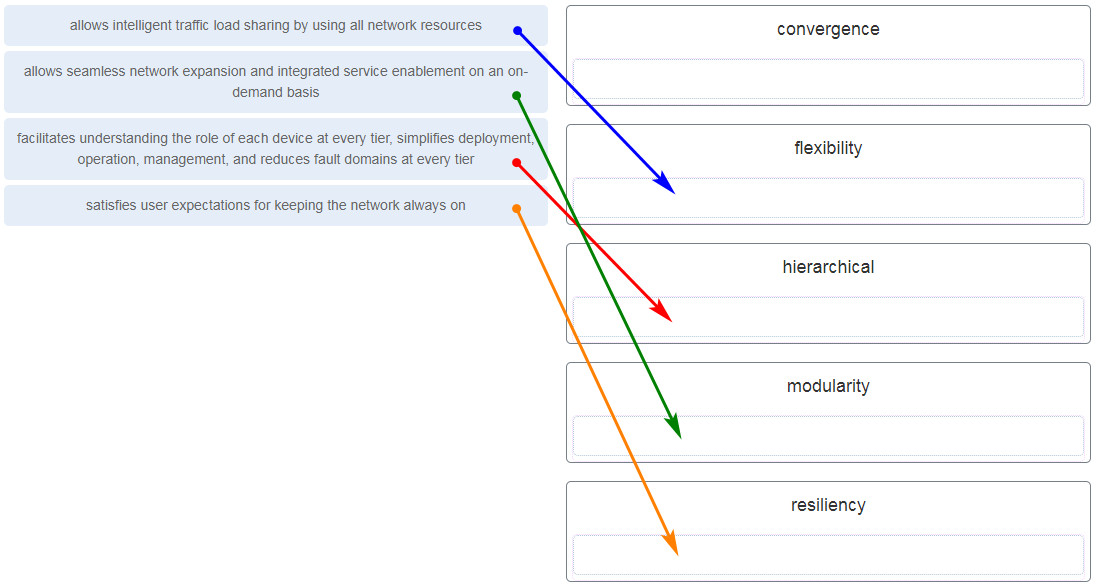 78. What are two characteristics of the best-effort QoS model? (Choose two.)
78. What are two characteristics of the best-effort QoS model? (Choose two.)
- It allows end hosts to signal their QoS needs to the network.
- It uses a connection-oriented approach with QoS.
- It provides preferential treatment for voice packets.
- It does not provide a delivery guarantee for packets.
- It treats all network packets in the same way.
Explanation: The
best-effort QoS model provides no guarantees and it is commonly used on
the Internet. The best-effort QoS model treats all network packets in
the same way.
79. Why is QoS an important issue in a converged network that combines voice, video, and data communications?
- Data communications are sensitive to jitter.
- Legacy equipment is unable to transmit voice and video without QoS.
Correct Response
- Voice and video communications are more sensitive to latency.
- Data communications must be given the first priority.
Explanation:
Without any QoS mechanisms in place, time-sensitive packets, such as
voice and video, will be dropped with the same frequency as email and
web browsing traffic.
80. A network administrator configures a router with the command sequence:
R1(config)# boot system tftp://c1900-universalk9-mz.SPA.152-4.M3.bin
R1(config)# boot system rom
What is the effect of the command sequence?
- On next reboot, the router will load the IOS image from ROM.
- The router will search and load a valid IOS image in the sequence of flash, TFTP, and ROM.
- The router will copy the IOS image from the TFTP server and then reboot the system.
- The router will load IOS from the TFTP server. If the image fails to load, it will load the IOS image from ROM.
Explanation: The boot system
command is a global configuration command that allows the user to
specify the source for the Cisco IOS Software image to load. In this
case, the router is configured to boot from the IOS image that is stored
on the TFTP server and will use the ROMmon imagethat is located in the
ROM if it fails to locate the TFTP server or fails to load a valid image
from the TFTP server.
81. Which statement describes SNMP operation?
- An SNMP agent that resides on a managed device collects information
about the device and stores that information remotely in the MIB that is
located on the NMS.
- A set request is used by the NMS to change configuration variables in the agent device.
- An NMS periodically polls the SNMP agents that are residing on managed devices by using traps to query the devices for data.
- A get request is used by the SNMP agent to query the device for data.
Explanation: An
SNMP agent that resides on a managed device collects and stores
information about the device and its operation. This information is
stored by the agent locally in the MIB. An NMS periodically polls the
SNMP agents that are residing on managed devices by using the get
request to query the devices for data.
82. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator issues the
show lldp neighbors command on a switch. What are two conclusions that
can be drawn? (Choose two.)
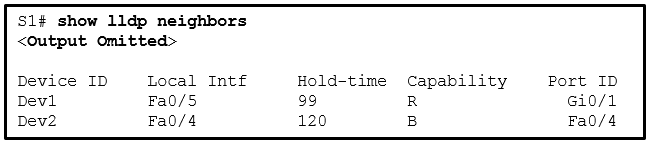
- Dev1 is connected to interface Fa0/5 of S1.
- Dev1 is a switch with mixed types of interfaces.
- Dev2 is a switch.
- Dev1 is connected to interface Fa0/4 of Dev2.
- S1 has only two interfaces.
Explanation: In the output from the show lldp
command, under Capability, R indicates a router and B indicates a
bridge (switch). Nothing indicates that Dev1 and Dev2 are connected to
one another.
83. What are the three layers of the switch hierarchical design model? (Choose three.)
- distribution
- network access
- data link
- enterprise
- access
- core
Explanation: The
access layer is the lowest layer and it provides network access to
users. The distribution layer has many functions, but it aggregates data
from the access layer, provides filtering, policy control, and sets
Layer 3 routing boundaries. The core layer provides high speed
connectivity.
84. Refer to the exhibit. Which devices exist in the failure domain when switch S3 loses power?
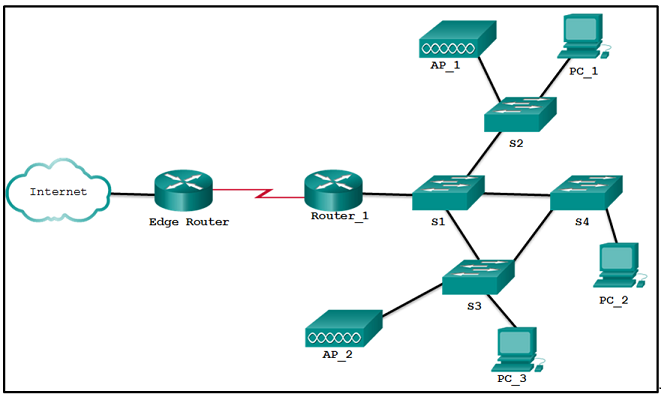
- S4 and PC_2
- PC_3 and PC_2
- PC_3 and AP_2
- S1 and S4
- AP_2 and AP_1
Explanation: A
failure domain is the area of a network that is impacted when a critical
device such as switch S3 has a failure or experiences problems.
85. A network designer is considering whether to implement a
switch block on the company network. What is the primary advantage of
deploying a switch block?
- This is network application software that prevents the failure of a single network device.
- The failure of a switch block will not impact all end users.
- This is a security feature that is available on all new Catalyst switches.
- A single core router provides all the routing between VLANs.
Explanation: The
configuration of a switch block provides redundancy so that the failure
of a single network device generally has little or no effect on end
users.
86. Which troubleshooting tool would a network administrator
use to check the Layer 2 header of frames that are leaving a particular
host?
- knowledge base
- protocol analyzer
- CiscoView
- baselining tool
Explanation: A protocol analyzer such as Wireshark is capable of displaying the headers of data at any OSI Layer.
87. Refer to the exhibit. R1 and R3 are connected to each
other via the local serial 0/0/0 interface. Why are they not forming an
adjacency?

- They have different routing processes.
- They have different router IDs.
- They are in different subnets.
- The connecting interfaces are configured as passive.
Explanation: The
routers need to be in the same subnet in order to form an adjacency. The
routing processes can be different on each router. The router IDs must
be different for routers that participate in the same routing domain.
The interfaces are not passive.
88. What type of traffic is described as not resilient to loss?
89. A network manager wants lists the contents of flash. What command should the administrator use on a Cisco router?
- show file systems
- dir
- lldp enable
- service timestamps log datetime
90. Which two statements accurately describe an advantage or a
disadvantage when deploying NAT for IPv4 in a network? (Choose two.)
- NAT improves packet handling.
- NAT adds authentication capability to IPv4.
- NAT will impact negatively on switch performance.
- NAT causes routing tables to include more information.
- NAT provides a solution to slow down the IPv4 address depletion.
- NAT introduces problems for some applications that require end-to-end connectivity.
91. A network administrator wants to examine the active NAT
translations on a border router. Which command would perform the task?
- Router# show ip nat translations
- Router# show ip nat statistics
- Router# clear ip nat translations
- Router# debug ip nat translations
92. What are two tasks to perform when configuring static NAT? (Choose two.)
- Configure a NAT pool.
- Create a mapping between the inside local and outside local addresses.
- Identify the participating interfaces as inside or outside interfaces.
- Define the inside global address on the server
- Define the outside global address.
93. What is a disadvantage of NAT?
- There is no end-to-end addressing.
- The router does not need to alter the checksum of the IPv4 packets.
- The internal hosts have to use a single public IPv4 address for external communication.
- The costs of readdressing hosts can be significant for a publicly addressed network.
94. Refer to the exhibit. From the perspective of R1, the NAT router, which address is the inside global address?
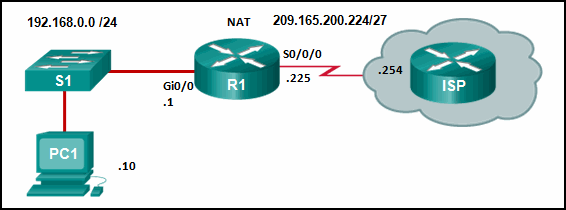
- 192.168.0.10
- 192.168.0.1
- 209.165.200.225
- 209.165.200.254
Explanation: There are four types of addresses in NAT terminology.
Inside local address
Inside global address
Outside local address
Outside global address
The inside global address of PC1 is the address that the ISP sees as the
source address of packets, which in this example is the IP address on
the serial interface of R1, 209.165.200.224.
95. Refer to the exhibit. Given the commands as shown, how
many hosts on the internal LAN off R1 can have simultaneous NAT
translations on R1?
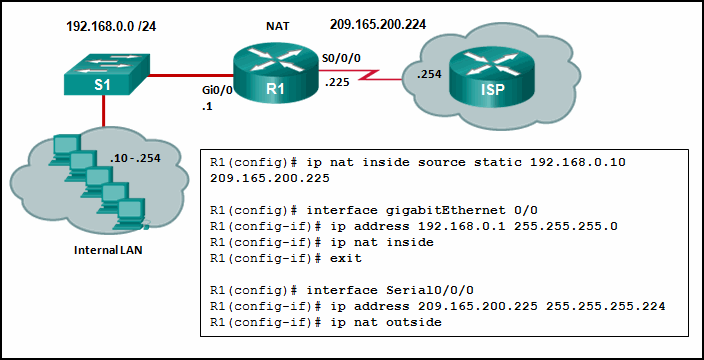
Explanation: The
NAT configuration on R1 is static NAT which translates a single inside
IP address, 192.168.0.10 into a single public IP address,
209.165.200.255. If more hosts need translation, then a NAT pool of
inside global address or overloading should be configured.
96. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator has just
configured address translation and is verifying the configuration. What
three things can the administrator verify? (Choose three.)
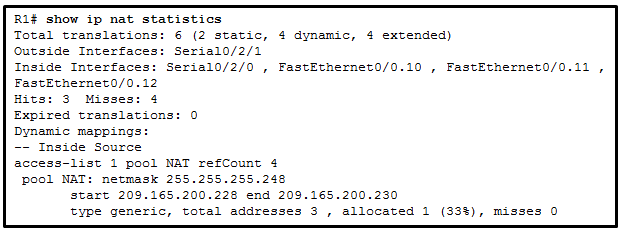
- A standard access list numbered 1 was used as part of the configuration process.
- Three addresses from the NAT pool are being used by hosts.
- Address translation is working.
- One port on the router is not participating in the address translation.
- The name of the NAT pool is refCount.
- Two types of NAT are enabled.
Explanation: The show ip nat statistics, show ip nat translations, and debug ip nat
commands are useful in determining if NAT is working and and also
useful in troubleshooting problems that are associated with NAT. NAT is
working, as shown by the hits and misses count. Because there are four
misses, a problem might be evident. The standard access list numbered 1
is being used and the translation pool is named NAT as evidenced by the
last line of the output. Both static NAT and NAT overload are used as
seen in the Total translations line.
