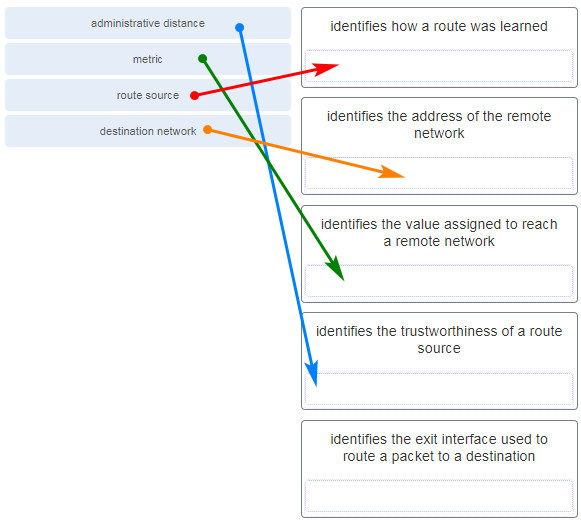
1. What additional information is contained in the 12-bit extended system ID of a BPDU?
7. In which two port states does a switch learn MAC addresses and process BPDUs in a PVST network? (Choose two.)
10. When the show spanning-tree vlan 33 command is issued on a switch, three ports are shown in the forwarding state. In which two port roles could these interfaces function while in the forwarding state? (Choose two.)
Which set of configuration commands issued on SW1 will successfully complete the EtherChannel link between SW1 and SW2?
SW1: on
SW2: on
SW1: desirable
SW2: desirable
SW1: auto
SW2: auto
trunking enabled on both switches
SW1: auto
SW2: auto
PortFast enabled on both switches
SW1: passive
SW2: active
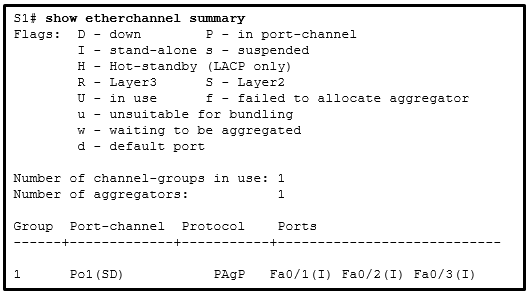
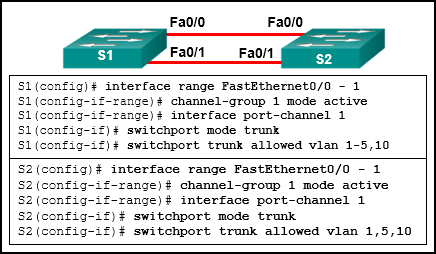
49. Refer to the exhibit. An EtherChannel was configured between switches S1 and S2, but the interfaces do not form an EtherChannel. What is the problem?
ip route 192.168.10.0 255.255.255.0 10.10.10.2 5
What does the 5 at the end of the command signify?
Gateway of last resort is not set
10.0.0.0/30 is subnetted, 2 subnets
C 10.0.0.0 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0
C 10.0.0.4 is directly connected, Serial0/0/1
192.168.10.0/26 is subnetted, 3 subnets
S 192.168.10.0 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0
C 192.168.10.64 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
S 192.168.10.128 [1/0] via 10.0.0.6
What will router R2 do with a packet destined for 192.168.10.129?
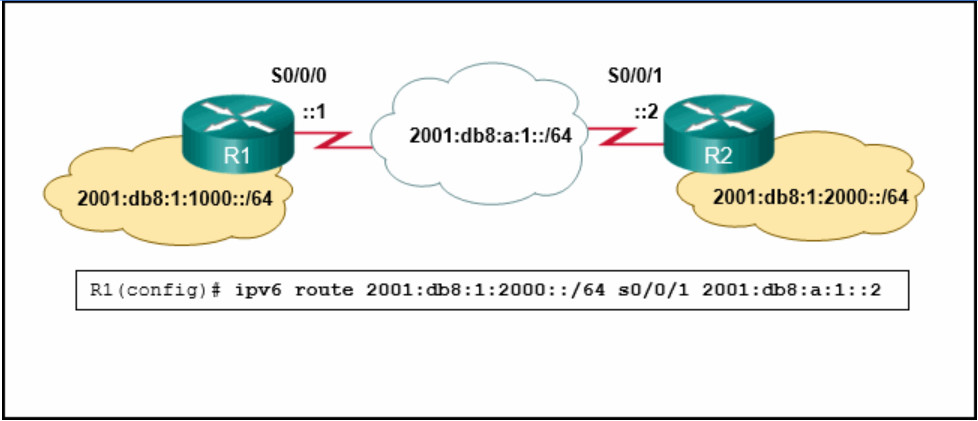
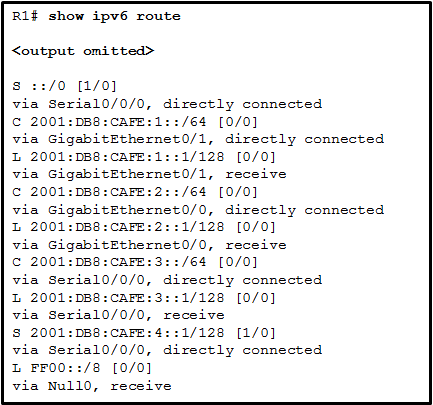
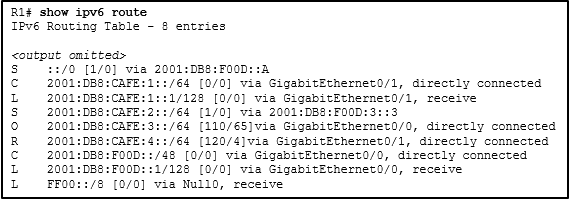
When an IPv6 static route is configured, the next-hop address can be ……
172.19.115.0/26 is variously subnetted, 7 subnets, 3 masks
O 172.19.115.0/26 [110/10] via 172.19.39.1, 00:00:24, Serial0/0/0
O 172.19.115.64/26 [110/20] via 172.19.39.6, 00:00:56, Serial 0/0/1
O 172.19.115.128/26 [110/10] via 172.19.39.1, 00:00:24, Serial 0/0/0
C 172.19.115.192/27 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
L 172.19.115.193/27 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
C 172.19.115.224/27 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
L 172.19.115.225/27 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
172.19.39.0/24 is variably subnetted, 4 subnets, 2 masks
C 172.19.39.0/30 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0
L 172.19.39.2/32 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0
C 172.19.39.4/30 is directly connected, Serial0/0/1
L 172.19.39.5/32 is directly connected, Serial0/0/1
S 172.19.40.0/26 [1/0] via 172.19.39.1, 00:00:24, Serial0/0/0
R1#
Refer to the exhibit. Which interface will be the exit interface to forward a data packet that has the destination IP address 172.19.115.206?
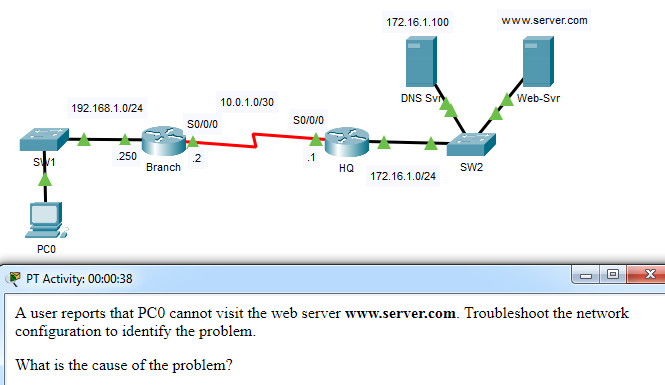 A user reports that PC0 cannot visit the web server
www.server.com. Troubleshoot the network configuration to identify the
problem.
A user reports that PC0 cannot visit the web server
www.server.com. Troubleshoot the network configuration to identify the
problem.
What is the cause of the problem?
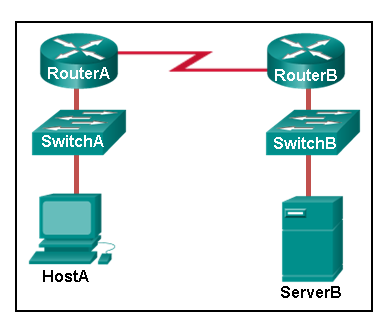
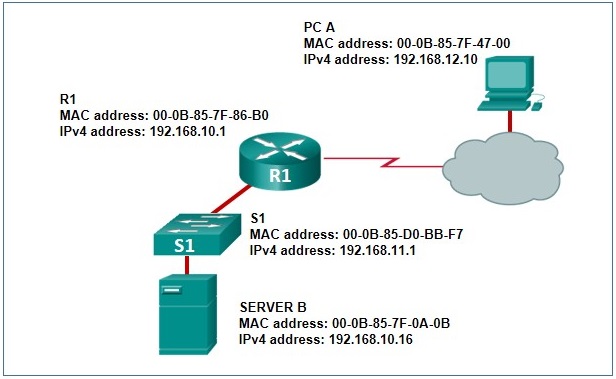
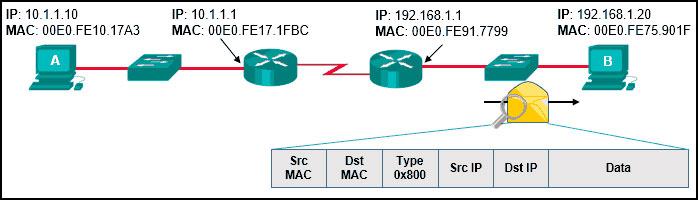
94. Refer to the exhibit. PC A sends a request to Server B. What IPv4 address is used in the destination field in the packet as the packet leaves PC A?