97. Refer to the exhibit. NAT is configured on RT1 and RT2.
The PC is sending a request to the web server. What IPv4 address is the
source IP address in the packet between RT2 and the web server?
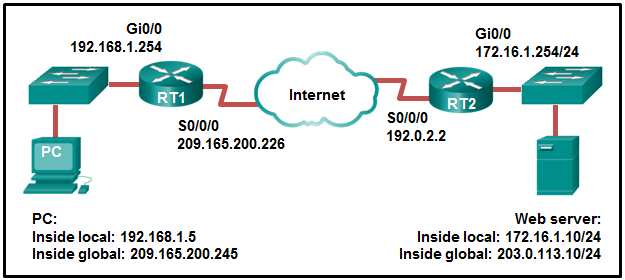
- 192.168.1.5
- 203.0.113.10
- 172.16.1.254
- 172.16.1.10
- 209.165.200.245
- 192.0.2.2
Explanation:
Because the packet is between RT2 and the web server, the source IP
address is the inside global address of PC, 209.165.200.245.
98. Refer to the exhibit. Based on the output that is shown, what type of NAT has been implemented?
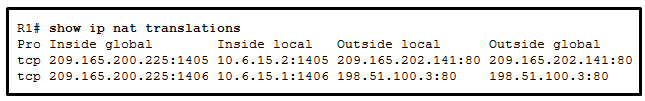
- dynamic NAT with a pool of two public IP addresses
- PAT using an external interface
- static NAT with a NAT pool
- static NAT with one entry
Explanation: The
output shows that there are two inside global addresses that are the
same but that have different port numbers. The only time port numbers
are displayed is when PAT is being used. The same output would be
indicative of PAT that uses an address pool. PAT with an address pool is
appropriate when more than 4,000 simultaneous translations are needed
by the company.
99. Refer to the exhibit. From the perspective of users behind the NAT router, what type of NAT address is 209.165.201.1?
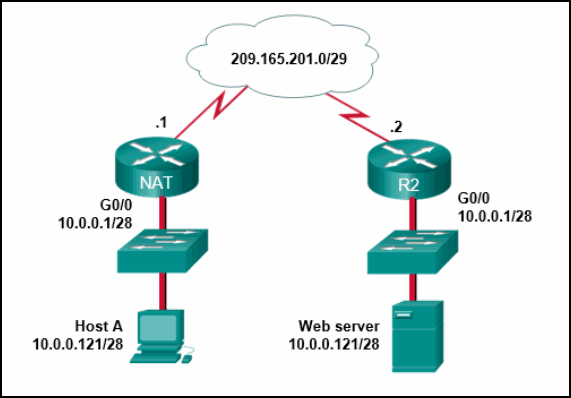
- inside global
- outside global
- outside local
- inside local
Explanation: From
the perspective of users behind NAT, inside global addresses are used by
external users to reach internal hosts. Inside local addresses are the
addresses assigned to internal hosts. Outside global addresses are the
addresses of destinations on the external network. Outside local
addresses are the actual private addresses of destination hosts behind
other NAT devices.
100. Refer to the exhibit. Static NAT is being configured to
allow PC 1 access to the web server on the internal network. What two
addresses are needed in place of A and B to complete the static NAT
configuration? (Choose two.)
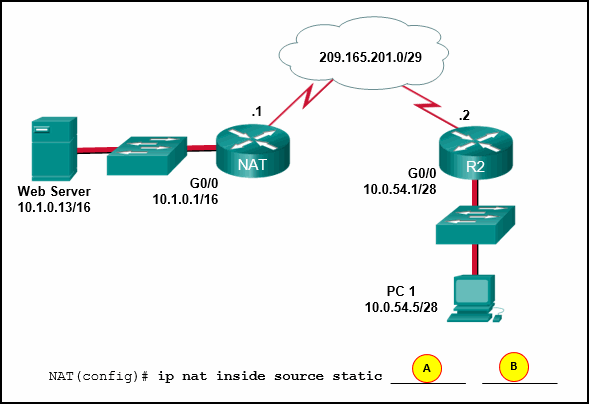
- A = 209.165.201.2
- A = 10.1.0.13
- B = 209.165.201.7
- B = 10.0.254.5
- B = 209.165.201.1
Explanation: Static
NAT is a one-to-one mapping between an inside local address and an
inside global address. By using static NAT, external devices can
initiate connections to internal devices by using the inside global
addresses. The NAT devices will translate the inside global address to
the inside local address of the target host.
101. What is the purpose of the overload keyword in the ip nat inside source list 1 pool NAT_POOL overload command?
- It allows many inside hosts to share one or a few inside global addresses.
- It allows a list of internal hosts to communicate with a specific group of external hosts.
- It allows external hosts to initiate sessions with internal hosts.
- It allows a pool of inside global addresses to be used by internal hosts.
Explanation:
Dynamic NAT uses a pool of inside global addresses that are assigned to
outgoing sessions. If there are more internal hosts than public
addresses in the pool, then an administrator can enable port address
translation with the addition of the overload keyword.
With port address translation, many internal hosts can share a single
inside global address because the NAT device will track the individual
sessions by Layer 4 port number.
102. Refer to the exhibit. Which source address is being used by router R1 for packets being forwarded to the Internet?
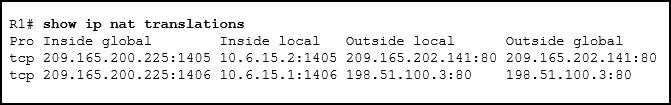
- 10.6.15.2
- 209.165.202.141
- 198.51.100.3
- 209.165.200.225
Explanation: The
source address for packets forwarded by the router to the Internet will
be the inside global address of 209.165.200.225. This is the address
that the internal addresses from the 10.6.15.0 network will be
translated to by NAT.
103. Refer to the exhibit. The NAT configuration applied to the router is as follows:
ERtr(config)# access-list 1 permit 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255
ERtr(config)# ip nat pool corp 209.165.201.6 209.165.201.30 netmask 255.255.255.224
ERtr(config)# ip nat inside source list 1 pool corp overload
ERtr(config)# ip nat inside source static 10.10.10.55 209.165.201.4
ERtr(config)# interface gigabitethernet 0/0
ERtr(config-if)# ip nat inside
ERtr(config-if)# interface serial 0/0/0
ERtr(config-if)# ip nat outside
Based on the configuration and the output shown, what can be determined about the NAT status within the organization?
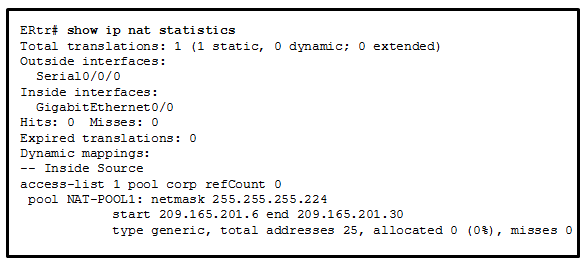
- Static NAT is working, but dynamic NAT is not.
- Dynamic NAT is working, but static NAT is not.
- Not enough information is given to determine if both static and dynamic NAT are working.
- NAT is working.
Explanation: There
is not enough information given because the router might not be attached
to the network yet, the interfaces might not have IP addresses assigned
yet, or the command could have been issued in the middle of the night.
The output does match the given configuration, so no typographical
errors were made when the NAT commands were entered.
104. Which situation describes data transmissions over a WAN connection?
- A network administrator in the office remotely accesses a web server
that is located in the data center at the edge of the campus.
- A manager sends an email to all employees in the department with offices that are located in several buildings.
- An employee prints a file through a networked printer that is located in another building.
- An employee shares a database file with a co-worker who is located in a branch office on the other side of the city.
Explanation: When
two offices across a city are communicating , it is most likely that the
data transmissions are over some type of WAN connection. Data
communications within a campus are typically over LAN connections.
105. Which two technologies are categorized as private WAN infrastructures? (Choose two.)
- Frame Relay
- VPN
- MetroE
- DSL
- cable
Explanation:
Private WAN technologies include leased lines, dialup, ISDN, Frame
Relay, ATM, Ethernet WAN (an example is MetroE), MPLS, and VSAT.
106. Which network scenario will require the use of a WAN?
- Employees need to connect to the corporate email server through a VPN while traveling.
- Employees need to access web pages that are hosted on the corporate web servers in the DMZ within their building.
- Employee workstations need to obtain dynamically assigned IP addresses.
- Employees in the branch office need to share files with the
headquarters office that is located in a separate building on the same
campus network.
Explanation: When
traveling employees need to connect to a corporate email server through a
WAN connection, the VPN will create a secure tunnel between an employee
laptop and the corporate network over the WAN connection. Obtaining
dynamic IP addresses through DHCP is a function of LAN communication.
Sharing files among separate buildings on a corporate campus is
accomplished through the LAN infrastructure. A DMZ is a protected
network inside the corporate LAN infrastructure.
107. What are two hashing algorithms used with IPsec AH to guarantee authenticity? (Choose two.)
Explanation: The
IPsec framework uses various protocols and algorithms to provide data
confidentiality, data integrity, authentication, and secure key
exchange. Two popular algorithms used to ensure that data is not
intercepted and modified (data integrity and authenticity) are MD5 and
SHA.
108. What two algorithms can be part of an IPsec policy to
provide encryption and hashing to protect interesting traffic? (Choose
two.)
Explanation: The
IPsec framework uses various protocols and algorithms to provide data
confidentiality, data integrity, authentication, and secure key
exchange. Two algorithms that can be used within an IPsec policy to
protect interesting traffic are AES, which is an encryption protocol,
and SHA, which is a hashing algorithm.
109. Which VPN solution allows the use of a web browser to establish a secure, remote-access VPN tunnel to the ASA?
- client-based SSL
- site-to-site using an ACL
- clientless SSL
- site-to-site using a preshared key
Explanation: When a
web browser is used to securely access the corporate network, the
browser must use a secure version of HTTP to provide SSL encryption. A
VPN client is not required to be installed on the remote host, so a
clientless SSL connection is used.
110. Which IPsec security function provides assurance that the data received via a VPN has not been modified in transit?
- integrity
- authentication
- confidentiality
- secure key exchange
Explanation:
Integrity is a function of IPsec and ensures data arrives unchanged at
the destination through the use of a hash algorithm. Confidentiality is a
function of IPsec and utilizes encryption to protect data transfers
with a key. Authentication is a function of IPsec and provides specific
access to users and devices with valid authentication factors. Secure
key exchange is a function of IPsec and allows two peers to maintain
their private key confidentiality while sharing their public key.
111. Which two types of VPNs are examples of enterprise-managed remote access VPNs? (Choose two.)
- clientless SSL VPN
- client-based IPsec VPN
- IPsec VPN
- IPsec Virtual Tunnel Interface VPN
- GRE over IPsec VPN
Explanation: Enterprise managed VPNs can be deployed in two configurations:
- Remote Access VPN – This VPN is created dynamically
when required to establish a secure connection between a client and a
VPN server. Remote access VPNs include client-based IPsec VPNs and
clientless SSL VPNs.
- Site-to-site VPN – This VPN is created when
interconnecting devices are preconfigured with information to establish a
secure tunnel. VPN traffic is encrypted only between the
interconnecting devices, and internal hosts have no knowledge that a VPN
is used. Site-to-site VPNs include IPsec, GRE over IPsec, Cisco Dynamic
Multipoint (DMVPN), and IPsec Virtual Tunnel Interface (VTI) VPNs.
112. Which is a requirement of a site-to-site VPN?
- It requires hosts to use VPN client software to encapsulate traffic.
- It requires the placement of a VPN server at the edge of the company network.
- It requires a VPN gateway at each end of the tunnel to encrypt and decrypt traffic.
- It requires a client/server architecture.
Explanation:
Site-to-site VPNs are static and are used to connect entire networks.
Hosts have no knowledge of the VPN and send TCP/IP traffic to VPN
gateways. The VPN gateway is responsible for encapsulating the traffic
and forwarding it through the VPN tunnel to a peer gateway at the other
end which decapsulates the traffic.
113. What is the function of the Diffie-Hellman algorithm within the IPsec framework?
- guarantees message integrity
- allows peers to exchange shared keys
- provides authentication
- provides strong data encryption
Explanation: The
IPsec framework uses various protocols and algorithms to provide data
confidentiality, data integrity, authentication, and secure key
exchange. DH (Diffie-Hellman) is an algorithm used for key exchange. DH
is a public key exchange method that allows two IPsec peers to establish
a shared secret key over an insecure channel.
114. What does NAT overloading use to track multiple internal hosts that use one inside global address?
- port numbers
- IP addresses
- autonomous system numbers
- MAC addresses
Explanation: NAT
overloading, also known as Port Address Translation (PAT), uses port
numbers to differentiate between multiple internal hosts.
115. Question as presented:
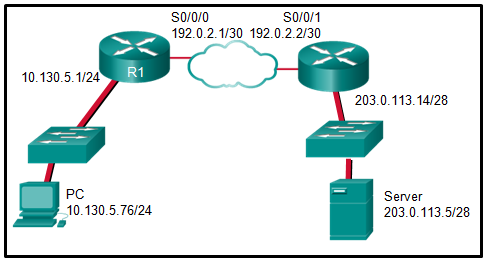
Explanation: The
inside local address is the private IP address of the source or the PC
in this instance. The inside global address is the translated address of
the source or the address as seen by the outside device. Since the PC
is using the outside address of the R1 router, the inside global address
is 192.0.2.1. The outside addressing is simply the address of the
server or 203.0.113.5.
116. Refer to the exhibit. R1 is configured for static NAT. What IP address will Internet hosts use to reach PC1?
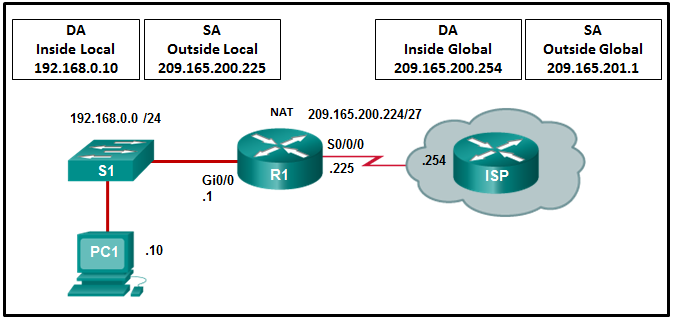
- 192.168.0.1
- 192.168.0.10
- 209.165.201.1
- 209.165.200.225
Explanation: In
static NAT a single inside local address, in this case 192.168.0.10,
will be mapped to a single inside global address, in this case
209.165.200.225. Internet hosts will send packets to PC1 and use as a
destination address the inside global address 209.165.200.225.
117. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is viewing
the output from the command show ip nat translations. Which statement
correctly describes the NAT translation that is occurring on router
RT2?
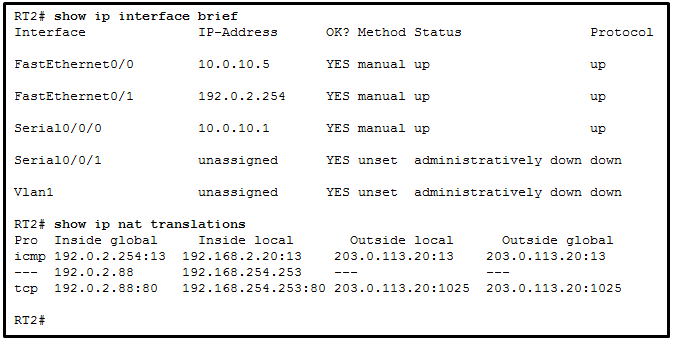
- The traffic from a source IPv4 address of 192.168.254.253 is being translated to 192.0.2.88 by means of static NAT.
- The traffic from a source IPv4 address of 192.0.2.88 is being
translated by router RT2 to reach a destination IPv4 address of
192.168.254.253.
- The traffic from a source IPv4 public address that originates
traffic on the internet would be able to reach private internal IPv4
addresses.
- The traffic from a source IPv4 address of 192.168.2.20 is being
translated by router RT2 to reach a destination IPv4 address of
192.0.2.254.
Explanation:
Because no outside local or outside global address is referenced, the
traffic from a source IPv4 address of 192.168.254.253 is being
translated to 192.0.2.88 by using static NAT. In the output from the
command show ip nat translations, the inside local IP
address of 192.168.2.20 is being translated into an outside IP address
of 192.0.2.254 so that the traffic can cross the public network. A
public IPv4 device can connect to the private IPv4 device
192.168.254.253 by targeting the destination IPv4 address of 192.0.2.88.
118. Which two WAN infrastructure services are examples of private connections? (Choose two.)
- cable
- DSL
- Frame Relay
- T1/E1
- wireless
Explanation: Private WANs can use T1/E1, T3/E3, PSTN, ISDN, Metro Ethernet, MPLS, Frame Relay, ATM, or VSAT technology.
119. Which two statements about the relationship between LANs and WANs are true? (Choose two.)
- Both LANs and WANs connect end devices.
- WANs are typically operated through multiple ISPs, but LANs are typically operated by single organizations or individuals.
- WANs must be publicly-owned, but LANs can be owned by either public or private entities.
- WANs connect LANs at slower speed bandwidth than LANs connect their internal end devices.
- LANs connect multiple WANs together.
Explanation:
Although LANs and WANs can employ the same network media and
intermediary devices, they serve very different areas and purposes. The
administrative and geographical scope of a WAN is larger than that of a
LAN. Bandwidth speeds are slower on WANs because of their increased
complexity. The Internet is a network of networks, which can function
under either public or private management.
120. Which statement describes an important characteristic of a site-to-site VPN?
- It must be statically set up.
- It is ideally suited for use by mobile workers.
- It requires using a VPN client on the host PC.
- After the initial connection is established, it can dynamically change connection information.
- It is commonly implemented over dialup and cable modem networks.
Explanation: A
site-to-site VPN is created between the network devices of two separate
networks. The VPN is static and stays established. The internal hosts of
the two networks have no knowledge of the VPN.
121. How is “tunneling” accomplished in a VPN?
- New headers from one or more VPN protocols encapsulate the original packets.
- All packets between two hosts are assigned to a single physical medium to ensure that the packets are kept private.
- Packets are disguised to look like other types of traffic so that they will be ignored by potential attackers.
- A dedicated circuit is established between the source and destination devices for the duration of the connection.
Explanation:
Packets in a VPN are encapsulated with the headers from one or more VPN
protocols before being sent across the third party network. This is
referred to as “tunneling”. These outer headers can be used to route the
packets, authenticate the source, and prevent unauthorized users from
reading the contents of the packets.
122. Which statement describes a VPN?
- VPNs use open source virtualization software to create the tunnel through the Internet.
- VPNs use logical connections to create public networks through the Internet.
- VPNs use dedicated physical connections to transfer data between remote users.
- VPNs use virtual connections to create a private network through a public network.
Explanation: A VPN
is a private network that is created over a public network. Instead of
using dedicated physical connections, a VPN uses virtual connections
routed through a public network between two network devices.
123. Open the PT Activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then answer the question.
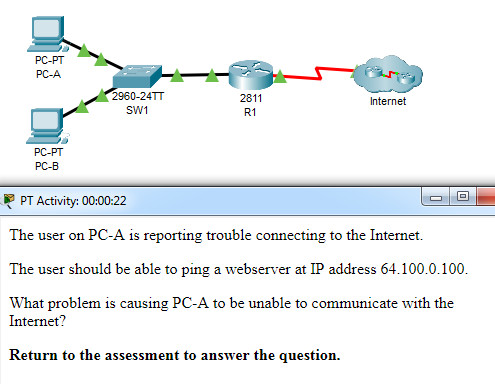
CCNA 3 v7 Modules 6 – 8: WAN Concepts Exam Answers
What problem is causing PC-A to be unable to communicate with the Internet?
- The ip nat inside source command refers to the wrong interface.
- The NAT interfaces are not correctly assigned.
- The static route should not reference the interface, but the outside address instead.
- The access list used in the NAT process is referencing the wrong subnet.
- This router should be configured to use static NAT instead of PAT.
Explanation: The output of show ip nat statistics
shows that the inside interface is FastEthernet0/0 but that no
interface has been designated as the outside interface. This can be
fixed by adding the command ip nat outside to interface Serial0/0/0.
124. What type of address is 64.100.190.189?
125. Which type of VPN routes packets through virtual tunnel interfaces for encryption and forwarding?
- MPLS VPN
- IPsec virtual tunnel interface
- dynamic multipoint VPN
- GRE over IPsec
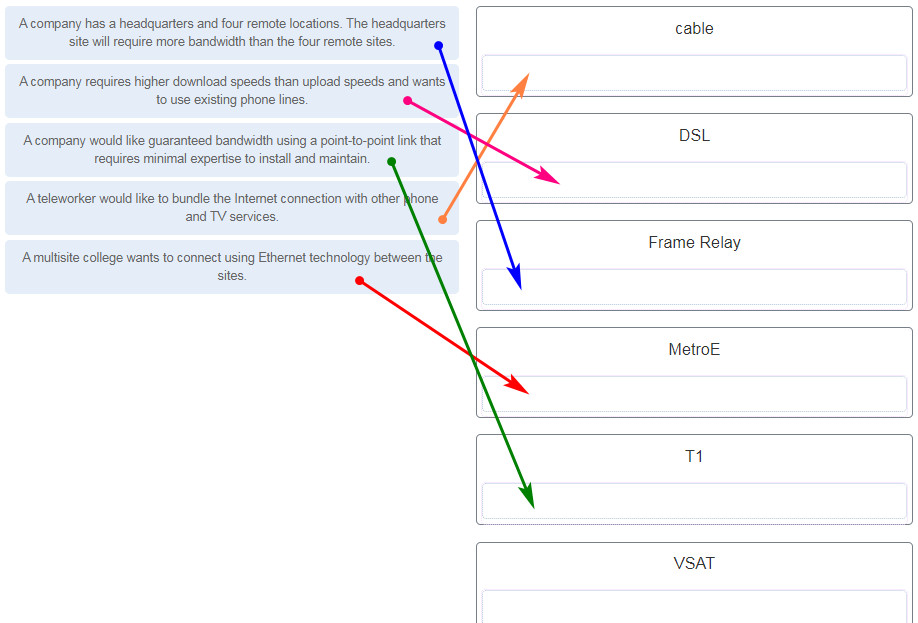
126. Match the scenario to the WAN solution. (Not all options are used.)
 127. Question as presented:
127. Question as presented:
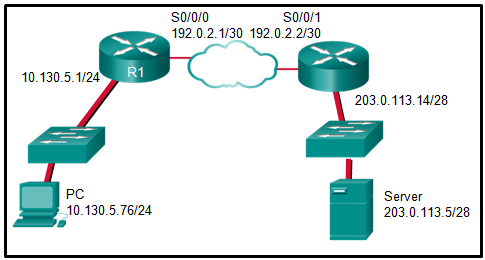 Refer to the exhibit. The PC is sending a packet to the Server
on the remote network. Router R1 is performing NAT overload. From the
perspective of the PC, match the NAT address type with the correct IP
address. (Not all options are used.)
Refer to the exhibit. The PC is sending a packet to the Server
on the remote network. Router R1 is performing NAT overload. From the
perspective of the PC, match the NAT address type with the correct IP
address. (Not all options are used.)
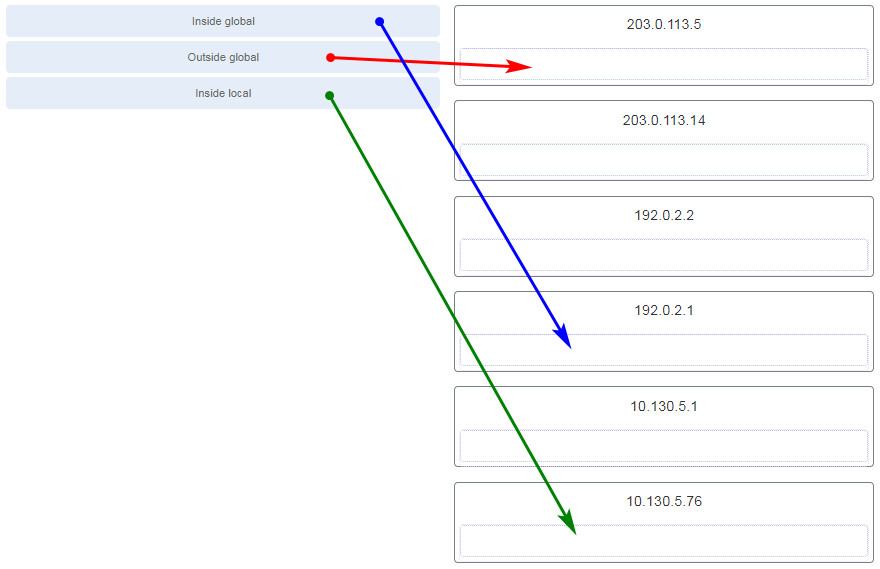 128. Refer to the exhibit. What has to be done in order to complete the static NAT configuration on R1?