When an IPv6 static route is configured, it is first necessary to configure ……
A user reports that PC0 cannot visit the web server www.server.com. Troubleshoot the network configuration to identify the problem.
What is the cause of the problem?
In the 802.1X standard, the client attempting to access the network is referred to as the supplicant.
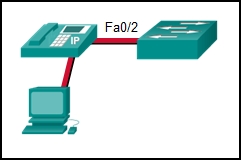
No one is allowed to disconnect the IP phone or the PC and connect some other wired device.
If a different device is connected, port Fa0/2 is shut down.
The switch should automatically detect the MAC address of the IP phone and the PC and add those addresses to the running configuration.
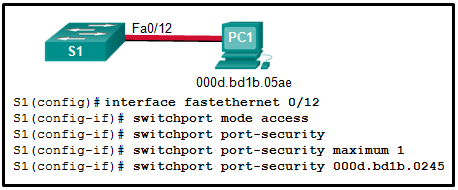
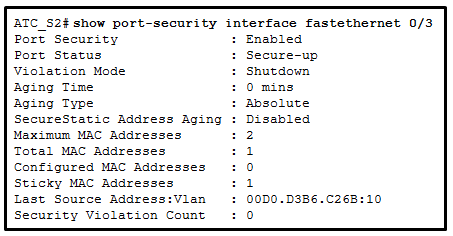
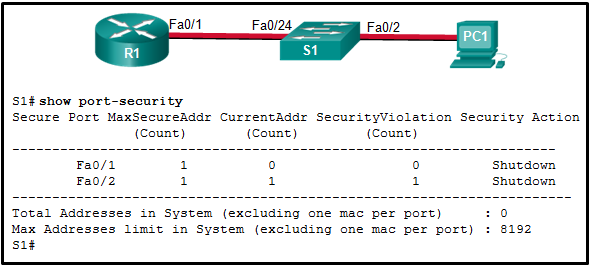
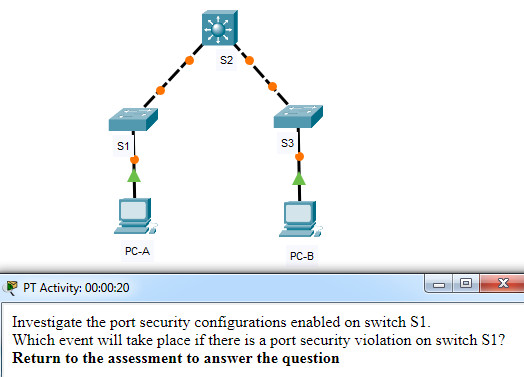 Which event will take place if there is a port security violation on switch S1 interface Fa0/1?
Which event will take place if there is a port security violation on switch S1 interface Fa0/1?
141. What are two protocols that are used by AAA to authenticate users against a central database of usernames and password? (Choose two.)
Destination address: 255.255.255.255
Client IPv4 address: 0.0.0.0
Default gateway address: 0.0.0.0
Subnet mask: 0.0.0.0
The DHCPDISCOVER message is used to identify any DHCP servers on a network. The DHCPOFFER message is used by a server to offer a lease to a client. The DHCPREQUEST message is used to identify both the specific DHCP server and the lease that the client is accepting.
The DHCPACK message is used by a server to finalize a successful lease with a client.
The DHCPNAK message is used when an offered lease is no longer valid.
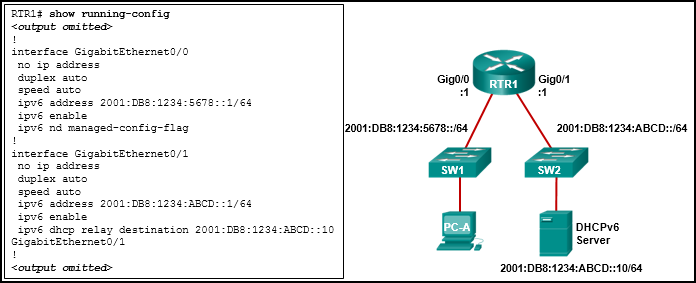
188. A network administrator configures a router to send RA messages with M flag as 0 and O flag as 1. Which statement describes the effect of this configuration when a PC tries to configure its IPv6 address?
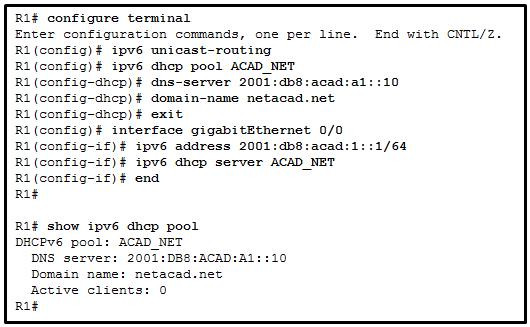
A stateless DHCPv6 client would send a DHCPv6 INFORMATION-REQUEST message as step 3 in the process.
192. A company uses the SLAAC method to configure IPv6 addresses for the employee workstations. Which address will a client use as its default gateway?

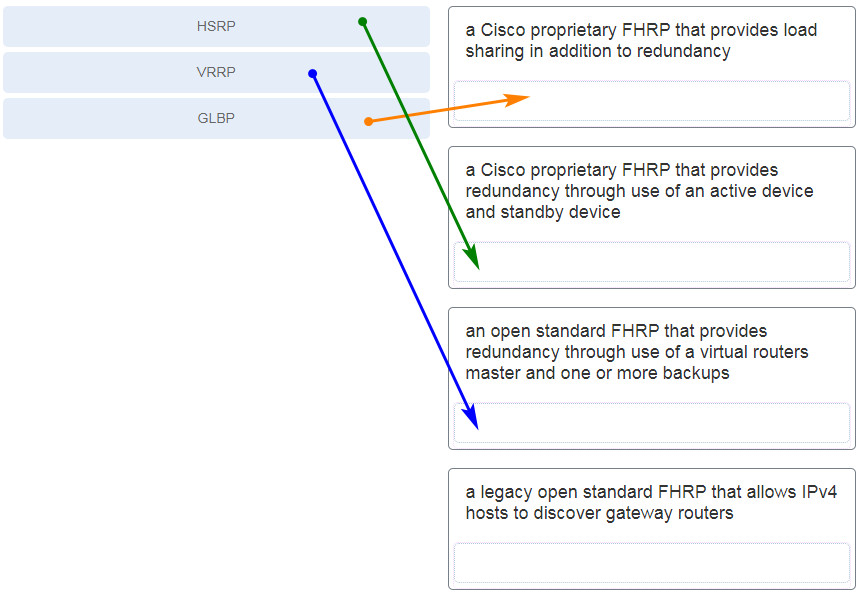
Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) is a Cisco-proprietary protocol that is designed to allow for transparent failover of a first-hop IPv4 device.
199. Which FHRP implementation is a Cisco-proprietary protocol that suppports IPv4 load sharing?
The broadcast DHCPDISCOVER message finds DHCPv4 servers on the network. When the DHCPv4 server receives a DHCPDISCOVER message, it reserves an available IPv4 address to lease to the client and sends the unicast DHCPOFFER message to the requesting client. When the client receives the DHCPOFFER from the server, it sends back a DHCPREQUEST. On receiving the DHCPREQUEST message the server replies with a unicast DHCPACK message. DHCPREPLY and DHCPINFORMATION-REQUEST are DHCPv6 messages.
202. After a host has generated an IPv6 address by using the DHCPv6 or SLAAC process, how does the host verify that the address is unique and therefore usable?
What is the keyword that is displayed on www.netacad.com?
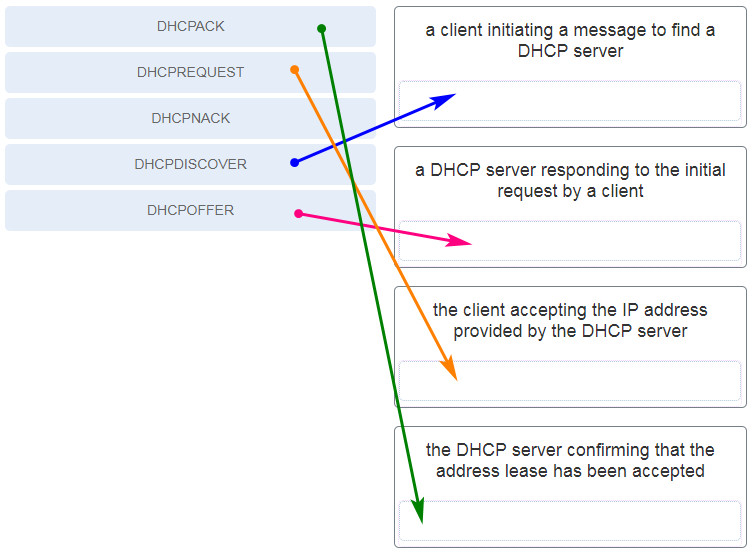
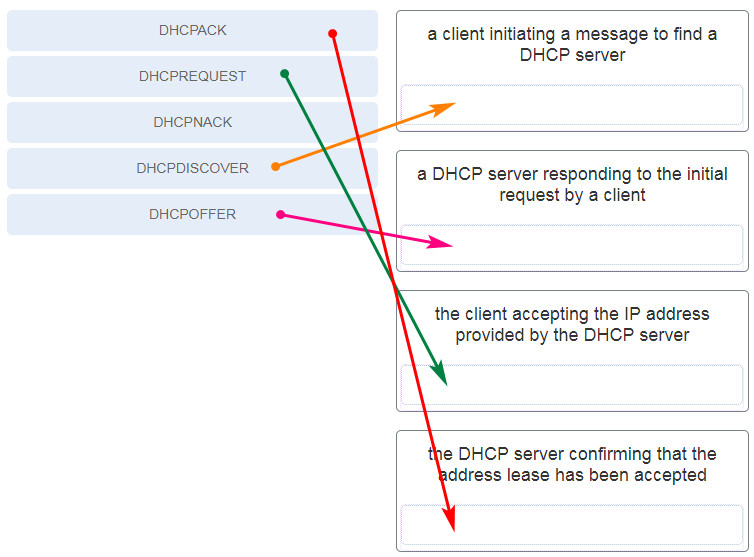
206. Match the purpose with its DHCP message type. (Not all options are used.)
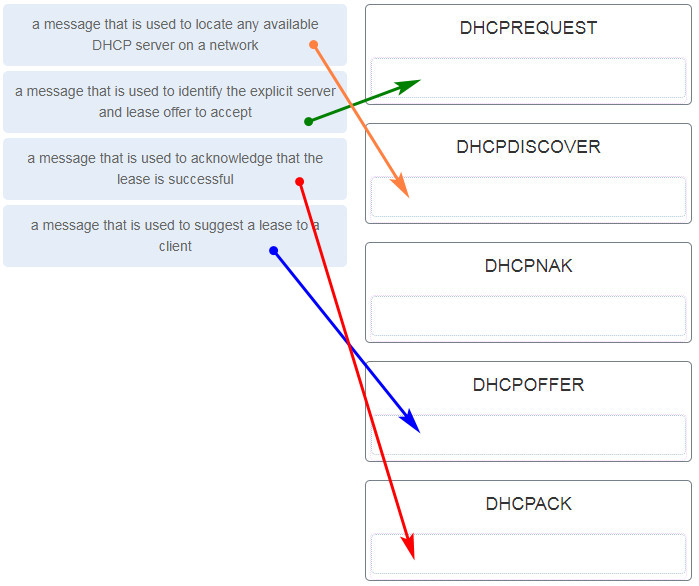
207. Match the DHCP message types to the order of the stateful DHCPv6 process when a client first connects to an IPv6 network. (Not all options are used.)
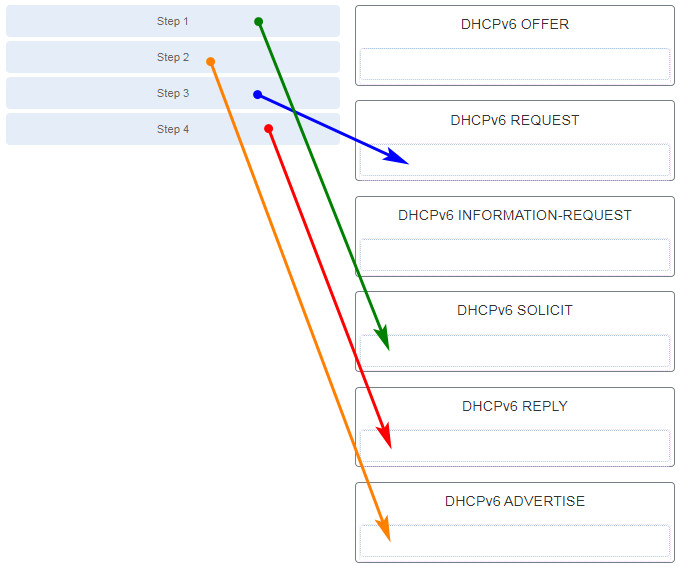
208. Match the step number to the sequence of stages that occur during the HSRP failover process. (Not all options are used.)
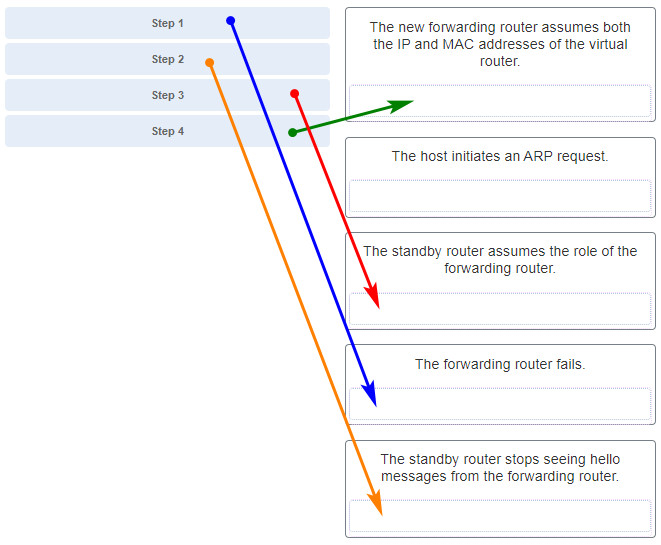
209. Match the FHRP protocols to the appropriate description. (Not all options are used.)
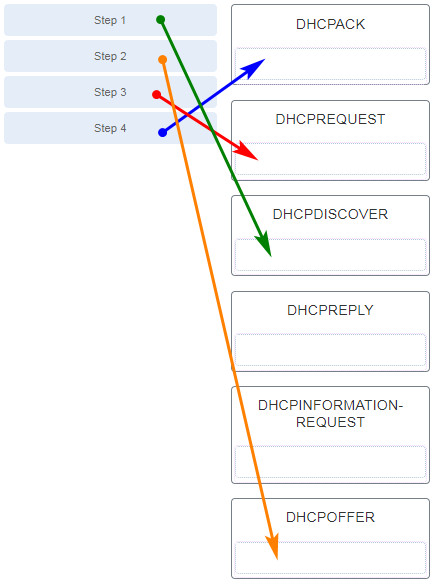
210. Match the DHCP message types to the order of the DHCPv4 process. (Not all options are used.)
211. The address pool of a DHCP server is configured with 192.168.234.0/27. The network administrator reserves 22 IP addresses for IP phones. How many IP addresses are left in the pool to be assigned to other hosts?
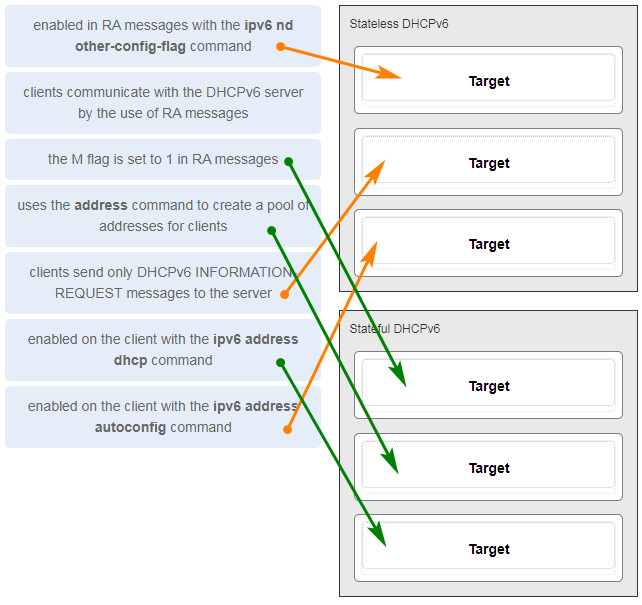
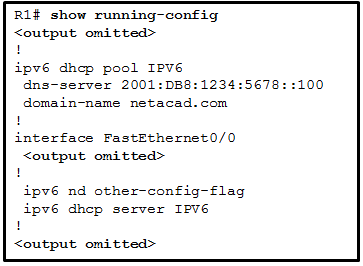
218. Refer to the exhibit. Based on the output that is shown, what kind of IPv6 addressing is being configured?

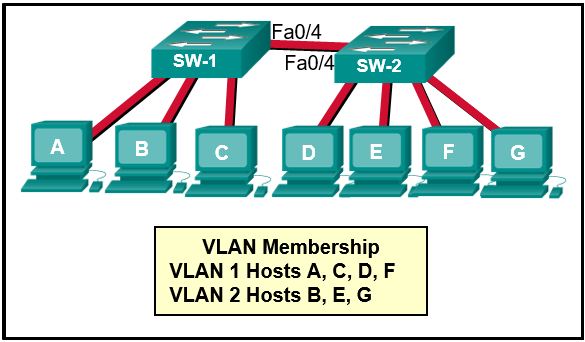
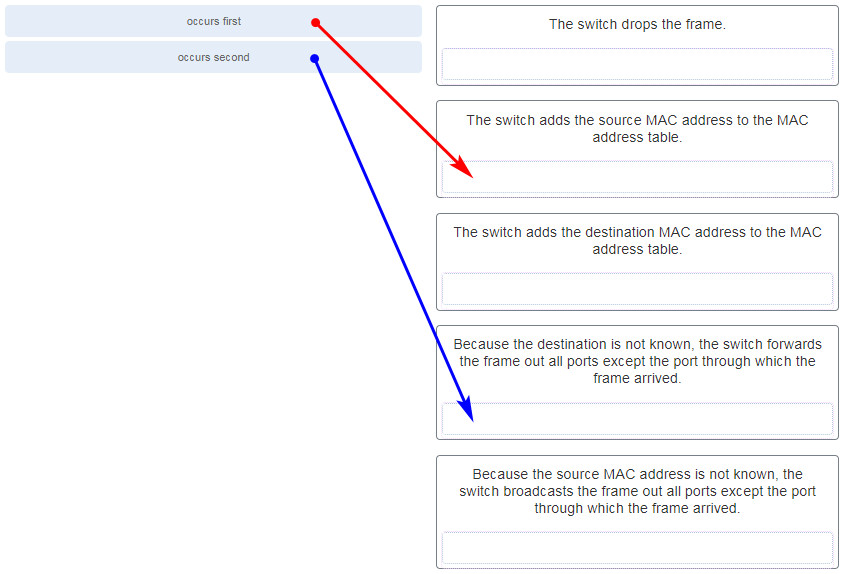 245. What information is added to the switch table from incoming frames?
245. What information is added to the switch table from incoming frames?
256. Refer to the exhibit. In what switch mode should port G0/1 be assigned if Cisco best practices are being used?
258. Port Fa0/11 on a switch is assigned to VLAN 30. If the
command no switchport access vlan 30 is entered on the Fa0/11 interface,
what will happen?
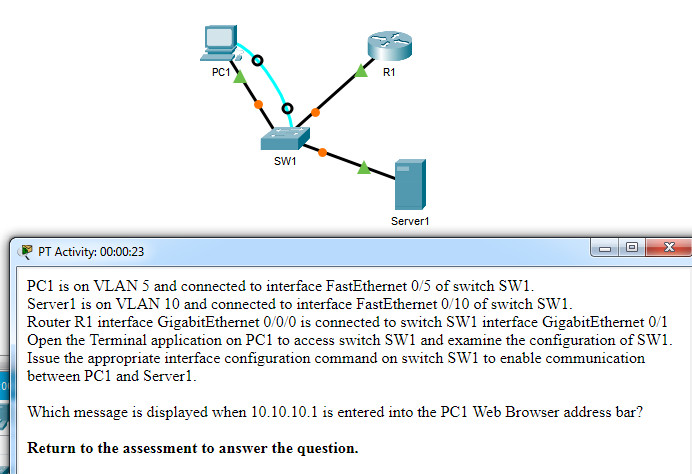
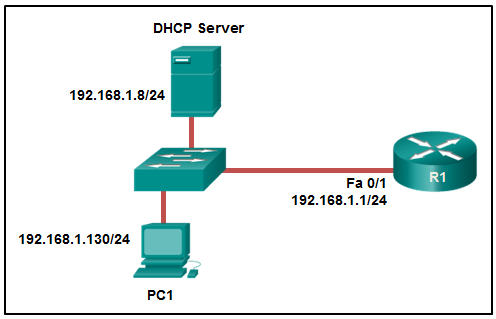
Which message is displayed when 10.10.10.1 is entered into the PC1 Web Browser address bar?
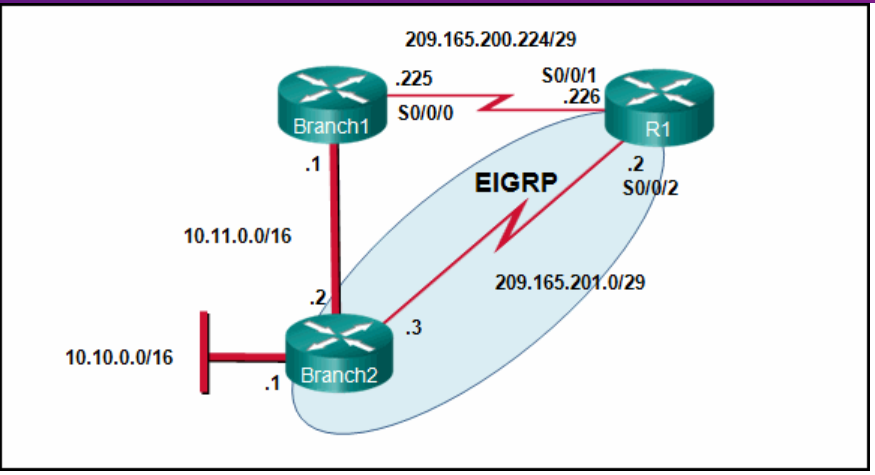
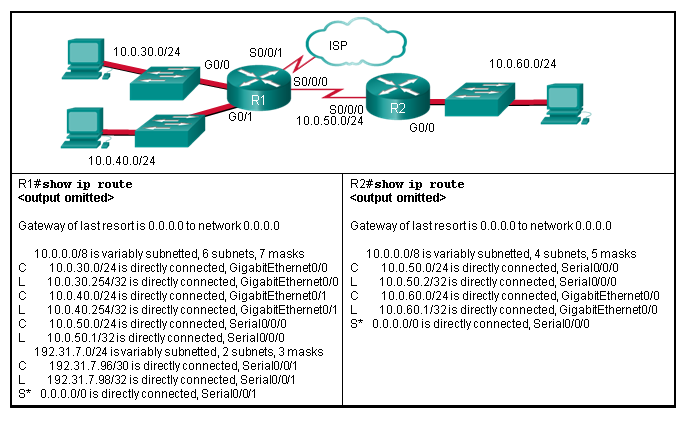
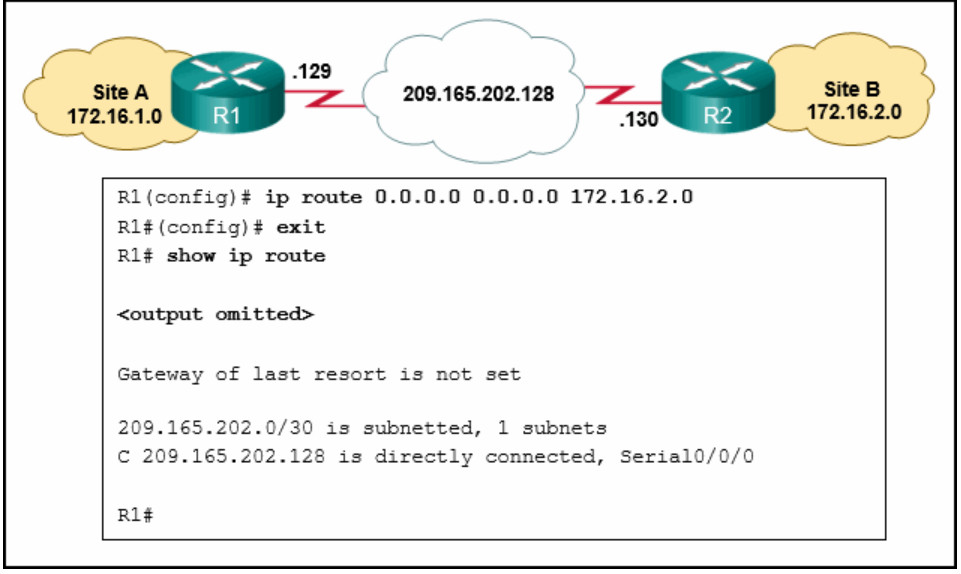
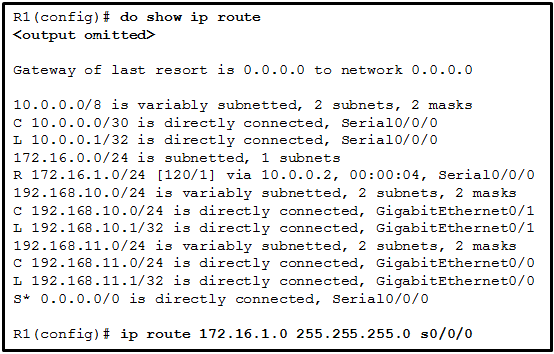
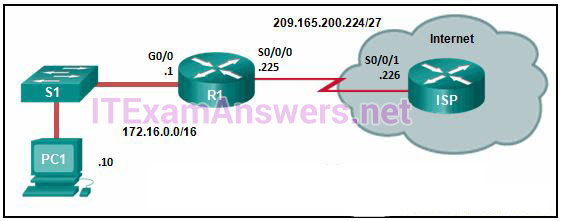 3. Refer to the exhibit. R1 was configured with the static
route command ip route 209.165.200.224 255.255.255.224 S0/0/0 and
consequently users on network 172.16.0.0/16 are unable to reach
resources on the Internet. How should this static route be changed to
allow user traffic from the LAN to reach the Internet?
3. Refer to the exhibit. R1 was configured with the static
route command ip route 209.165.200.224 255.255.255.224 S0/0/0 and
consequently users on network 172.16.0.0/16 are unable to reach
resources on the Internet. How should this static route be changed to
allow user traffic from the LAN to reach the Internet?
11. Which statement is correct about how a Layer 2 switch determines how to forward frames?
14.Refer to the exhibit. How is a frame sent from PCA forwarded to PCC if the MAC address table on switch SW1 is empty?
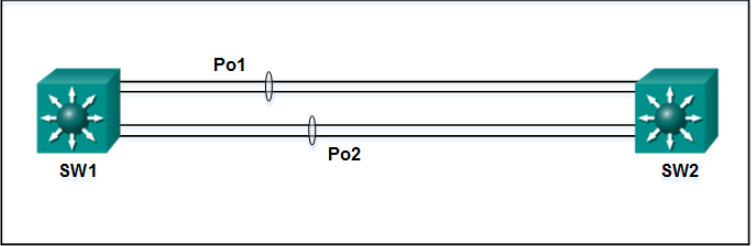
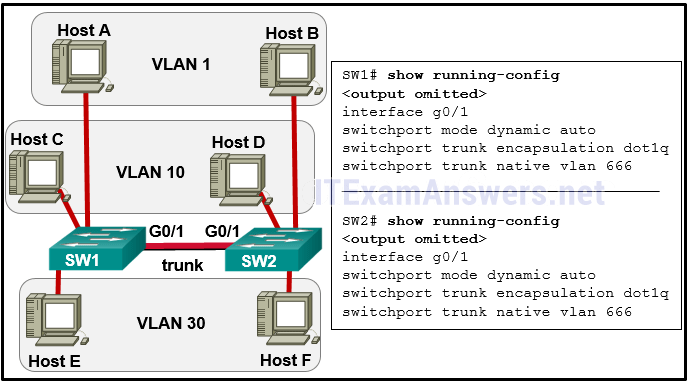
 17. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator has
connected two switches together using EtherChannel technology. If STP is
running, what will be the end result?
17. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator has
connected two switches together using EtherChannel technology. If STP is
running, what will be the end result?