128. Refer to the exhibit. What has to be done in order to complete the static NAT configuration on R1?
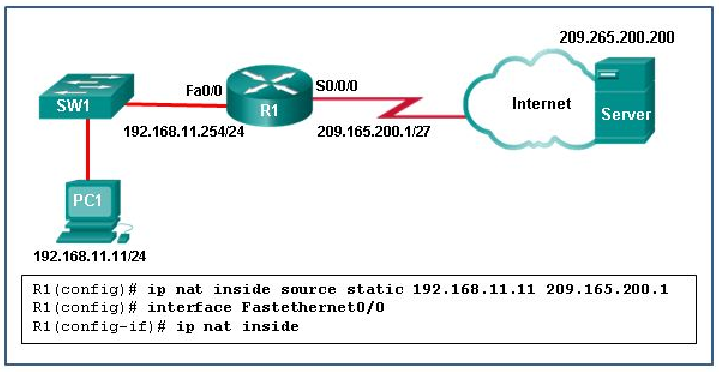
- Interface Fa0/0 should be configured with the command no ip nat inside.
- Interface S0/0/0 should be configured with the command ip nat outside.
- R1 should be configured with the command ip nat inside source static 209.165.200.200 192.168.11.11.
- R1 should be configured with the command ip nat inside source static 209.165.200.1 192.168.11.11.
Explanation: In
order for NAT translations to work properly, both an inside and outside
interface must be configured for NAT translation on the router.
129. In NAT terms, what address type refers to the globally routable IPv4 address of a destination host on the Internet?
- outside global
- inside global
- outside local
- inside local
Explanation: From
the perspective of a NAT device, inside global addresses are used by
external users to reach internal hosts. Inside local addresses are the
addresses assigned to internal hosts. Outside global addresses are the
addresses of destinations on the external network. Outside local
addresses are the actual private addresses of destination hosts behind
other NAT devices.
130. Refer to the exhibit. Which two statements are correct based on the output as shown in the exhibit? (Choose two.)

- The output is the result of the show ip nat translations command.
- The host with the address 209.165.200.235 will respond to requests by using a source address of 192.168.10.10.
- The output is the result of the show ip nat statistics command.
- Traffic with the destination address of a public web server will be sourced from the IP of 192.168.1.10.
- The host with the address 209.165.200.235 will respond to requests by using a source address of 209.165.200.235.
Explanation: The output displayed in the exhibit is the result of the show ip nat translations command. Static NAT entries are always present in the NAT table, while dynamic entries will eventually time out.
131. Which circumstance would result in an enterprise deciding to implement a corporate WAN?
- when the enterprise decides to secure its corporate LAN
- when its employees become distributed across many branch locations
- when the number of employees exceeds the capacity of the LAN
- when the network will span multiple buildings
Explanation: WANs
cover a greater geographic area than LANs do, so having employees
distributed across many locations would require the implementation of
WAN technologies to connect those locations. Customers will access
corporate web services via a public WAN that is implemented by a service
provider, not by the enterprise itself. When employee numbers grow, the
LAN has to expand as well. A WAN is not required unless the employees
are in remote locations. LAN security is not related to the decision to
implement a WAN.
132. What is the function of the Hashed Message Authentication Code (HMAC) algorithm in setting up an IPsec VPN?
- protects IPsec keys during session negotiation
- authenticates the IPsec peers
- creates a secure channel for key negotiation
- guarantees message integrity
Explanation: The
IPsec framework uses various protocols and algorithms to provide data
confidentiality, data integrity, authentication, and secure key
exchange. The Hashed Message Authentication Code (HMAC) is a data
integrity algorithm that uses a hash value to guarantee the integrity of
a message.
133. What algorithm is used with IPsec to provide data confidentiality?
- Diffie-Hellman
- SHA
- MD5
- RSA
- AES
Explanation: The
IPsec framework uses various protocols and algorithms to provide data
confidentiality, data integrity, authentication, and secure key
exchange. Two popular algorithms that are used to ensure that data is
not intercepted and modified (data integrity) are MD5 and SHA. AES is an
encryption protocol and provides data confidentiality. DH
(Diffie-Hellman) is an algorithm that is used for key exchange. RSA is
an algorithm that is used for authentication.
134. Which two technologies provide enterprise-managed VPN solutions? (Choose two.)
- remote access VPN
- Frame Relay
- Layer 2 MPLS VPN
- site-to-site VPN
- Layer 3 MPLS VPN
Explanation: VPNs can be managed and deployed as either of two types:
- Enterprise VPNs – Enterprise-managed VPNs are a
common solution for securing enterprise traffic across the internet.
Site-to-site and remote access VPNs are examples of enterprise managed
VPNs.
- Service Provider VPNs – Service provider managed
VPNs are created and managed over the provider network. Layer 2 and
Layer 3 MPLS are examples of service provider managed VPNs. Other legacy
WAN solutions include Frame Relay and ATM VPNs.
135. Question as presented:
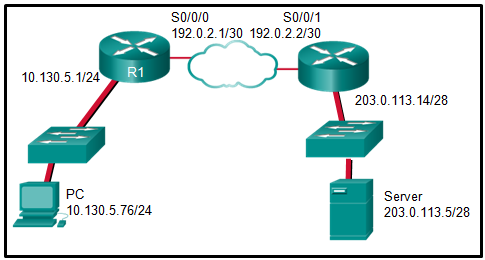
Explanation: The
inside local address is the private IP address of the source or the PC
in this instance. The inside global address is the translated address of
the source or the address as seen by the outside device. Since the PC
is using the outside address of the R1 router, the inside global address
is 192.0.2.1. The outside addressing is simply the address of the
server or 203.0.113.5.
136. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is viewing
the output from the command show ip nat translations. Which statement
correctly describes the NAT translation that is occurring on router
RT2?
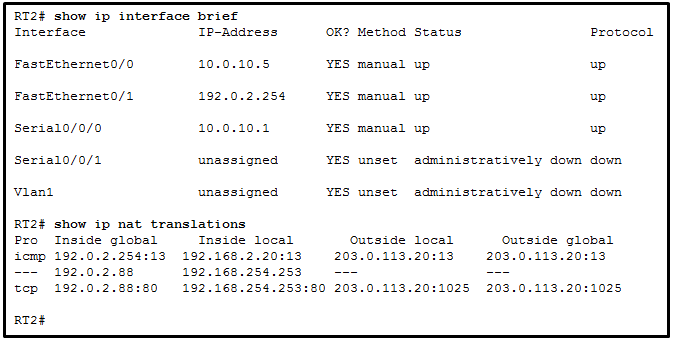
- The traffic from a source IPv4 address of 192.168.254.253 is being translated to 192.0.2.88 by means of static NAT.
- The traffic from a source IPv4 address of 192.0.2.88 is being
translated by router RT2 to reach a destination IPv4 address of
192.168.254.253.
- The traffic from a source IPv4 public address that originates
traffic on the internet would be able to reach private internal IPv4
addresses.
- The traffic from a source IPv4 address of 192.168.2.20 is being
translated by router RT2 to reach a destination IPv4 address of
192.0.2.254.
Explanation:
Because no outside local or outside global address is referenced, the
traffic from a source IPv4 address of 192.168.254.253 is being
translated to 192.0.2.88 by using static NAT. In the output from the
command show ip nat translations, the inside local IP
address of 192.168.2.20 is being translated into an outside IP address
of 192.0.2.254 so that the traffic can cross the public network. A
public IPv4 device can connect to the private IPv4 device
192.168.254.253 by targeting the destination IPv4 address of 192.0.2.88.
137. What type of address is 10.100.126.126?
138. Which type of VPN connects using the Transport Layer Security (TLS) feature?
- SSL VPN
- MPLS VPN
- IPsec virtual tunnel interface
- dynamic multipoint VPN
139. The IT department is reporting that a company web server
is receiving an abnormally high number of web page requests from
different locations simultaneously. Which type of security attack is
occurring?
- adware
- DDoS
- phishing
- social engineering
- spyware
140. What causes a buffer overflow?
- launching a security countermeasure to mitigate a Trojan horse
- downloading and installing too many software updates at one time
- attempting to write more data to a memory location than that location can hold
- sending too much information to two or more interfaces of the same device, thereby causing dropped packets
- sending repeated connections such as Telnet to a particular device, thus denying other data sources
141. Which objective of secure communications is achieved by encrypting data?
- authentication
- availability
- confidentiality
- integrity
142. What type of malware has the primary objective of spreading across the network?
- worm
- virus
- Trojan horse
- botnet
143. What commonly motivates cybercriminals to attack networks as compared to hactivists or state-sponsored hackers?
- financial gain
- fame seeking
- status among peers
- political reasons
Explanation:
Cybercriminals are commonly motivated by money. Hackers are known to
hack for status. Cyberterrorists are motivated to commit cybercrimes for
religious or political reasons.
144. Which type of hacker is motivated to protest against political and social issues?
- hacktivist
- cybercriminal
- script kiddie
- vulnerability broker
Explanation: Hackers are categorized by motivating factors. Hacktivists are motivated by protesting political and social issues.
145. What is a ping sweep?
- a query and response protocol that identifies information about a
domain, including the addresses that are assigned to that domain.
- a scanning technique that examines a range of TCP or UDP port numbers on a host to detect listening services.
- a software application that enables the capture of all network packets that are sent across a LAN.
- a network scanning technique that indicates the live hosts in a range of IP addresses.
Explanation: A ping
sweep is a tool that is used during a reconnaissance attack. Other
tools that might be used during this type of attack include a ping
sweep, port scan, or Internet information query. A reconnaissance attack
is used to gather information about a particular network, usually in
preparation for another type of network attack.
146. In what type of attack is a cybercriminal attempting to prevent legitimate users from accessing network services?
- address spoofing
- MITM
- session hijacking
- DoS
Explanation: In a DoS or denial-of-service attack, the goal of the attacker is to prevent legitimate users from accessing network services.
147. Which requirement of secure communications is ensured by the implementation of MD5 or SHA hash generating algorithms?
- nonrepudiation
- authentication
- integrity
- confidentiality
Explanation:
Integrity is ensured by implementing either MD5 or SHA hash generating
algorithms. Many modern networks ensure authentication with protocols,
such as HMAC. Data confidentiality is ensured through symmetric
encryption algorithms, including DES, 3DES, and AES. Data
confidentiality can also be ensured using asymmetric algorithms,
including RSA and PKI.
148. If an asymmetric algorithm uses a public key to encrypt data, what is used to decrypt it?
- a digital certificate
- a different public key
- a private key
- DH
Explanation: When
an asymmetric algorithm is used, public and private keys are used for
the encryption. Either key can be used for encryption, but the
complementary matched key must be used for the decryption. For example
if the public key is used for encryption, then the private key must be
used for the decryption.
149. Refer to the exhibit. Which two ACLs would permit only
the two LAN networks attached to R1 to access the network that connects
to R2 G0/1 interface? (Choose two.)
- access-list 1 permit 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.127
- access-list 2 permit host 192.168.10.9
access-list 2 permit host 192.168.10.69
- access-list 5 permit 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.63
access-list 5 permit 192.168.10.64 0.0.0.63
- access-list 3 permit 192.168.10.128 0.0.0.63
- access-list 4 permit 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255
Explanation: The permit 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.127
command ignores bit positions 1 through 7, which means that addresses
192.168.10.0 through 192.168.10.127 are allowed through. The two ACEs of
permit 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.63 and permit 192.168.10.64 0.0.0.63 allow the same address range through the router.
150. Which two packet filters could a network administrator use on an IPv4 extended ACL? (Choose two.)
- destination UDP port number
- computer type
- destination MAC address
- ICMP message type
- source TCP hello address
Explanation:
Extended access lists commonly filter on source and destination IPv4
addresses and TCP or UDP port numbers. Additional filtering can be
provided for protocol types.
151. What type of ACL offers greater flexibility and control over network access?
- numbered standard
- named standard
- extended
- flexible
Explanation: The
two types of ACLs are standard and extended. Both types can be named or
numbered, but extended ACLs offer greater flexibility.
152. What is the quickest way to remove a single ACE from a named ACL?
- Use the no keyword and the sequence number of the ACE to be removed.
- Copy the ACL into a text editor, remove the ACE, then copy the ACL back into the router.
- Create a new ACL with a different number and apply the new ACL to the router interface.
- Use the no access-list command to remove the entire ACL, then recreate it without the ACE.
Explanation: Named ACL ACEs can be removed using the no command followed by the sequence number.
153. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is
configuring a standard IPv4 ACL. What is the effect after the command no
access-list 10 is entered?
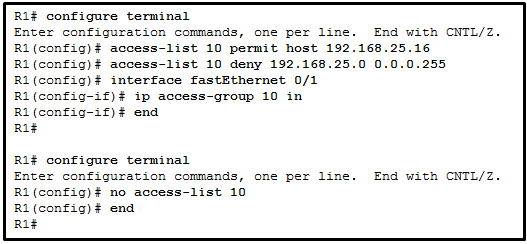
- ACL 10 is removed from both the running configuration and the interface Fa0/1.
- ACL 10 is removed from the running configuration.