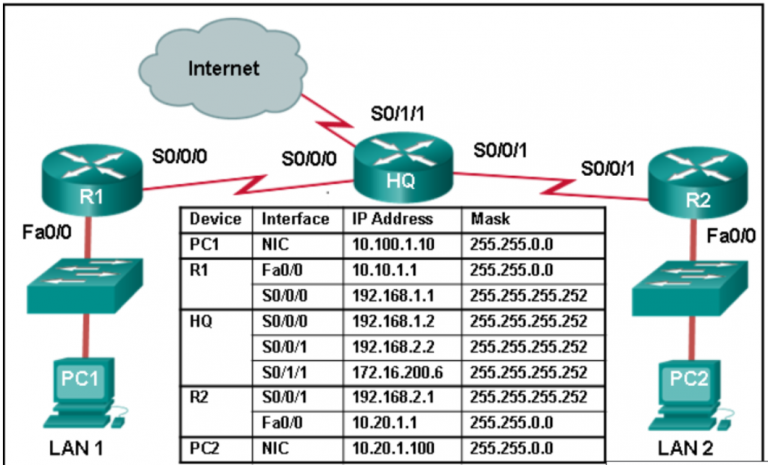

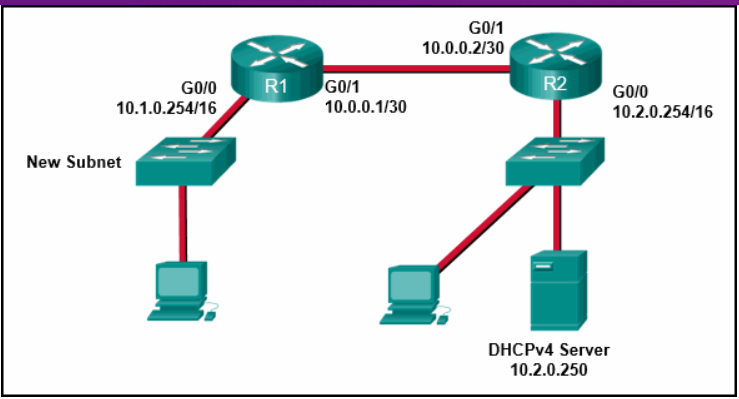 What two commands will allow hosts on the new subnet to receive addresses from the DHCP4 server? (Choose two.)
What two commands will allow hosts on the new subnet to receive addresses from the DHCP4 server? (Choose two.)
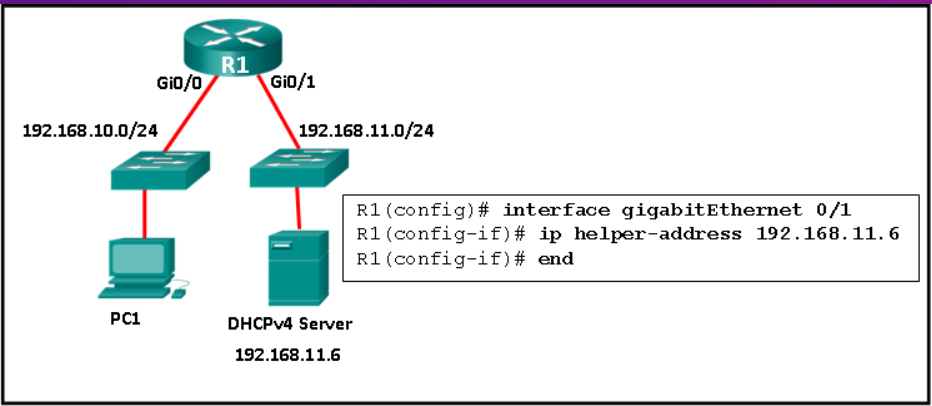
45. What two default wireless router settings can affect network security? (Choose two.)
46. What is the common term given to SNMP log messages that are generated by network devices and sent to the SNMP server?
52. Why is DHCP snooping required when using the Dynamic ARP Inspection feature?
(config)# interface gigabitethernet1/1
(config-if)# switchport mode trunk
(config)# interface gigabitethernet 1/1
(config-if)# no switchport
(config-if)# ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.252
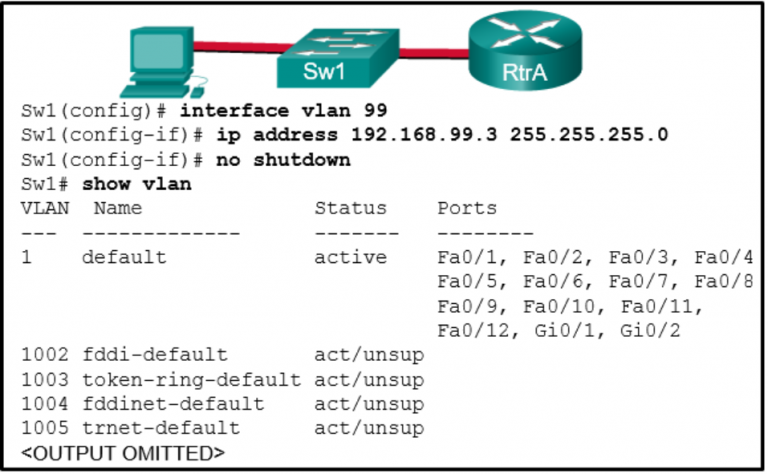
(config)# interface vlan 1
(config-if)# ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0
(config-if)# no shutdown
(config)# interface fastethernet0/4
(config-if)# switchport mode trunk
(config)# ip routing
58. A technician is troubleshooting a slow WLAN and decides to use the split-the-traffic approach. Which two parameters would have to be configured to do this? (Choose two.)