- ACL 10 is disabled on Fa0/1.
- ACL 10 will be disabled and removed after R1 restarts.
Explanation: The R1(config)# no access-list <access-list number>
command removes the ACL from the running-config immediately. However,
to disable an ACL on an interface, the command R1(config-if)# no ip access-group should be entered.
154. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator has
configured ACL 9 as shown. Users on the 172.31.1.0 /24 network cannot
forward traffic through router CiscoVille. What is the most likely cause
of the traffic failure?
- The established keyword is not specified.
- The sequence of the ACEs is incorrect.
- The port number for the traffic has not been identified with the eq keyword.
- The permit statement specifies an incorrect wildcard mask.
Explanation: When
verifying an ACL, the statements are always listed in a sequential
order. Even though there is an explicit permit for the traffic that is
sourced from network 172.31.1.0 /24, it is being denied due to the
previously implemented ACE of CiscoVille(config)# access-list 9 deny 172.31.0.0 0.0.255.255.
The sequence of the ACEs must be modified to permit the specific
traffic that is sourced from network 172.31.1.0 /24 and then to deny
172.31.0.0 /16.
155. A network administrator needs to configure a standard
ACL so that only the workstation of the administrator with the IP
address 192.168.15.23 can access the virtual terminal of the main
router. Which two configuration commands can achieve the task? (Choose
two.)
- Router1(config)# access-list 10 permit 192.168.15.23 0.0.0.0
- Router1(config)# access-list 10 permit 192.168.15.23 0.0.0.255
- Router1(config)# access-list 10 permit 192.168.15.23 255.255.255.255
- Router1(config)# access-list 10 permit host 192.168.15.23
- Router1(config)# access-list 10 permit 192.168.15.23 255.255.255.0
Explanation: To permit or deny one specific IP address, either the wildcard mask 0.0.0.0 (used after the IP address) or the wildcard mask keyword host (used before the IP address) can be used.
156. Refer to the exhibit. Which command would be used in a
standard ACL to allow only devices on the network attached to R2 G0/0
interface to access the networks attached to R1?
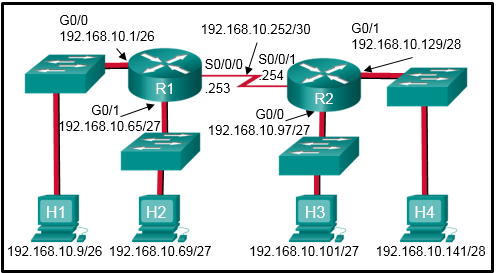
- access-list 1 permit 192.168.10.128 0.0.0.63
- access-list 1 permit 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255
- access-list 1 permit 192.168.10.96 0.0.0.31
- access-list 1 permit 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.63
Explanation:
Standard access lists only filter on the source IP address. In the
design, the packets would be coming from the 192.168.10.96/27 network
(the R2 G0/0 network). The correct ACL is access-list 1 permit 192.168.10.96 0.0.0.31.
157. A network administrator is writing a standard ACL that
will deny any traffic from the 172.16.0.0/16 network, but permit all
other traffic. Which two commands should be used? (Choose two.)
- Router(config)# access-list 95 deny 172.16.0.0 255.255.0.0
- Router(config)# access-list 95 permit any
- Router(config)# access-list 95 host 172.16.0.0
- Router(config)# access-list 95 deny 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255
- Router(config)# access-list 95 172.16.0.0 255.255.255.255
- Router(config)# access-list 95 deny any
Explanation: To deny traffic from the 172.16.0.0/16 network, the access-list 95 deny 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255 command is used. To permit all other traffic, the access-list 95 permit any statement is added.
158. Refer to the exhibit. An ACL was configured on R1 with
the intention of denying traffic from subnet 172.16.4.0/24 into subnet
172.16.3.0/24. All other traffic into subnet 172.16.3.0/24 should be
permitted. This standard ACL was then applied outbound on interface
Fa0/0. Which conclusion can be drawn from this configuration?
- The ACL should be applied outbound on all interfaces of R1.
- The ACL should be applied to the FastEthernet 0/0 interface of R1 inbound to accomplish the requirements.
- All traffic will be blocked, not just traffic from the 172.16.4.0/24 subnet.
- Only traffic from the 172.16.4.0/24 subnet is blocked, and all other traffic is allowed.
- An extended ACL must be used in this situation.
Explanation: Because of the implicit deny at the end of all ACLs, the access-list 1 permit any
command must be included to ensure that only traffic from the
172.16.4.0/24 subnet is blocked and that all other traffic is allowed.
159. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator needs to
add an ACE to the TRAFFIC-CONTROL ACL that will deny IP traffic from the
subnet 172.23.16.0/20. Which ACE will meet this requirement?
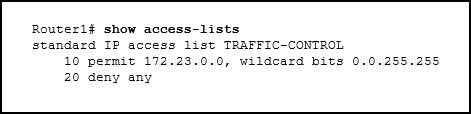
- 30 deny 172.23.16.0 0.0.15.255
- 15 deny 172.23.16.0 0.0.15.255
- 5 deny 172.23.16.0 0.0.15.255
- 5 deny 172.23.16.0 0.0.255.255
Explanation: The
only filtering criteria specified for a standard access list is the
source IPv4 address. The wild card mask is written to identify what
parts of the address to match, with a 0 bit, and what parts of the
address should be ignored, which a 1 bit. The router will parse the ACE
entries from lowest sequence number to highest. If an ACE must be added
to an existing access list, the sequence number should be specified so
that the ACE is in the correct place during the ACL evaluation process.
160. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator configures
an ACL on the router. Which statement describes the result of the
configuration?
- An SSH connection is allowed from a workstation with IP 172.16.45.16 to a device with IP 192.168.25.18.
- An SSH connection is allowed from a workstation with IP 192.168.25.18 to a device with IP 172.16.45.16.
- A Telnet connection is allowed from a workstation with IP 192.168.25.18 to a device with IP 172.16.45.16.
- A Telnet connection is allowed from a workstation with IP 172.16.45.16 to a device with IP 192.168.25.18.
Explanation: In an
extended ACL, the first address is the source IP address and the second
one is the destination IP address. TCP port number 22 is a well-known
port number reserved for SSH connections. Telnet connections use TCP
port number 23.
161. Refer to the exhibit. What can be determined from this output?
- The ACL is missing the deny ip any any ACE.
- The ACL is only monitoring traffic destined for 10.23.77.101 from three specific hosts.
- Because there are no matches for line 10, the ACL is not working.
- The router has not had any Telnet packets from 10.35.80.22 that are destined for 10.23.77.101.
Explanation: ACL
entry 10 in MyACL matches any Telnet packets between host 10.35.80.22
and 10.23.77.101. No matches have occurred on this ACE as evidenced by
the lack of a “(xxx matches)” ACE. The deny ip any any ACE is not
required because there is an implicit deny ACE added to every access
control list. When no matches exist for an ACL, it only means that no
traffic has matched the conditions that exist for that particular line.
The ACL is monitoring traffic that matches three specific hosts going to
very specific destination devices. All other traffic is not permitted
by the implicit deny ip any any ACE.
162. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator wants to
permit only host 192.168.1.1 /24 to be able to access the server
192.168.2.1 /24. Which three commands will achieve this using best ACL
placement practices? (Choose three.)
- R2(config)# interface fastethernet 0/1
- R2(config-if)# ip access-group 101 out
- R2(config)# access-list 101 permit ip 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.2.0 255.255.255.0
- R2(config-if)# ip access-group 101 in
- R2(config)# access-list 101 permit ip any any
- R2(config)# interface fastethernet 0/0
- R2(config)# access-list 101 permit ip host 192.168.1.1 host 192.168.2.1
Explanation: An
extended ACL is placed as close to the source of the traffic as
possible. In this case.it is placed in an inbound direction on interface
fa0/0 on R2 for traffic entering the router from host with the IP
address192.168.1.1 bound for the server with the IP address192.168.2.1.
163. Consider the following access list.
access-list 100 permit ip host 192.168.10.1 any
access-list 100 deny icmp 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255 any echo
access-list 100 permit ip any any
Which two actions are taken if the access list is placed
inbound on a router Gigabit Ethernet port that has the IP address
192.168.10.254 assigned? (Choose two.)
- Only Layer 3 connections are allowed to be made from the router to any other network device.
- Devices on the 192.168.10.0/24 network are not allowed to reply to any ping requests.
- Devices on the 192.168.10.0/24 network can sucessfully ping devices on the 192.168.11.0 network.
- A Telnet or SSH session is allowed from any device on the 192.168.10.0 into the router with this access list assigned.
- Only the network device assigned the IP address 192.168.10.1 is allowed to access the router.
Explanation: The
first ACE allows the 192.168.10.1 device to do any TCP/IP-based
transactions with any other destination. The second ACE stops devices on
the 192.168.10.0/24 network from issuing any pings to any other
location. Everything else is permitted by the third ACE. Therefore, a
Telnet/SSH session or ping reply is allowed from a device on the
192.168.10.0/24 network.
164. Refer to the exhibit. The named ACL “Managers” already
exists on the router. What will happen when the network administrator
issues the commands that are shown in the exhibit?
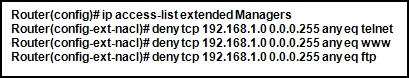
- The commands are added at the end of the existing Managers ACL.
- The commands overwrite the existing Managers ACL.
- The commands are added at the beginning of the existing Managers ACL.
- The network administrator receives an error that states that the ACL already exists.
165. In which TCP attack is the cybercriminal attempting to overwhelm a target host with half-open TCP connections?
- port scan attack
- SYN flood attack
- session hijacking attack
- reset attack
Explanation: In a
TCP SYN flood attack, the attacker sends to the target host a continuous
flood of TCP SYN session requests with a spoofed source IP address. The
target host responds with a TCP-SYN-ACK to each of the SYN session
requests and waits for a TCP ACK that will never arrive. Eventually the
target is overwhelmed with half-open TCP connections.
166. Which protocol is attacked when a cybercriminal provides an invalid gateway in order to create a man-in-the-middle attack?
- DHCP
- DNS
- ICMP
- HTTP or HTTPS
Explanation: A cybercriminal could set up a rogue DHCP server that provides one or more of the following:
- Wrong default gateway that is used to create a man-in-the-middle attack and allow the attacker to intercept data
- Wrong DNS server that results in the user being sent to a malicious website
- Invalid default gateway IP address that results in a denial of service attack on the DHCP client
167. Refer to the exhibit. An administrator has configured a
standard ACL on R1 and applied it to interface serial 0/0/0 in the
outbound direction. What happens to traffic leaving interface serial
0/0/0 that does not match the configured ACL statements?
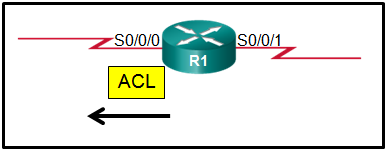
- The traffic is dropped.
- The source IP address is checked and, if a match is not found, traffic is routed out interface serial 0/0/1.
- The resulting action is determined by the destination IP address.
- The resulting action is determined by the destination IP address and port number.
Explanation: Any
traffic that does not match one of the statements in an ACL has the
implicit deny applied to it, which means the traffic is dropped.
168. Refer to the exhibit. The Gigabit interfaces on both
routers have been configured with subinterface numbers that match the
VLAN numbers connected to them. PCs on VLAN 10 should be able to print
to the P1 printer on VLAN 12. PCs on VLAN 20 should print to the
printers on VLAN 22. What interface and in what direction should you
place a standard ACL that allows printing to P1 from data VLAN 10, but
stops the PCs on VLAN 20 from using the P1 printer? (Choose two.)
- inbound
- R2 S0/0/1
- R1 Gi0/1.12
- outbound
- R1 S0/0/0
- R2 Gi0/1.20
Explanation: A
standard access list is commonly placed as close to the destination
network as possible because access control expressions in a standard ACL
do not include information about the destination network.
The destination in this example is printer VLAN 12 which has router R1
Gigabit subinterface 0/1/.12 as its gateway. A sample standard ACL that
only allows printing from data VLAN 10 (192.168.10.0/24), for example,
and no other VLAN would be as follows:
R1(config)# access-list 1 permit 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255
R1(config)# access-list 1 deny any
R1(config)# interface gigabitethernet 0/1.12
R1(config-if)# ip access-group 1 out
169. Which statement describes a characteristic of standard IPv4 ACLs?
- They are configured in the interface configuration mode.
- They can be configured to filter traffic based on both source IP addresses and source ports.
- They can be created with a number but not with a name.
- They filter traffic based on source IP addresses only.
Explanation: A
standard IPv4 ACL can filter traffic based on source IP addresses only.
Unlike an extended ACL, it cannot filter traffic based on Layer 4 ports.
However, both standard and extended ACLs can be identified with either a
number or a name, and both are configured in global configuration mode.
170. What is considered a best practice when configuring ACLs on vty lines?
- Place identical restrictions on all vty lines.
- Remove the vty password since the ACL restricts access to trusted users.
- Apply the ip access-group command inbound.
- Use only extended access lists.
171.

Refer to the exhibit. An administrator first configured an extended ACL
as shown by the output of the show access-lists command. The
administrator then edited this access-list by issuing the commands
below.
Router(config)# ip access-list extended 101
Router(config-ext-nacl)# no 20
Router(config-ext-nacl)# 5 permit tcp any any eq 22
Router(config-ext-nacl)# 20 deny udp any any
Which two conclusions can be drawn from this new configuration? (Choose two.)
- TFTP packets will be permitted.
- Ping packets will be permitted.
- Telnet packets will be permitted.
- SSH packets will be permitted.
- All TCP and UDP packets will be denied.
Explanation: After the editing, the final configuration is as follows:
Router# show access-lists
Extended IP access list 101
5 permit tcp any any eq ssh
10 deny tcp any any
20 deny udp any any
30 permit icmp any any
So, only SSH packets and ICMP packets will be permitted.
172. Which set of access control entries would allow all
users on the 192.168.10.0/24 network to access a web server that is
located at 172.17.80.1, but would not allow them to use Telnet?
- access-list 103 deny tcp host 192.168.10.0 any eq 23
access-list 103 permit tcp host 192.168.10.1 eq 80
- access-list 103 permit tcp 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255 any eq 80
access-list 103 deny tcp 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255 any eq 23
- access-list 103 permit 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255 host 172.17.80.1
access-list 103 deny tcp 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255 any eq telnet
- access-list 103 permit tcp 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255 host 172.17.80.1 eq 80
access-list 103 deny tcp 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255 any eq 23
Explanation: For an extended ACL to meet these requirements the following need to be included in the access control entries:
- identification number in the range 100-199 or 2000-2699
- permit or deny parameter
- protocol
- source address and wildcard
- destination address and wildcard
- port number or name
173. What is the term used to describe a mechanism that takes advantage of a vulnerability?
- mitigation
- exploit
- vulnerability
- threat
174. Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator has an
IP address of 192.168.11.10 and needs access to manage R1. What is the
best ACL type and placement to use in this situation?
- extended ACL outbound on R2 WAN interface towards the internet
- standard ACL inbound on R1 vty lines
- extended ACLs inbound on R1 G0/0 and G0/1
- extended ACL outbound on R2 S0/0/1
Explanation:
Standard ACLs permit or deny packets based only on the source IPv4
address. Because all traffic types are permitted or denied, standard
ACLs should be located as close to the destination as possible.
Extended ACLs permit or deny packets based on the source IPv4 address
and destination IPv4 address, protocol type, source and destination TCP
or UDP ports and more. Because the filtering of extended ACLs is so
specific, extended ACLs should be located as close as possible to the
source of the traffic to be filtered. Undesirable traffic is denied
close to the source network without crossing the network infrastructure.
175. A technician is tasked with using ACLs to secure a
router. When would the technician use the any configuration option or
command?
- to add a text entry for documentation purposes
- to generate and send an informational message whenever the ACE is matched
- to identify any IP address
- to identify one specific IP address
176. Which statement accurately characterizes the evolution of threats to network security?
- Internet architects planned for network security from the beginning.
- Early Internet users often engaged in activities that would harm other users.
- Internal threats can cause even greater damage than external threats.
- Threats have become less sophisticated while the technical knowledge needed by an attacker has grown.
Explanation: Internal
threats can be intentional or accidental and cause greater damage than
external threats because the internal user has direct access to the
internal corporate network and corporate data.
177. A user receives a phone call from a person who claims to
represent IT services and then asks that user for confirmation of
username and password for auditing purposes. Which security threat does
this phone call represent?
- spam
- social engineering
- DDoS
- anonymous keylogging
Explanation: Social
engineering attempts to gain the confidence of an employee and convince
that person to divulge confidential and sensitive information, such as
usernames and passwords. DDoS attacks, spam, and keylogging are all
examples of software based security threats, not social engineering.
178. In what way are zombies used in security attacks?
- They target specific individuals to gain corporate or personal information.
- They probe a group of machines for open ports to learn which services are running.
- They are maliciously formed code segments used to replace legitimate applications.
- They are infected machines that carry out a DDoS attack.
Explanation: Zombies
are infected computers that make up a botnet. The zombies are used to
deploy a distributed denial of service (DDoS) attack.
179. Which attack involves threat actors positioning
themselves between a source and destination with the intent of
transparently monitoring, capturing, and controlling the communication?
- man-in-the-middle attack
- SYN flood attack
- DoS attack
- ICMP attack
Explanation: The
man-in-the-middle attack is a common IP-related attack where threat
actors position themselves between a source and destination to
transparently monitor, capture, and control the communication.
180. Which two keywords can be used in an access control list
to replace a wildcard mask or address and wildcard mask pair? (Choose
two.)
- host
- most
- gt
- some
- any
- all
Explanation: The host keyword is used when using a specific device IP address in an ACL. For example, the deny host 192.168.5.5 command is the same is the deny 192.168.5.5 0.0.0.0 command. The any keyword is used to allow any mask through that meets the criteria. For example, the permit any command is the same as permit 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 command.
181. Refer to the exhibit. The student on the H1 computer
continues to launch an extended ping with expanded packets at the
student on the H2 computer. The school network administrator wants to
stop this behavior, but still allow both students access to web-based
computer assignments. What would be the best plan for the network
administrator?
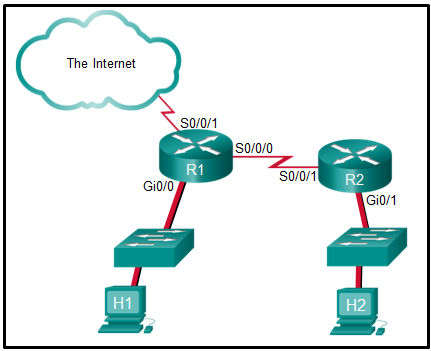
CCNA 3 v7 Modules 3 – 5: Network Security Exam Answers 42
- Apply an inbound standard ACL on R1 Gi0/0.
- Apply an inbound extended ACL on R2 Gi0/1.
- Apply an outbound extended ACL on R1 S0/0/1.
- Apply an inbound extended ACL on R1 Gi0/0.
- Apply an outbound standard ACL on R2 S0/0/1.
Explanation: This
access list must be an extended ACL in order to filter on specific
source and destination host addresses. Commonly, the best place for an
extended ACL is closest to the source, which is H1. Traffic from H1
travels into the switch, then out of the switch into the R1 Gi0/0
interface. This Gi0/0 interface would be the best location for this type
of extended ACL. The ACL would be applied on the inbound interface
since the packets from H1 would be coming into the R1 router.
182. Which statement describes a difference between the operation of inbound and outbound ACLs?
- Inbound ACLs are processed before the packets are routed while outbound ACLs are processed after the routing is completed.
- In contrast to outbound ALCs, inbound ACLs can be used to filter packets with multiple criteria.
- On a network interface, more than one inbound ACL can be configured but only one outbound ACL can be configured.
- Inbound ACLs can be used in both routers and switches but outbound ACLs can be used only on routers.
Explanation: With
an inbound ACL, incoming packets are processed before they are routed.
With an outbound ACL, packets are first routed to the outbound
interface, then they are processed. Thus processing inbound is more
efficient from the router perspective. The structure, filtering methods,
and limitations (on an interface, only one inbound and one outbound ACL
can be configured) are the same for both types of ACLs.
183. What effect would the Router1(config-ext-nacl)# permit
tcp 172.16.4.0 0.0.0.255 any eq www command have when implemented
inbound on the f0/0 interface?
- All TCP traffic is permitted, and all other traffic is denied.
- Traffic originating from 172.16.4.0/24 is permitted to all TCP port 80 destinations.
- All traffic from 172.16.4.0/24 is permitted anywhere on any port.
- The command is rejected by the router because it is incomplete.
184. Which ACE will permit a packet that originates from any network and is destined for a web server at 192.168.1.1?
- access-list 101 permit tcp any host 192.168.1.1 eq 80
- access-list 101 permit tcp host 192.168.1.1 eq 80 any
- access-list 101 permit tcp host 192.168.1.1 any eq 80
- access-list 101 permit tcp any eq 80 host 192.168.1.1
185. Refer to the exhibit. A new network policy requires an
ACL denying FTP and Telnet access to a Corp file server from all
interns. The address of the file server is 172.16.1.15 and all interns
are assigned addresses in the 172.18.200.0/24 network. After
implementing the ACL, no one in the Corp network can access any of the
servers. What is the problem?
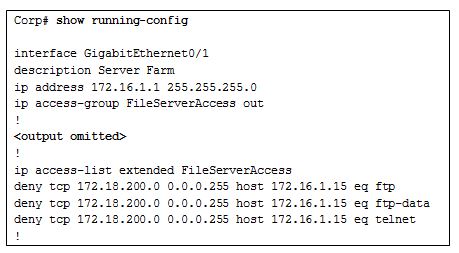
CCNA 3 v7 Modules 3 – 5: Network Security Exam Answers 46
- Inbound ACLs must be routed before they are processed.
- The ACL is implicitly denying access to all the servers.
- Named ACLs require the use of port numbers.
- The ACL is applied to the interface using the wrong direction.
Explanation: Both named and numbered ACLs have an implicit deny ACE at the end of the list. This implicit deny blocks all traffic.
186. A technician is tasked with using ACLs to secure a
router. When would the technician use the access-class 20 in
configuration option or command?
- to secure administrative access to the router
- to remove an ACL from an interface
- to remove a configured ACL
- to apply a standard ACL to an interface
187. What is the term used to describe the same pre-shared
key or secret key, known by both the sender and receiver to encrypt and
decrypt data?
- symmetric encryption algorithm
- data integrity
- exploit
- risk
188. Refer to the exhibit. Internet privileges for an
employee have been revoked because of abuse but the employee still needs
access to company resources. What is the best ACL type and placement to
use in this situation?
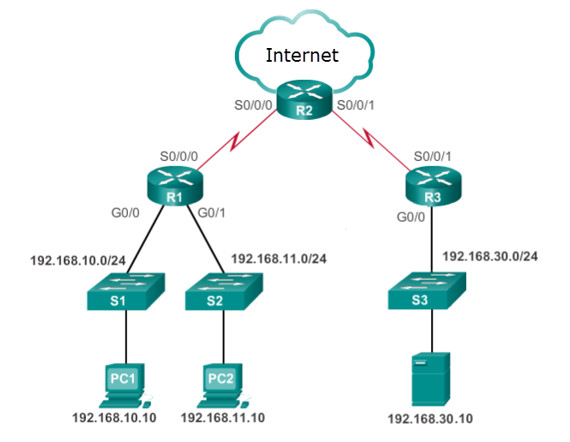
CCNA 3 v7 Modules 3 – 5: Network Security Exam Answers 49
- standard ACL inbound on R2 WAN interface connecting to the internet
- standard ACL outbound on R2 WAN interface towards the internet
- standard ACL inbound on R1 G0/0
- standard ACL outbound on R1 G0/0
Explanation: –
Standard ACLs permit or deny packets based only on the source IPv4
address. Because all traffic types are permitted or denied, standard
ACLs should be located as close to the destination as possible.
– Extended ACLs permit or deny packets based on the source IPv4 address
and destination IPv4 address, protocol type, source and destination TCP
or UDP ports and more. Because the filtering of extended ACLs is so
specific, extended ACLs should be located as close as possible to the
source of the traffic to be filtered. Undesirable traffic is denied
close to the source network without crossing the network infrastructure.
189. What is a function of OSPF hello packets?
- to send specifically requested link-state records
- to discover neighbors and build adjacencies between them
- to ensure database synchronization between routers
- to request specific link-state records from neighbor routers
190. Which OPSF packet contains the different types of link-state advertisements?
191. Which three statements describe features of the OSPF topology table? (Choose three.)
- It is a link-state database that represents the network topology.
- Its contents are the result of running the SPF algorithm.
- When converged, all routers in an area have identical topology tables.
- The topology table contains feasible successor routes.
- The table can be viewed via the show ip ospf database command.
- After convergence, the table only contains the lowest cost route entries for all known networks.
192. What does an OSPF area contain?
- routers that share the same router ID
- routers whose SPF trees are identical
- routers that have the same link-state information in their LSDBs
- routers that share the same process ID
193. What is used to facilitate hierarchical routing in OSPF?
- the use of multiple areas
- frequent SPF calculations
- autosummarization
- the election of designated routers
Explanation: OSPF
supports the concept of areas to prevent larger routing tables,
excessive SPF calculations, and large LSDBs. Only routers within an area
share link-state information. This allows OSPF to scale in a
hierarchical fashion with all areas that connect to a backbone area.