- MAC address
- VLAN ID
- IP address
- port ID
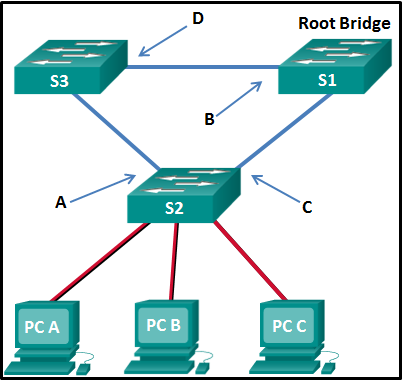
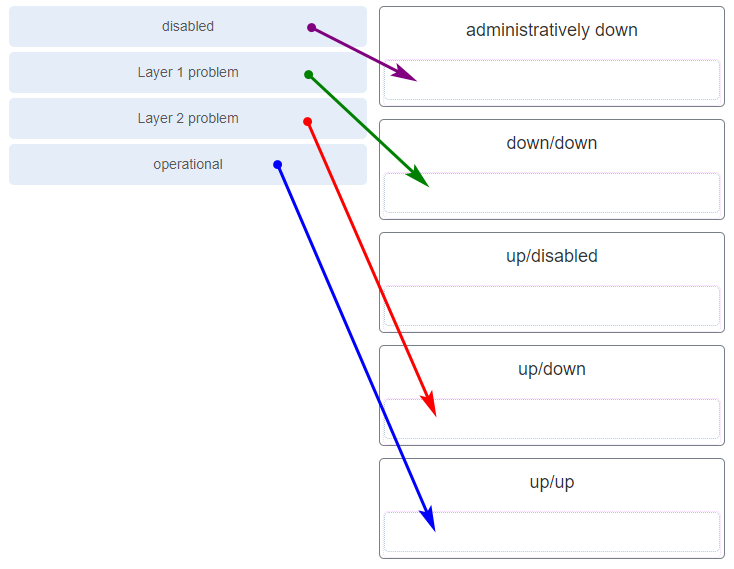
- Each switch with a lower root ID than its neighbor will not send BPDUs.
- All the switches send out BPDUs advertising themselves as the root bridge.
- Each switch determines the best path to forward traffic.
- Each switch determines what port to block to prevent a loop from occurring.
- designated port
- root port
- alternate
- disabled port
- bridge ID
- edge port
- extended system ID
- PortFast
- PVST+
- extended system ID
- cost
- IP address
- bridge priority
- MAC address
- port ID
7. In which two port states does a switch learn MAC addresses and process BPDUs in a PVST network? (Choose two.)
- disabled
- forwarding
- listening
- blocking
- learning
- lowest MAC address
- lowest IP address
- highest IP address
- highest MAC address
10. When the show spanning-tree vlan 33 command is issued on a switch, three ports are shown in the forwarding state. In which two port roles could these interfaces function while in the forwarding state? (Choose two.)
- alternate
- designated
- disabled
- blocked
- root
- It decreases the size of the failure domain to contain the impact of failures.
- It protects the edge of the enterprise network from malicious activity.
- It combines multiple switch trunk links to act as one logical link for increased bandwidth.
- It disables redundant paths to eliminate Layer 2 loops.
- It is enabled by default on Cisco switches.
- It is used to discover information about an adjacent Cisco device.
- It has a TTL mechanism that works at Layer 2.
- It prevents propagation of Layer 2 broadcast frames.
- PVST+
- 802.1D
- MST
- Rapid PVST
- creates smaller collision domains
- prevents routing loops on a router
- prevents Layer 2 loops
- allows Cisco devices to exchange routing table updates
- creates smaller broadcast domains
- the path cost
- the highest MAC address of all the ports in the switch
- the lowest MAC address of all the ports in the switch
- the VTP revision number
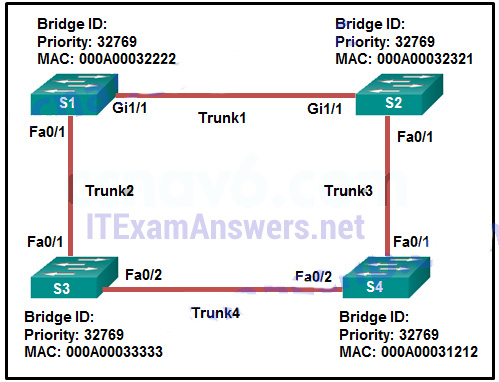
- S1
- S2
- S3
- S4
- The MAC address table becomes unstable.
- The switch acts like a hub.
- Port security becomes unstable.
- Broadcast frames are transmitted indefinitely.
- Port security shuts down all of the ports that have attached devices.
- 1
- 28672
- 32768
- 34816
- 61440
- Traffic cannot be sent to two different switches through the same EtherChannel link.
- Traffic cannot be sent to two different switches, but only to two different devices like an EtherChannel-enabled server and a switch.
- Traffic can only be sent to two different switches if EtherChannel is implemented on Gigabit Ethernet interfaces.
- Traffic can only be sent to two different switches if EtherChannel is implemented on Layer 3 switches.
- It requires full duplex.
- It increases the number of ports that are participating in spanning tree.
- It requires more physical links than LACP does.
- It mandates that an even number of ports (2, 4, 6, etc.) be used for aggregation.
- It is Cisco proprietary.
- All the interfaces need to work at the same speed.
- All interfaces need to be assigned to different VLANs.
- Different allowed ranges of VLANs must exist on each end.
- All the interfaces need to be working in the same duplex mode.
- The interfaces that are involved need to be contiguous on the switch.
- The EtherChannel bundle is down.
- Two Gigabit Ethernet ports are used to form the EtherChannel.
- A Cisco proprietary protocol was used to negotiate the EtherChannel link.
- The EtherChannel bundle is operating at both Layer 2 and Layer 3.
- port ID
- PAgP mode
- MAC address
- speed
- VLAN information
- The EtherChannel is established after SW2 initiates the link request.
- The EtherChannel is established after SW1 initiates the link request.
- The EtherChannel is established without negotiation.
- The EtherChannel fails to establish.
- Configure SW2 EtherChannel mode to desirable.
- Configure SW2 EtherChannel mode to on.
- Configure SW1 EtherChannel mode to on.
- Configure SW2 EtherChannel mode to auto.
- The remaining two interfaces continue to load balance traffic.
- The remaining two interfaces become separate links between the two switches.
- One interface becomes an active link for data traffic and the other becomes a backup link.
- The EtherChannel fails.
- SW2(config-if-range)# channel-group 1 mode passive
- SW2(config-if-range)# channel-group 1 mode desirable
- SW2(config-if-range)# channel-group 1 mode on
- SW2(config-if-range)# channel-group 1 mode active
- PAgP
- LACP
- Multilink PPP
- DTP
- The allowed range of VLANs must be the same on both switches.
- The participating interfaces must be assigned the same VLAN number on both switches.
- The participating interfaces must be physically contiguous on a switch.
- The participating interfaces must be on the same module on a switch.
- It allows directly connected switches to negotiate an EtherChannel link.
- It eliminates the need for configuring trunk interfaces when deploying VLANs on multiple switches.
- It decreases the amount of configuration that is needed on a switch.
- It provides a simulated environment for testing link aggregation.
- It allows the use of multivendor devices.
- LACP allows Fast Ethernet and Gigabit Ethernet interfaces to be mixed within a single EtherChannel.
- root port
- designated port
- alternate port
- disabled
- Spanning Tree Protocol views the physical links in an EtherChannel as one logical connection.
- Load balancing occurs between links configured as different EtherChannels.
- Configuring the EtherChannel interface provides consistency in the configuration of the physical links.
- Spanning Tree Protocol ensures redundancy by transitioning failed interfaces in an EtherChannel to a forwarding state.
- EtherChannel uses upgraded physical links to provide increased bandwidth.

Modules 5 – 6: Redundant Networks Exam 33
- alternate, designated, root, root
- designated, alternate, root, root
- alternate, root, designated, root
- designated, root, alternate, root
- trunking
- HSRP
- PortFast
- EtherChannel
- auto
- on
- off
- desirable
Which set of configuration commands issued on SW1 will successfully complete the EtherChannel link between SW1 and SW2?
CCNA-2-v7-Modules 5 – 6 Redundant Networks Exam 36
- interface GigabitEthernet0/1
no shutdown - interface Port-channel 1
no shutdown - interface GigabitEthernet0/2
channel-group 2 mode desirable - interface GigabitEthernet0/1
channel-group 1 mode desirable
- 65535
- 4096
- 32768
- 61440
- learning
- forwarding
- disabled
- listening
- blocking
- designated port
- disabled port
- root port
- non-designated port
- root port
- designated port
- alternate port
- disabled
- extended system ID
- port ID
- bridge priority
- bridge ID
- root bridge
- root port
- designated port
- alternate port
- bridge priority
- MAC Address
- extended system ID
- bridge ID
- EtherChannel operates only at Layer 2.
- PAgP cannot be used in conjunction with EtherChannel.
- A trunked port can be part of an EtherChannel bundle.
- EtherChannel can support up to a maximum of ten separate links.

CCNA2 v7 SRWE – Modules 5 – 6 Redundant Networks Exam Answers
- The EtherChannel is suspended.
- The EtherChannel is not functional.
- The port aggregation protocol PAgP is misconfigured.
- FastEthernet ports Fa0/1, Fa0/2, and Fa0/3 do not join the EtherChannel.
- It can combine up to a maximum of 4 physical links.
- It can bundle mixed types of 100 Mb/s and 1Gb/s Ethernet links.
- It consists of multiple parallel links between a switch and a router.
- It is made by combining multiple physical links that are seen as one link between two switches.
- on
- desirable
- active
- auto
- passive
SW1: on
SW2: on
SW1: desirable
SW2: desirable
SW1: auto
SW2: auto
trunking enabled on both switches
SW1: auto
SW2: auto
PortFast enabled on both switches
SW1: passive
SW2: active
49. Refer to the exhibit. An EtherChannel was configured between switches S1 and S2, but the interfaces do not form an EtherChannel. What is the problem?

CCNA2 v7 SRWE – Modules 5 – 6 Redundant Networks Exam Answers 50
- The interface port-channel number has to be different on each switch.
- The switch ports were not configured with speed and duplex mode.
- The switch ports have to be configured as access ports with each port having a VLAN assigned.
- The EtherChannel was not configured with the same allowed range of VLANs on each interface.
- active
- auto
- on
- desirable
- combination of source port and IP to destination port and IP
- source IP to destination IP
- source port to destination port
- combination of source MAC and IP to destination MAC and IP
- source MAC to destination MAC
- STP
- Rapid PVST+
- PVST+
- MST
- Routers will take over the forwarding of frames as switches become congested.
- New traffic is discarded by the switch because it is unable to be processed.
- CSMA/CD will cause each host to continue transmitting frames.
- ARP broadcast requests are returned to the transmitting host.
- static default routes
- implementing VLANs to contain broadcasts
- redundant links between Layer 2 switches
- link-state dynamic routing that provides redundant routes
- removing single points of failure with multiple Layer 2 switches
- Spanning Tree Protocol will transition the failed physical interface into forwarding mode.
- Spanning Tree Protocol will recalculate the remaining trunk links.
- The EtherChannel will transition to a down state.
- The EtherChannel will remain functional.
- next-hop
- gateway of last resort
- route source
- outgoing interface
- Static routing does not advertise over the network, thus providing better security.
- Configuration of static routes is error-free.
- Static routes scale well as the network grows.
- Static routing typically uses less network bandwidth and fewer CPU operations than dynamic routing does.
- The path a static route uses to send data is known.
- No intervention is required to maintain changing route information.
- to maintain routing tables
- to assure low router overhead
- to avoid exposing network information
- to discover the network
- to choose the path that is specified by the administrator
- easier to implement
- more secure in controlling routing updates
- fewer router resource overhead requirements
- ability to actively search for new routes if the current path becomes unavailable
- The static route is removed from the routing table.
- The router polls neighbors for a replacement route.
- The router automatically redirects the static route to use another interface.
- The static route remains in the table because it was defined as static.
- It uses a single network address to send multiple static routes to one destination address.
- It identifies the gateway IP address to which the router sends all IP packets for which it does not have a learned or static route.
- It backs up a route already discovered by a dynamic routing protocol.
- It is configured with a higher administrative distance than the original dynamic routing protocol has.
- in an organization where routers suffer from performance issues
- on a stub network that has a single exit point
- in an organization with a smaller network that is not expected to grow in size
- on a network where there is a lot of topology changes
- C 192.168.10.0/30 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
- O 10.1.1.0/24 [110/65] via 192.168.200.2, 00:01:20, Serial0/1/0
- S* 0.0.0.0/0 [1/0] via 172.16.1.1
- S 10.1.0.0/16 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0

- 120
- 110
- 1
- 4
- administrative distance
- metric
- outgoing interface
- routing protocol
- The interface fa0/0 has not been activated.
- No packets with a destination network of 172.16.1.0 have been sent to R1.
- The configuration needs to be saved first.
- The subnet mask is incorrect for the IPv4 address.