194. Which OSPF data structure is identical on all OSPF routers that share the same area?
- forwarding database
- link-state database
- adjacency database
- routing table
Explanation:
Regardless of which OSPF area a router resides in, the adjacency
database, routing table, and forwarding database are unique for each
router. The link-state database lists information about all other
routers within an area and is identical across all OSPF routers
participating in that area.
195. Which step does an OSPF-enabled router take immediately after establishing an adjacency with another router?
- builds the topology table
- exchanges link-state advertisements
- chooses the best path
- executes the SPF algorithm
Explanation: The OSPF operation steps are as follows:
- Establish neighbor adjacencies
- Exchange link-state advertisements
- Build the topology table
- Execute the SPF algorithm
- Choose the best route
196. A network engineer has manually configured the hello
interval to 15 seconds on an interface of a router that is running
OSPFv2. By default, how will the dead interval on the interface be
affected?
- The dead interval will not change from the default value.
- The dead interval will now be 30 seconds.
- The dead interval will now be 60 seconds.
- The dead interval will now be 15 seconds.
Explanation: Cisco IOS automatically modifies the dead interval to four times the hello interval.
197. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator has
configured the OSPF timers to the values that are shown in the graphic.
What is the result of having those manually configured timers?
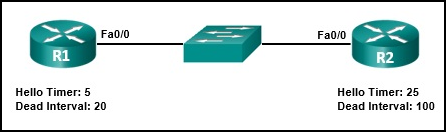
- R1 automatically adjusts its own timers to match the R2 timers.
- The R1 dead timer expires between hello packets from R2.
- The hello timer on R2 expires every ten seconds.
- The neighbor adjacency has formed.
Explanation: The dead timer (20 seconds) on R1 expires before the next hello packet from R2 (25 seconds).
198. To establish a neighbor adjacency two OSPF routers will
exchange hello packets. Which two values in the hello packets must match
on both routers? (Choose two.)
- dead interval
- router priority
- list of neighbors
- router ID
- hello interval
Explanation: The
hello and dead interval timers contained in a hello packet must be the
same on neighboring routers in order to form an adjacency.
199. What is the default router priority value for all Cisco OSPF routers?
Explanation: The
router priority value is used in a DR/BDR election. The default priority
for all OSPF routers is 1 but it can be manually altered to any value 0
to 255.
200. Which type of OSPFv2 packet contains an abbreviated list
of the LSDB of a sending router and is used by receiving routers to
check against the local LSDB?
- database description
- link-state update
- link-state request
- link-state acknowledgment
Explanation: The
database description (DBD) packet contains an abbreviated list of the
LSDB sent by a neighboring router and is used by receiving routers to
check against the local LSDB.
201. In an OSPF network when are DR and BDR elections required?
- when the two adjacent neighbors are interconnected over a point-to-point link
- when all the routers in an OSPF area cannot form adjacencies
- when the routers are interconnected over a common Ethernet network
- when the two adjacent neighbors are in two different networks
Explanation: When
the routers are interconnected over a common Ethernet network, then a
designated router (DR) and a backup DR (BDR) must be elected.
202. When an OSPF network is converged and no network
topology change has been detected by a router, how often will LSU
packets be sent to neighboring routers?
- every 5 minutes
- every 10 minutes
- every 30 minutes
- every 60 minutes
Explanation:
After all LSRs have been satisfied for a given router, the adjacent
routers are considered synchronized and in a full state. Updates (LSUs)
are sent to neighbors only under the following conditions:
- when a network topology change is detected (incremental updates)
- every 30 minutes
203. What will an OSPF router prefer to use first as a router ID?
- a loopback interface that is configured with the highest IP address on the router
- any IP address that is configured using the router-id command
- the highest active interface IP that is configured on the router
- the highest active interface that participates in the routing process because of a specifically configured network statement
Explanation: The
first preference for an OSPF router ID is an explicitly configured
32-bit address. This address is not included in the routing table and is
not defined by the network command. If a router ID that is configured through the router-id
command is not available, OSPF routers next use the highest IP address
available on a loopback interface, as loopbacks used as router IDs are
also not routable addresses. Lacking either of these alternatives, an
OSPF router will use the highest IP address from its active physical
interfaces.
204. What are the two purposes of an OSPF router ID? (Choose two.)
- to uniquely identify the router within the OSPF domain
- to facilitate router participation in the election of the designated router
- to enable the SPF algorithm to determine the lowest cost path to remote networks
- to facilitate the establishment of network convergence
- to facilitate the transition of the OSPF neighbor state to Full
Explanation: OSPF
router ID does not contribute to SPF algorithm calculations, nor does it
facilitate the transition of the OSPF neighbor state to Full. Although
the router ID is contained within OSPF messages when router adjacencies
are being established, it has no bearing on the actual convergence
process.
205. Refer to the exhibit. If no router ID was manually configured, what would router Branch1 use as its OSPF router ID?
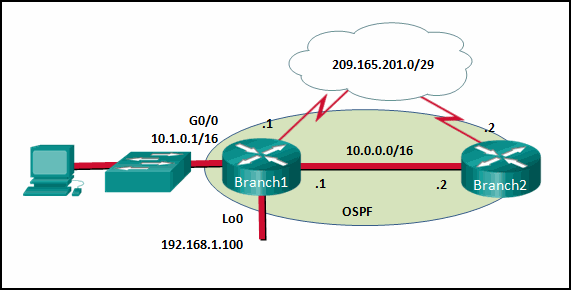
- 10.0.0.1
- 10.1.0.1
- 192.168.1.100
- 209.165.201.1
Explanation: In
OSPFv2, a Cisco router uses a three-tier method to derive its router ID.
The first choice is the manually configured router ID with the router-id
command. If the router ID is not manually configured, the router will
choose the highest IPv4 address of the configured loopback interfaces.
Finally if no loopback interfaces are configured, the router chooses the
highest active IPv4 address of its physical interfaces.
206. A network technician issues the following commands when configuring a router:
R1(config)# router ospf 11
R1(config-router)# network 10.10.10.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
What does the number 11 represent?
- the OSPF process ID on R1
- the cost of the link to R1
- the autonomous system number to which R1 belongs
- the administrative distance that is manually assigned to R1
- the area number where R1 is located
Explanation: There
is no autonomous system number to configure on OSPF. The area number is
located at the end of the network statement. The cost of a link can be
modified in the interface configuration mode. The process ID is local to
the router.
207. An OSPF router has three directly connected networks;
172.16.0.0/16, 172.16.1.0/16, and 172.16.2.0/16. Which OSPF network
command would advertise only the 172.16.1.0 network to neighbors?
- router(config-router)# network 172.16.1.0 0.0.255.255 area 0
- router(config-router)# network 172.16.0.0 0.0.15.255 area 0
- router(config-router)# network 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0 area 0
- router(config-router)# network 172.16.1.0 0.0.0.0 area 0
Explanation: To
advertise only the 172.16.1.0/16 network the wildcard mask used in the
network command must match the first 16-bits exactly. To match bits
exactly, a wildcard mask uses a binary zero. This means that the first
16-bits of the wildcard mask must be zero. The low order 16-bits can all
be set to 1.
208. Refer to the exhibit. Which three statements describe
the results of the OSPF election process of the topology that is shown
in the exhibit? (Choose three.)
- R3 will be elected BDR.
- The R4 FastEthernet 0/0 priority is 128.
- The R4 router ID is 172.16.1.1.
- R1 will be elected BDR.
- The router ID on R2 is the loopback interface.
- R2 will be elected DR.
Explanation: R2
will be elected DR because it has the highest priority of 255, all of
the others have a priority of 1. R3 will be elected BDR because it has
the numerically highest router-ID of 192.168.1.4. The R4 router-ID is
172.16.1.1 because it is the IPv4 address attached to the loopback 0
interface.
209. Refer to the exhibit. If the switch reboots and all
routers have to re-establish OSPF adjacencies, which routers will become
the new DR and BDR?
- Router R4 will become the DR and router R1 will become the BDR.
- Router R2 will become the DR and router R3 will become the BDR.
- Router R1 will become the DR and router R2 will become the BDR.
- Router R4 will become the DR and router R3 will become the BDR.
Explanation: OSPF elections of a DR are based on the following in order of precedence:
- highest pritority from 1 -255 (0 = never a DR)
- highest router ID
- highest IP address of a loopback or active interface in the absence
of a manually configured router ID. Loopback IP addresses take higher
precedence than other interfaces.
In this case routers R4 and R1 have the highest router priority.
Between the two, R3 has the higher router ID. Therefore, R4 will become
the DR and R1 will become the BDR.
210. By default, what is the OSPF cost for any link with a bandwidth of 100 Mb/s or greater?
Explanation: OSPF
uses the formula: Cost = 100,000,000 / bandwidth. Because OSPF will only
use integers as cost, any bandwidth of 100 Mb/s or greater will all
equal a cost of 1.
211. Refer to the exhibit. What is the OSPF cost to reach the router A LAN 172.16.1.0/24 from B?
Explanation: The formula used to calculate the OSPF cost is as follows:
Cost = reference bandwidth / interface bandwidth
The default reference bandwidth is 10^8 (100,000,000); therefore, the formula is
Cost = 100,000,000 bps / interface bandwidth in bps
Thus the cost to reach the A LAN 172.16.1.0/24 from B is as follows:
Serial link (1544 Kbps) from B to A cost => 100,000,000 / 1,544,000 = 64
Gigabit Ethernet link on A cost => 100,000,000 / 1,000,000,000 = 1
Total cost to reach 172.16.1.0/24 = 64 + 1 = 65
212. Refer to the exhibit. On which router or routers would a
default route be statically configured in a corporate environment that
uses single area OSPF as the routing protocol?
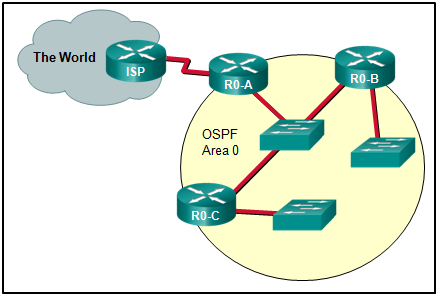
- R0-A
- ISP, R0-A, R0-B, and R0-C
- ISP
- R0-B and R0-C
- ISP and R0-A
- R0-A, R0-B, and R0-C
Explanation: The
default route is applied to the router that connects to the Internet, or
R0-A. R0-A then distributes that default route using the OSPF routing
protocol.
213. What command would be used to determine if a routing protocol-initiated relationship had been made with an adjacent router?
- ping
- show ip ospf neighbor
- show ip interface brief
- show ip protocols
Explanation: While the show ip interface brief and ping
commands can be used to determine if Layer 1, 2, and 3 connectivity
exists, neither command can be used to determine if a particular OSPF or
EIGRP-initiated relationship has been made. The show ip protocols
command is useful in determining the routing parameters such as timers,
router ID, and metric information associated with a specific routing
protocol. The show ip ospf neighbor command shows if two adjacent routers have exchanged OSPF messages in order to form a neighbor relationship.
214. Refer to the exhibit. Which command did an administrator issue to produce this output?

- R1# show ip ospf interface serial0/0/1
- R1# show ip route ospf
- R1# show ip ospf
- R1# show ip ospf neighbor
215. Which command is used to verify that OSPF is enabled and
also provides a list of the networks that are being advertised by the
network?
- show ip interface brief
- show ip ospf interface
- show ip protocols
- show ip route ospf
Explanation: The command show ip ospf interface verifies the active OSPF interfaces. The command show ip interface brief is used to check that the interfaces are operational. The command show ip route ospf displays the entries that are learned via OSPF in the routing table. The command show ip protocols checks that OSPF is enabled and lists the networks that are advertised.
216. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator has
configured OSPFv2 on the two Cisco routers but PC1 is unable to connect
to PC2. What is the most likely problem?
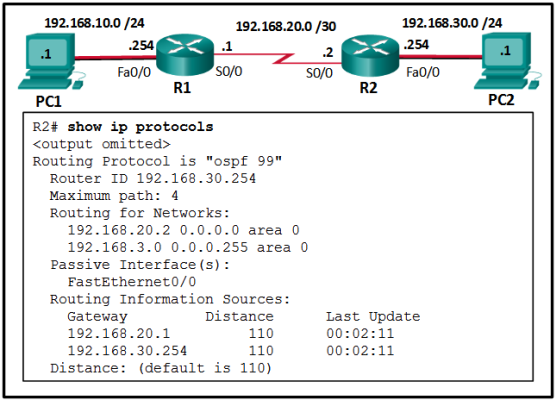
- Interface Fa0/0 has not been activated for OSPFv2 on router R2.