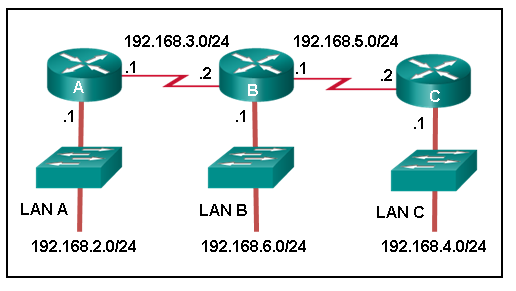
- A(config)# ip route 192.168.3.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.3.1
- A(config)# ip route 192.168.3.2 255.255.255.0 192.168.4.0
- A(config)# ip route 192.168.4.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.5.2
- A(config)# ip route 192.168.5.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.3.2
- A(config)# ip route 192.168.4.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.3.2
- any router where a backup route to dynamic routing is needed for reliability
- the router that serves as the gateway of last resort
- any router running an IOS prior to 12.0
- stub router connection to the rest of the corporate or campus network
- edge router connection to the ISP

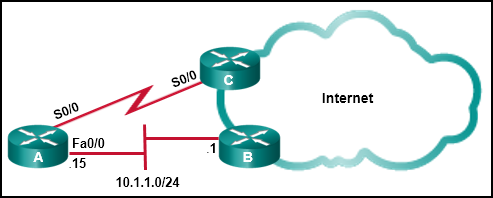
- Create a static route pointing to 10.1.1.1 with an AD of 95.
- Create a fully specified static route pointing to Fa0/0 with an AD of 1.
- Create a fully specified static route pointing to Fa0/0 with an AD of 95.
- Create a static route pointing to 10.1.1.1 with an AD of 1.
- Create a static route pointing to Fa0/0 with an AD of 1.
- When it is configured, it creates a gateway of last resort.
- It is used to provide load balancing between static routes.
- It is simply a static route with 0.0.0.0/0 as the destination IPv4 address.
- It is configured with a higher administrative distance than the original dynamic routing protocol has.
- FFFF::/128
- ::1/64
- ::/128
- ::/0
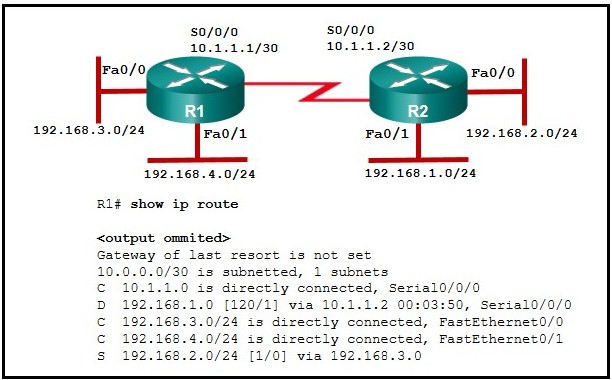
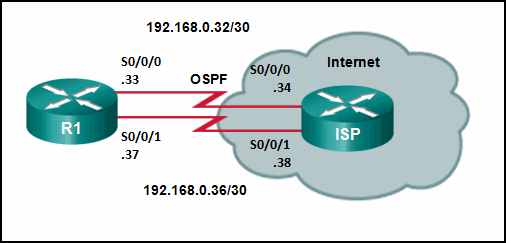
ip route 192.168.10.0 255.255.255.0 10.10.10.2 5
What does the 5 at the end of the command signify?
- exit interface
- maximum number of hops to the 192.168.10.0/24 network
- metric
- administrative distance
Gateway of last resort is not set
10.0.0.0/30 is subnetted, 2 subnets
C 10.0.0.0 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0
C 10.0.0.4 is directly connected, Serial0/0/1
192.168.10.0/26 is subnetted, 3 subnets
S 192.168.10.0 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0
C 192.168.10.64 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
S 192.168.10.128 [1/0] via 10.0.0.6
What will router R2 do with a packet destined for 192.168.10.129?

- send the packet out interface FastEthernet0/0
- send the packet out interface Serial0/0/1
- drop the packet
- send the packet out interface Serial0/0/0
- 0
- 1
- 32
- 100

- R1(config)# ipv6 route 2001:db8:32::/64 G0/0
- R1(config)# ipv6 route ::/0 G0/0 fe80::2
- R1(config)# ipv6 route 2001:db8:32::/64 G0/1 fe80::2
- R1(config)# ipv6 route ::/0 G0/1 fe80::2

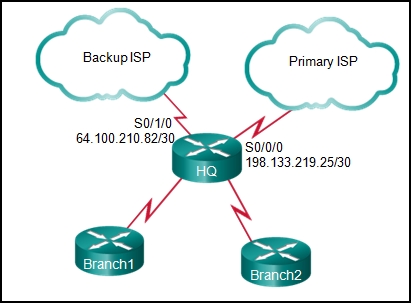
- ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 s0/0/0
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 s0/1/0 - ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 s0/0/0
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 s0/1/0 10 - ip route 198.133.219.24 255.255.255.252
ip route 64.100.210.80 255.255.255.252 10 - ip route 198.133.219.24 255.255.255.252
ip route 64.100.210.80 255.255.255.252

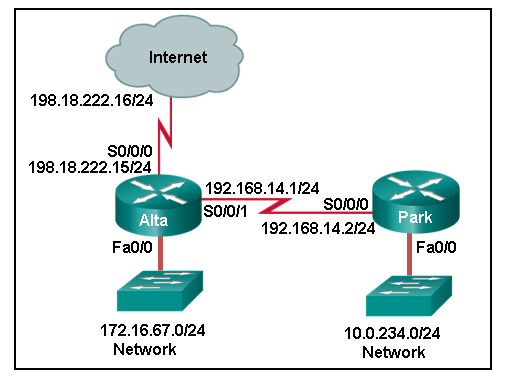
- Park(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.14.1
Alta(config)# ip route 10.0.234.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.14.2
Alta(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 s0/0/0 - Park(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.14.1
Alta(config)# ip route 10.0.234.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.14.2
Alta(config)# ip route 198.18.222.0 255.255.255.255 s0/0/0 - Park(config)# ip route 172.16.67.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.14.1
Park(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.14.1
Alta(config)# ip route 10.0.234.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.14.2 - Park(config)# ip route 172.16.67.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.14.1
Alta(config)# ip route 10.0.234.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.14.2
Alta(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 s0/0/1

- R1 needs a static route to the R2 LAN.
- R2 needs a static route to the R1 LANs.
- R1 needs a default route to R2.
- R2 needs a static route to the Internet.
- R1 and R2 must use a dynamic routing protocol.

- The next hop address is incorrect.
- The interface is incorrect.
- The destination network is incorrect.
- The network prefix is incorrect.

- The route was dynamically created by router R1.
- The route was dynamically learned from another router.
- The route was manually entered by an administrator.
- The route was automatically installed when an IP address was configured on an active interface.

- A packet with the destination IP address of RouterA.
- A frame with the destination MAC address of SwitchA.
- A packet with the destination IP address of ServerB.
- A frame with the destination MAC address of RouterA.
- A frame with the destination MAC address of ServerB.
- A packet with the destination IP address of RouterB.

- There is no gateway of last resort at R1.
- The static route for 192.168.2.0 is incorrectly configured.
- A default route is not configured on R1.
- The serial interface between the two routers is down.

- The netmask is incorrect.
- The exit interface is missing.
- The next hop address is incorrect.
- The destination network is incorrect.
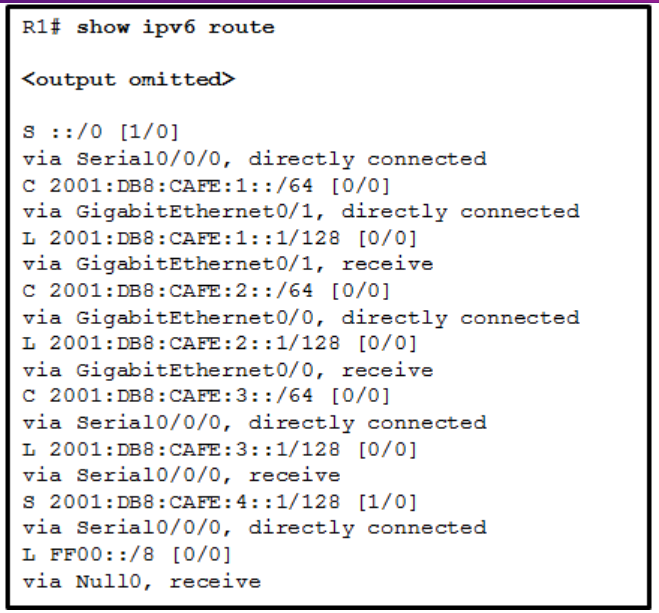
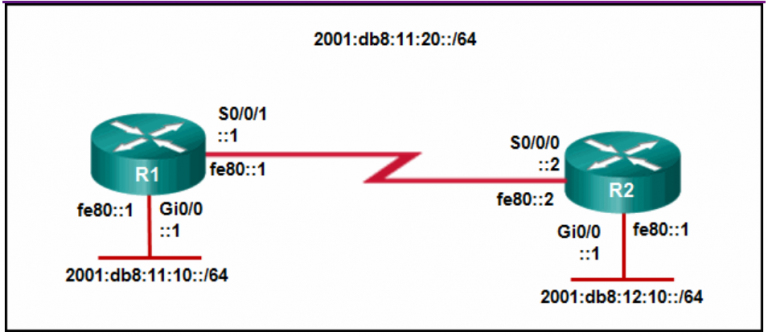
When an IPv6 static route is configured, the next-hop address can be ……
- a destination host route with a /128 prefix.
- the “show ipv6 route static” command.
- an IPv6 link-local address on the adjacent router.
- the interface type and interface number.
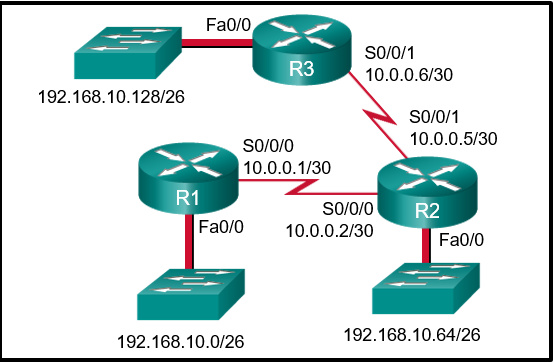
172.19.115.0/26 is variously subnetted, 7 subnets, 3 masks
O 172.19.115.0/26 [110/10] via 172.19.39.1, 00:00:24, Serial0/0/0
O 172.19.115.64/26 [110/20] via 172.19.39.6, 00:00:56, Serial 0/0/1
O 172.19.115.128/26 [110/10] via 172.19.39.1, 00:00:24, Serial 0/0/0
C 172.19.115.192/27 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
L 172.19.115.193/27 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
C 172.19.115.224/27 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
L 172.19.115.225/27 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
172.19.39.0/24 is variably subnetted, 4 subnets, 2 masks
C 172.19.39.0/30 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0
L 172.19.39.2/32 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0
C 172.19.39.4/30 is directly connected, Serial0/0/1
L 172.19.39.5/32 is directly connected, Serial0/0/1
S 172.19.40.0/26 [1/0] via 172.19.39.1, 00:00:24, Serial0/0/0
R1#
Refer to the exhibit. Which interface will be the exit interface to forward a data packet that has the destination IP address 172.19.115.206?
- GigabitEthernet0/1
- None, the packet will be dropped.
- GigabitEthernet0/0
- Serial0/0/1

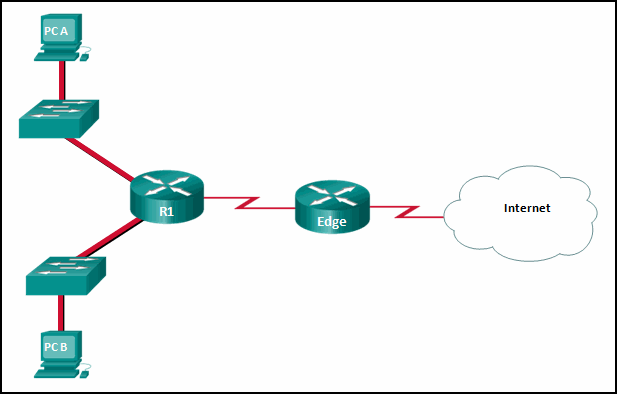
- Configure a dynamic routing protocol between R1 and Edge and advertise all routes.
- Configure a static route from R1 to Edge and a dynamic route from Edge to R1.
- Configure a static default route from R1 to Edge, a default route from Edge to the Internet, and a static route from Edge to R1.
- Configure a dynamic route from R1 to Edge and a static route from Edge to R1.

- The 172.16.1.0 static route would be entered into the running-config but not shown in the routing table.
- The 172.16.1.0 route learned from RIP would be replaced with the 172.16.1.0 static route.
- The 0.0.0.0 default route would be replaced with the 172.16.1.0 static route.
- The 172.16.1.0 static route is added to the existing routes in the routing table.
- the interface ID of the next-hop neighbor
- the interface ID exit interface
- the IP address of the exit interface
- the IP address of the next-hop neighbor
- the administrative distance for the destination network

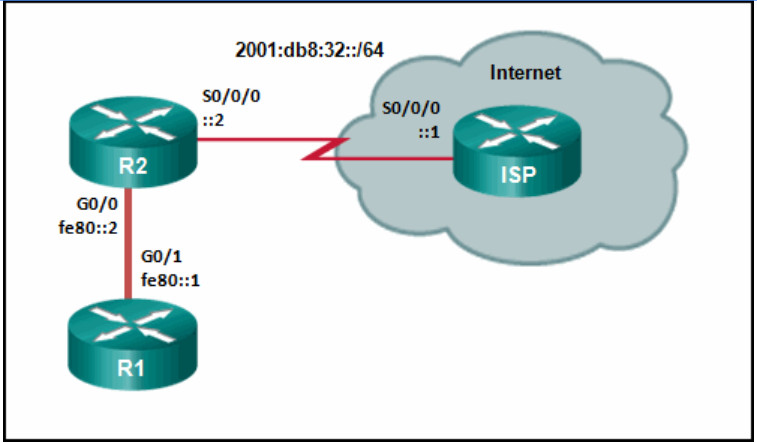
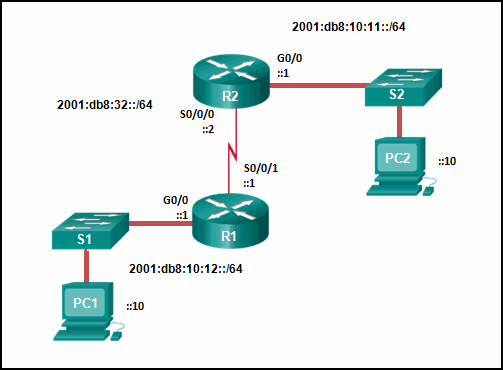
- R2(config)# ipv6 route ::/0 2001:db8:32::1
- R2(config)# ipv6 route 2001:db8:10:12::/64 S0/0/0
- R2(config)# ipv6 route 2001:db8:10:12::/64 2001:db8:32::1
- R2(config)# ipv6 route 2001:db8:10:12::/64 S0/0/1

- ip route 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0 s0/0/0
- ip route 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0 s0/0/0 121
- ip route 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0 s0/0/0 111
- ip route 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0 s0/0/0 91

Modules 14 – 16: Routing Concepts and Configuration Exam
What is the cause of the problem?
- The clock rate on one of the serial links is configured incorrectly.
- A serial interface on Branch is configured incorrectly.
- The DNS server address on PC0 is configured incorrectly.
- Routing between HQ and Branch is configured incorrectly.

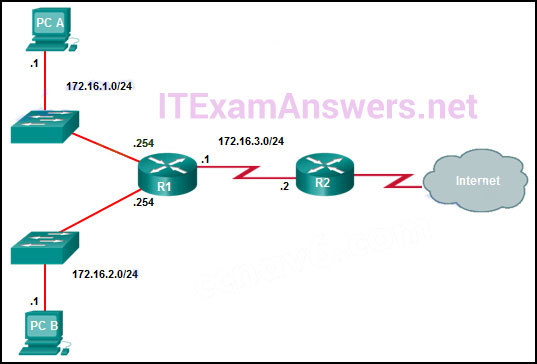
94. Refer to the exhibit. PC A sends a request to Server B. What IPv4 address is used in the destination field in the packet as the packet leaves PC A?

- 192.168.11.1
- 192.168.10.1
- 192.168.12.16
- 192.168.10.10

- If the destination MAC address that corresponds to the IPv4 address is not in the ARP cache, R1 sends an ARP request.
- R1 uses the destination MAC address of S1.
- The packet is encapsulated into a PPP frame, and R1 adds the PPP destination address to the frame.
- R1 leaves the field blank and forwards the data to the PC.
- a route received through the OSPF routing protocol
- a directly connected network
- a static route
- a route received through the EIGRP routing protocol
- The subnet mask is incorrect for the IPv4 address.
- The interface fa0/0 has not been activated.
- The configuration needs to be saved first.
- No packets with a destination network of 172.16.1.0 have been sent to R1.
- ip route 172.16.0.0 255.255.224.0 S0/0/0 100
- ip route 172.16.0.0 255.255.240.0 S0/0/0 200
- ip route 172.16.32.0 255.255.224.0 S0/0/0 200
- ip route 172.16.32.0 255.255.0.0 S0/0/0 100
ip route 192.168.10.0 255.255.255.0 10.10.10.2 5How would an administrator test this configuration?
- Delete the default gateway route on the router.
- Manually shut down the router interface used as a primary route.
- Ping from the 192.168.10.0 network to the 10.10.10.2 address.
- Ping any valid address on the 192.168.10.0/24 network.
- floating static route
- fully specified static route
- recursive static route
- directly attached static route
When an IPv6 static route is configured, it is first necessary to configure ……
- the next-hop address of two different adjacent routers.
- the “ipv6 unicast-routing” command.
- an IPv6 link-local address on the adjacent router.
- an administrative distance of 2.
172.18.109.0/26 is variously subnetted, 7 subnets, 3 masks O 172.18.109.0/26 [110/10] via 172.18.32.1, 00:00:24, Serial0/0/0 O 172.18.109.64/26 [110/20] via 172.18.32.6, 00:00:56, Serial 0/0/1 O 172.18.109.128/26 [110/10] via 172.18.32.1, 00:00:24, Serial 0/0/0 C 172.18.109.192/27 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0 L 172.18.109.193/27 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0 C 172.18.109.224/27 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1 L 172.18.109.225/27 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1 172.18.32.0/24 is variably subnetted, 4 subnets, 2 masks C 172.18.32.0/30 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0 L 172.18.32.2/32 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0 C 172.18.32.4/30 is directly connected, Serial0/0/1 L 172.18.32.5/32 is directly connected, Serial0/0/1 S 172.18.33.0/26 [1/0] via 172.18.32.1, 00:00:24, Serial0/0/0 R1#Refer to the exhibit. Which interface will be the exit interface to forward a data packet that has the destination IP address 172.18.109.152?
- GigabitEthernet0/0
- GigabitEthernet0/1
- Serial0/0/0
- None, the packet will be dropped.
A user reports that PC0 cannot visit the web server www.server.com. Troubleshoot the network configuration to identify the problem.
What is the cause of the problem?
- The clock rate on one of the serial links is configured incorrectly.
- A serial interface on Branch is configured incorrectly.
- The DNS server address on PC0 is configured incorrectly.
- Routing between HQ and Branch is configured incorrectly.
- ARP spoofing
- DHCP starvation
- IP address spoofing
- MAC address flooding
- Disable DTP.
- Disable STP.
- Enable port security.
- Place unused ports in an unused VLAN.
- IPS Sensor Appliance
- Web Security Appliance
- Email Security Appliance
- SSL/IPsec VPN Appliance
- Adaptive Security Appliance
- NAC Appliance
In the 802.1X standard, the client attempting to access the network is referred to as the supplicant.
- true
- false
- server-based AAA over TACACS+
- local AAA over RADIUS
- server-based AAA
- local AAA over TACACS+
- local AAA
- server-based AAA over RADIUS
- Enable CDP on edge devices, and enable LLDP on interior devices.
- Use the open standard LLDP rather than CDP.
- Use the default router settings for CDP and LLDP.
- Disable both protocols on all interfaces where they are not required.
- SNMP
- TFTP
- SSH
- SCP
- It treats frames as unknown unicast and floods all incoming frames to all ports on the switch.
- It treats frames as unknown unicast and floods all incoming frames to all ports across multiple switches.
- It treats frames as unknown unicast and floods all incoming frames to all ports within the local VLAN.
- It treats frames as unknown unicast and floods all incoming frames to all ports within the collision domain.
- the router that is serving as the default gateway
- the authentication server that is performing client authentication
- the client that is requesting authentication
- the switch that is controlling network access

No one is allowed to disconnect the IP phone or the PC and connect some other wired device.
If a different device is connected, port Fa0/2 is shut down.
The switch should automatically detect the MAC address of the IP phone and the PC and add those addresses to the running configuration.
- SWA(config-if)# switchport port-security
SWA(config-if)# switchport port-security mac-address sticky - SWA(config-if)# switchport port-security
SWA(config-if)# switchport port-security maximum 2
SWA(config-if)# switchport port-security mac-address sticky
SWA(config-if)# switchport port-security violation restrict - SWA(config-if)# switchport port-security mac-address sticky
SWA(config-if)# switchport port-security maximum 2 - SWA(config-if)# switchport port-security
SWA(config-if)# switchport port-security maximum 2
SWA(config-if)# switchport port-security mac-address sticky

- Frames from PC1 will be forwarded since the switchport port-security violation command is missing.
- Frames from PC1 will be forwarded to its destination, and a log entry will be created.
- Frames from PC1 will be forwarded to its destination, but a log entry will not be created.
- Frames from PC1 will cause the interface to shut down immediately, and a log entry will be made.
- Frames from PC1 will be dropped, and there will be no log of the violation.
- Frames from PC1 will be dropped, and a log message will be created.
- DHCP spoofing
- DHCP starvation
- VLAN double-tagging
- DTP spoofing
- It checks the source MAC address in the Ethernet header against the user-configured ARP ACLs.
- It checks the source MAC address in the Ethernet header against the MAC address table.
- It checks the source MAC address in the Ethernet header against the sender MAC address in the ARP body.
- It checks the source MAC address in the Ethernet header against the target MAC address in the ARP body.
- S1(config)# spanning-tree bpduguard default
- S1(config-if)# spanning-tree portfast bpduguard
- S1(config)# spanning-tree portfast bpduguard default
- S1(config-if)# enable spanning-tree bpduguard
- S1(config-if)# spanning-tree bpduguard enable
- auto secure MAC addresses
- dynamic secure MAC addresses
- static secure MAC addresses
- sticky secure MAC addresses
- authentication
- probe request
- probe response
- beacon
- delivering a broadcast frame
- receiving a broadcast beacon frame
- initiating a three-way handshake
- sending an ARP request
- transmitting a probe request
- to enable different 802.11 standards
- to avoid interference from nearby wireless devices
- to disable broadcasting of the SSID
- to provide stronger security modes
- mixed
- passive
- active
- open
- 802.11n
- 802.11ac
- 802.11g
- 802.11b
- Enable MAC address filtering on the wireless router.
- Configure encryption on the wireless router and the connected wireless devices.
- Change the default user-name and password of the wireless router.
- Disable the wireless network SSID broadcast.
- Access Points
- Network Summary
- Advanced
- Rogues
- Create a new SSID.
- Build or have an SNMP server available.
- Build or have a RADIUS server available.
- Create a new VLAN interface.
- Requiring the users to switch to the 5 GHz band for streaming media is inconvenient and will result in fewer users accessing these services.
- The 5 GHz band has more channels and is less crowded than the 2.4 GHz band, which makes it more suited to streaming multimedia.
- The 5 GHz band has a greater range and is therefore likely to be interference-free.
- The only users that can switch to the 5 GHz band will be those with the latest wireless NICs, which will reduce usage.
- It is used by the RADIUS server to authenticate WLAN users.
- It is used to authenticate and encrypt user data on the WLAN.
- It is used to encrypt the messages between the WLC and the RADIUS server.
- It allows users to authenticate and access the WLAN.
- wireless client operating system password
- antenna frequency
- wireless network password
- wireless beacon time
- AP password
- SSID
- 802.1X
- accounting
- authentication
- authorization
- wireless metropolitan-area network
- wireless wide-area network
- wireless local-area network
- wireless personal-area network
- DHCP Snooping
- IP Source Guard
- Dynamic ARP Inspection
- Port Security
- Web Security Appliance
- Enable trunking manually.
- Disable DTP.
- Enable Source Guard.
- Set the native VLAN to an unused VLAN.
- Use private VLANs.
- Enable BPDU guard.