- Interface Fa0/0 is configured as a passive-interface on router R2.
- Interface S0/0 is configured as a passive-interface on router R2.
- Interface s0/0 has not been activated for OSPFv2 on router R2.
Explanation: If a
LAN network is not advertised using OSPFv2, a remote network will not be
reachable. The output displays a successful neighbor adjacency between
router R1 and R2 on the interface S0/0 of both routers.
217. What is the recommended Cisco best practice for
configuring an OSPF-enabled router so that each router can be easily
identified when troubleshooting routing issues?
- Configure a value using the router-id command.
- Use the highest active interface IP address that is configured on the router.
- Use a loopback interface configured with the highest IP address on the router.
- Use the highest IP address assigned to an active interface participating in the routing process.
Explanation: A
Cisco router is assigned a router ID to uniquely identify it. It can be
automatically assigned and take the value of the highest configured IP
address on any interface, the value of a specifically-configured
loopback address, or the value assigned (which is in the exact form of
an IP address) using the router-id command. Cisco recommends using the router-id command.
218. Which step in the link-state routing process is
described by a router running an algorithm to determine the best path to
each destination?
- load balancing equal-cost paths
- declaring a neighbor to be inaccessible
- choosing the best route
- executing the SPF algorithm
219. An administrator is configuring single-area OSPF on a
router. One of the networks that must be advertised is 192.168.223.0
255.255.254.0. What wildcard mask would the administrator use in the
OSPF network statement?
- 0.0.1.255
- 0.0.7.255
- 0.0.15.255
- 0.0.31.255
220. What is the format of the router ID on an OSPF-enabled router?
- a unique router host name that is configured on the router
- a unique phrase with no more than 16 characters
- a 32-bit number formatted like an IPv4 address
- an 8-bit number with a decimal value between 0 and 255
- a character string with no space
Explanation: A
router ID is a 32-bit number formatted like an IPv4 address and assigned
in order to uniquely identify a router among OSPF peers.
221. Question as presented:
DUAL is the algorithm used by EIGRP. In multiarea OSPF, OSPF is
implemented using multiple areas, and all of them must be connected to
the backbone area.
222. After modifying the router ID on an OSPF router, what is the preferred method to make the new router ID effective?
- HQ# copy running-config startup-config
- HQ# resume
- HQ# clear ip route *
- HQ# clear ip ospf process
Explanation: To modify a router-id on an OSPF-enabled router, it is necessary to reset the OSPF routing process by entering either the clear ip ospf process command or the reload command.
223. In an OSPFv2 configuration, what is the effect of entering the command network 192.168.1.1 0.0.0.0 area 0?
- It allows all 192.168.1.0 networks to be advertised.
- It tells the router which interface to turn on for the OSPF routing process.
- It changes the router ID of the router to 192.168.1.1.
- It enables OSPF on all interfaces on the router.
Explanation: Entering the command network 192.168.1.1 0.0.0.0 area 0
will turn on only the interface with that IP address for OSPF routing.
It does not change the router ID. Instead, OSPF will use the network
that is configured on that interface.
224. What is the reason for a network engineer to alter the default reference bandwidth parameter when configuring OSPF?
- to force that specific link to be used in the destination route
- to more accurately reflect the cost of links greater than 100 Mb/s
- to enable the link for OSPF routing
- to increase the speed of the link
Explanation: By
default, Fast Ethernet, Gigabit, and 10 Gigabit Ethernet interfaces all
have a cost of 1. Altering the default reference bandwidth alters the
cost calculation, allowing each speed to be more accurately reflected in
the cost.
225. Open the PT Activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then answer the question.
Which task has to be performed on Router 1 for it to establish an OSPF adjacency with Router 2?
- Issue the clear ip ospf process command.
- Change the subnet mask of interface FastEthernet 0/0 to 255.255.255.0.
- Remove the passive interface command from interface FastEthernet 0/0.
- Add the network 10.0.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 command to the OSPF process.
Explanation: Each
interface on the link connecting the OSPF routers must be in the same
subnet for an adjacency to be established. The IP address subnet mask on
FastEthernet interface 0/0 must be changed to 255.255.255.0. The
FastEthernet interface 0/0 is not passive. The 10.0.1.0/24 network is
only connected to Router2 so should not be advertised by Router1. The clear ip ospf process
command will start the OPSF process on Router1 but will not cause an
adjacency to be established if the subnet mask mismatch on the
connecting interfaces still exists.
226. Match the description to the term. (Not all options are used.)
 227. What is a benefit of multiarea OSPF routing?
227. What is a benefit of multiarea OSPF routing?
- Topology changes in one area do not cause SPF recalculations in other areas.
- Routers in all areas share the same link-state database and have a complete picture of the entire network.
- A backbone area is not required.
- Automatic route summarization occurs by default between areas.
Explanation: With
multiarea OSPF, only routers within an area share the same link-state
database. Changes to the network topology in one area do not impact
other areas, which reduces the number of SPF algorithm calculations and
the of link-state databases.
228. Match the OSPF state with the order in which it occurs. (Not all options are used.)
 229. What indicates to a link-state router that a neighbor is unreachable?
229. What indicates to a link-state router that a neighbor is unreachable?
- if the router no longer receives hello packets
- if the router receives an update with a hop count of 16
- if the router receives an LSP with previously learned information
- if the router no longer receives routing updates
Explanation: OSPF
routers send hello packets to monitor the state of a neighbor. When a
router stops receiving hello packets from a neighbor, that neighbor is
considered unreachable and the adjacency is broken.
230. Which three OSPF states are involved when two routers are forming an adjacency? (Choose three.)
- Exchange
- Init
- ExStart
- Two-way
- Loading
- Down
Explanation: OSPF
operation progresses through 7 states for establishing neighboring
router adjacency, exchanging routing information, calculating the best
routes, and reaching convergence. The Down, Init, and Two-way states are
involved in the phase of neighboring router adjacency establishment.
231. Refer to the exhibit. Suppose that routers B, C, and D
have a default priority, and router A has a priority 0. Which conclusion
can be drawn from the DR/BDR election process?
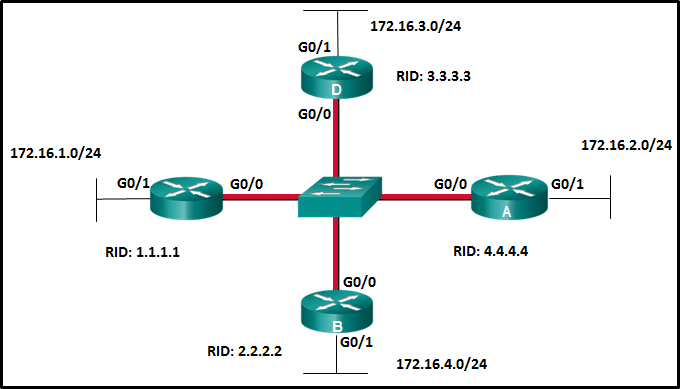
CCNA 3 v7 Modules 1 – 2: OSPF Concepts and Configuration Exam
- If the priority of router C is changed to 255, then it will become the DR.
- Router A will become the DR and router D will become the BDR.
- If the DR fails, the new DR will be router B.
- If a new router with a higher priority is added to this network, it will become the DR.
Explanation: If the
priority is set to 0, the router is not capable of becoming the DR, so
router A cannot be the DR. OSPF DR and BDR elections are not preemptive.
If a new router with a higher priority or higher router ID is added to
the network after the DR and BDR election, the newly added router does
not take over the DR or the BDR role.
232. An administrator is configuring single-area OSPF on a
router. One of the networks that must be advertised is 64.102.0.0
255.255.255.128. What wildcard mask would the administrator use in the
OSPF network statement?
- 0.0.31.255
- 0.0.0.63
- 0.0.63.255
- 0.0.0.127
1. Which design feature will limit the size of a failure domain in an enterprise network?
- the purchase of enterprise equipment that is designed for large traffic volume
- the installation of redundant power supplies
- the use of a collapsed core design
- the use of the building switch block approach
2. Which two things should a network administrator modify on a router to perform password recovery? (Choose two.)
- the system image file
- the NVRAM file system
- the configuration register value
- the startup configuration file
- system ROM
3. What type of network uses one common infrastructure to carry voice, data, and video signals?
- borderless
- converged
- managed
- switched
4. What are three advantages of using private IP addresses and NAT? (Choose three.)
- hides private LAN addressing from outside devices that are connected to the Internet
- permits LAN expansion without additional public IP addresses
- reduces CPU usage on customer routers
- creates multiple public IP addresses
- improves the performance of the router that is connected to the Internet
- conserves registered public IP addresses
5. Which two scenarios are examples of remote access VPNs? (Choose two.)
- All users at a large branch office can access company resources through a single VPN connection.
- A small branch office with three employees has a Cisco ASA that is used to create a VPN connection to the HQ.
- A toy manufacturer has a permanent VPN connection to one of its parts suppliers.
- A mobile sales agent is connecting to the company network via the Internet connection at a hotel.
- An employee who is working from home uses VPN client software on a laptop in order to connect to the company network.
6. What are three benefits of cloud computing? (Choose three.)
- It utilizes end-user clients to do a substantial amount of data preprocessing and storage.
- It uses open-source software for distributed processing of large datasets.
- It streamlines the IT operations of an organization by subscribing only to needed services.
- It enables access to organizational data anywhere and at any time.
- It turns raw data into meaningful information by discovering patterns and relationships.
- It eliminates or reduces the need for onsite IT equipment, maintenance, and management.
7. What is a characteristic of a single-area OSPF network?
- All routers share a common forwarding database.
- All routers have the same neighbor table.
- All routers are in the backbone area.
- All routers have the same routing table.
8. What is a WAN?
- a network infrastructure that spans a limited physical area such as a city
- a network infrastructure that provides access to other networks over a large geographic area
- a network infrastructure that provides access in a small geographic area
- a network infrastructure designed to provide data storage, retrieval, and replication
9. What is a purpose of establishing a network baseline?
- It creates a point of reference for future network evaluations.
- It provides a statistical average for network performance.
- It checks the security configuration of network devices.
- It manages the performance of network devices.
10. Which type of OSPF packet is used by a router to discover neighbor routers and establish neighbor adjacency?
- link-state update
- hello
- database description
- link-state request
11. Which two statements are characteristics of a virus? (Choose two.)
- A virus has an enabling vulnerability, a propagation mechanism, and a payload.
- A virus can be dormant and then activate at a specific time or date.
- A virus provides the attacker with sensitive data, such as passwords.
- A virus replicates itself by independently exploiting vulnerabilities in networks.
- A virus typically requires end-user activation.
12. Which public WAN access technology utilizes copper
telephone lines to provide access to subscribers that are multiplexed
into a single T3 link connection?
13. A customer needs a metropolitan area WAN connection that
provides high-speed, dedicated bandwidth between two sites. Which type
of WAN connection would best fulfill this need?
- packet-switched network
- Ethernet WAN
- circuit-switched network
- MPLS
14. A company has contracted with a network security firm to
help identify the vulnerabilities of the corporate network. The firm
sends a team to perform penetration tests to the company network. Why
would the team use debuggers?
- to detect installed tools within files and directories that provide
threat actors remote access and control over a computer or network
- to reverse engineer binary files when writing exploits and when analyzing malware
- to obtain specially designed operating systems preloaded with tools optimized for hacking
- to detect any evidence of a hack or malware in a computer or network
15. Consider the following output for an ACL that has been
applied to a router via the access-class in command. What can a network
administrator determine from the output that is shown?
R1#
Standard IP access list 2
10 permit 192.168.10.0, wildcard bits 0.0.0.255 (2 matches)
20 deny any (1 match)
- Two devices connected to the router have IP addresses of 192.168.10. x .
- Two devices were able to use SSH or Telnet to gain access to the router.
- Traffic from one device was not allowed to come into one router port and be routed outbound a different router port.
- Traffic from two devices was allowed to enter one router port and be routed outbound to a different router port.
16. What command would be used as part of configuring NAT or PAT to clear dynamic entries before the timeout has expired?
- clear ip dhcp
- clear ip nat translation
- clear access-list counters
- clear ip pat statistics
17. What are two characteristics of video traffic? (Choose two.)
- Video traffic consumes less network resources than voice traffic consumes.
- Video traffic latency should not exceed 400 ms.
- Video traffic is more resilient to loss than voice traffic is.
- Video traffic requires a minimum of 30 kbs of bandwidth.
- Video traffic is unpredictable and inconsistent.















































