- The port has the maximum number of MAC addresses that is supported by a Layer 2 switch port which is configured for port security.
- The port has been shut down.
- The port violation mode is the default for any port that has port security enabled.
- The port has two attached devices.
- AAA
- NAT
- RADIUS
- SNMP
- Split the wireless traffic between the 802.11n 2.4 GHz band and the 5 GHz band.
- Update the firmware on the new router.
- Configure devices to use a different channel.
- Change the SSID.
- improperly configured devices
- rogue access points
- accidental interference
- interception of data
- CAPWAP creates a tunnel on Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) ports in order to allow a WLC to configure an autonomous access point.
- CAPWAP provides the encapsulation and forwarding of wireless user traffic between an access point and a wireless LAN controller.
- CAPWAP provides connectivity between an access point using IPv6 addressing and a wireless client using IPv4 addressing.
- CAPWAP provides the encryption of wireless user traffic between an access point and a wireless client.

Modules 10 – 13: L2 Security and WLANs Exam Answers
- A syslog message is logged.
- The interface will go into error-disabled state.
- Packets with unknown source addresses will be dropped.
- A notification is sent.

141. What are two protocols that are used by AAA to authenticate users against a central database of usernames and password? (Choose two.)
- SSH
- HTTPS
- TACACS+
- RADIUS
- CHAP
- NTP
- The attacker provides incorrect DNS and default gateway information to clients.
- The IP addresses assigned to legitimate clients are hijacked.
- Clients receive IP address assignments from a rogue DHCP server.
- Legitimate clients are unable to lease IP addresses.
- the limited size of content-addressable memory space
- the automatic trunking port feature enabled for all ports by default
- the native VLAN of the trunking port being the same as a user VLAN
- mixed duplex mode enabled for all ports by default
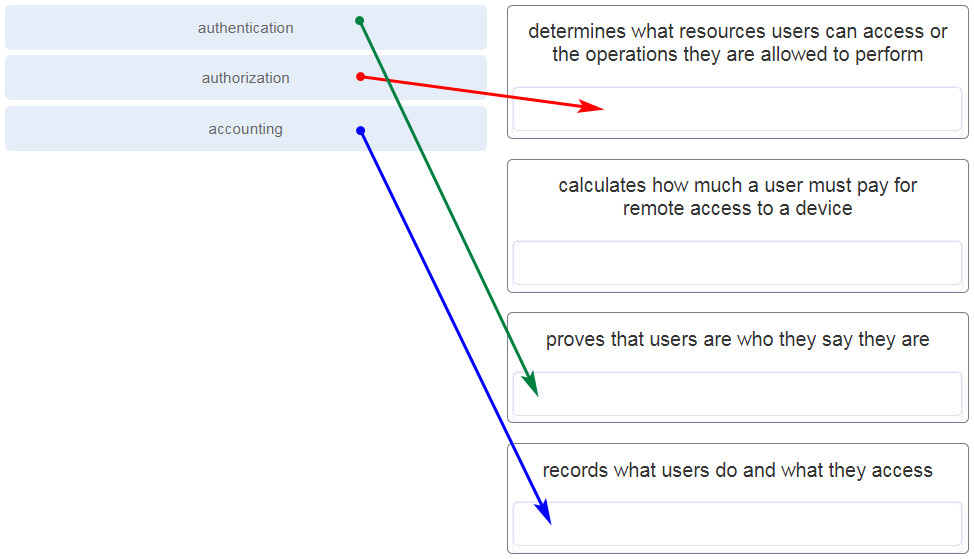
- authentication
- accounting
- accessibility
- authorization

- 1
- 3
- 5
- 7
- shutdown
- disabled
- restrict
- protect
- It checks the source MAC address in the Ethernet header against the MAC address table.
- It checks the source MAC address in the Ethernet header against the user-configured ARP ACLs.
- It checks the source MAC address in the Ethernet header against the target MAC address in the ARP body.
- It checks the source MAC address in the Ethernet header against the sender MAC address in the ARP body.
- Clients will have to manually identify the SSID to connect to the network.
- It is the best way to secure a wireless network.
- SSIDs are very difficult to discover because APs do not broadcast them.
- It provides free Internet access in public locations where knowing the SSID is of no concern.
- personal
- shared key
- enterprise
- WEP
- Disable DHCP on the access point and assign static addresses to the wireless clients.
- Upgrade the firmware on the wireless access point.
- Split the traffic between the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands.
- Replace the wireless NICs on the computers that are experiencing slow connections.
- DHCP
- SNMP
- RADIUS
- AAA
- DHCP
- RADIUS
- DNS
- NAT
- QoS
- DNS
- DHCP
- NAT
- accounting
- authentication
- authorization
- 802.1X
- wireless metropolitan-area network
- wireless local-area network
- wireless personal-area network
- wireless wide-area network
- the mixed duplex mode enabled for all ports by default
- the limited size of content-addressable memory space
- mixed port bandwidth support enabled for all ports by default
- the automatic trunking port feature enabled for all ports by default
- accounting
- authentication
- auditing
- authorization

CCNA 2 v7 Modules 10 – 13: L2 Security and WLANs Exam Answers 55
- The Fa0/24 interface of S1 is configured with the same MAC address as the Fa0/2 interface.
- The connection between S1 and PC1 is via a crossover cable.
- S1 has been configured with a
switchport port-security agingcommand. - The MAC address of PC1 that connects to the Fa0/2 interface is not the configured MAC address.
SW1(config)# interface range fa0/5 - 10 SW1(config-if)# ip dhcp snooping limit rate 6What is the effect after these commands are entered?
- If any of the FastEthernet ports 5 through 10 receive more than 6 DHCP messages per second, the port will be shut down.
- FastEthernet ports 5 through 10 can receive up to 6 DHCP messages per second of any type.
- If any of the FastEthernet ports 5 through 10 receive more than 6 DHCP messages per second, the port will continue to operate and an error message will be sent to the network administrator.
- FastEthernet ports 5 through 10 can receive up to 6 DHCP discovery messages per second.
- It checks the source MAC address in the Ethernet header against the user-configured ARP ACLs.
- It checks the source MAC address in the Ethernet header against the MAC address table.
- It checks the source MAC address in the Ethernet header against the target MAC address in the ARP body.
- It checks the source MAC address in the Ethernet header against the sender MAC address in the ARP body.
- Add a Wi-Fi range extender to the WLAN and set the AP and the range extender to serve different bands.
- Check and keep the firmware of the wireless router updated.
- Make sure that different SSIDs are used for the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands.
- Require all wireless devices to use the 802.11n standard.
- accounting
- 802.1X
- authorization
- authentication
- wireless wide-area network
- wireless personal-area network
- wireless local-area network
- wireless metropolitan-area network
- MANAGEMENT
- WIRELESS
- WLANs
- SECURITY
- Yagi
- omnidirectional
- dish
- directional
- 802.11g
- 802.11ad
- 802.11ac
- 802.11a
- 802.11n
- 802.11b
- preventing buffer overflow attacks
- preventing rogue switches from being added to the network
- protecting against Layer 2 loops
- enforcing the placement of root bridges
- authentication
- authorization
- 802.1X
- accounting
- DHCPDISCOVER
- DHCPACK
- DHCPOFFER
- DHCPREQUEST
- DHCPNAK
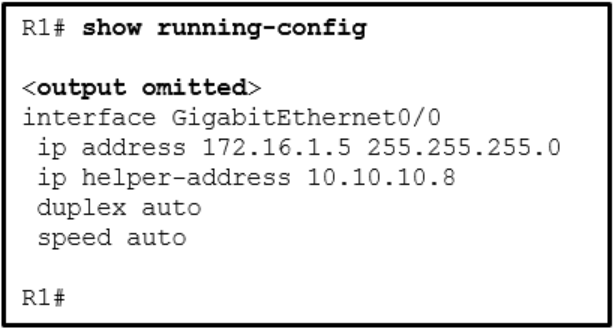
Router(config)# interface g0/1 Router(config-if)# ip address dhcpWhat is the administrator trying to achieve?
- configuring the router to act as a DHCPv4 server
- configuring the router to obtain IP parameters from a DHCPv4 server
- configuring the router to act as a relay agent
- configuring the router to resolve IP address conflicts
- The client does not yet know the IP address of the DHCP server that sent the offer.
- The DHCP server may be on a different subnet, so the request must be sent as a broadcast.
- The client does not have a MAC address assigned yet, so it cannot send a unicast message at Layer 2.
- The client may have received offers from multiple servers, and the broadcast serves to implicitly decline those other offers.
Destination address: 255.255.255.255
Client IPv4 address: 0.0.0.0
Default gateway address: 0.0.0.0
Subnet mask: 0.0.0.0
- DHCPACK
- DHCPDISCOVER
- DHCPOFFER
- DHCPREQUEST
- a client initiating a message to find a DHCP server – DHCPDISCOVER
- a DHCP server responding to the initial request by a client – DHCPOFFER
- the client accepting the IP address provided by the DHCP server – DHCPREQUEST
- the DHCP server confirming that the lease has been accepted – DHCPACK
- DHCP
- DNS
- SMB
- 53
- 67
- 80

- 192.168.1.1
- 192.168.1.255
- 255.255.255.255
- 192.168.1.8
- DHCPOFFER
- DHCPDISCOVER
- DHCPREQUEST
- DHCPACK
- service dhcp
- ip address dhcp
- ip helper-address
- ip dhcp pool
- a DHCPDISCOVER unicast message
- a DHCPREQUEST broadcast message
- a DHCPREQUEST unicast message
- a DHCPDISCOVER broadcast message
- DHCPDISCOVER
- DHCPOFFER
- DHCPREQUEST
- DHCPACK
- DHCPNACK
- The computer cannot ping 127.0.0.1.
- The computer receives an IP address that starts with 169.254.
- Windows displays a DHCP timeout message.
- The computer cannot ping other devices on the same network with IP addresses in the 169.254.0.0/16 range.
- broadcast DHCPACK
- broadcast DHCPREQUEST
- unicast DHCPACK
- unicast DHCPREQUEST
- Set the WAN connection in the wireless router as a DHCP client.
- Set the connection between the wireless router and the DSL modem as a private IP network.
- Set the DSL modem as a DHCP client to get a public IP address from the wireless router.
- Set the DSL modem as a DHCP client to the phone company and a DHCP server for the internal connection.
- 23
- 53
- 67
- 68
- 80
- Send a DHCPACK packet to the default gateway address.
- Use a statically configured IP address from the pool of IP addresses that is offered by the DHCP server.
- Send a DHCPDISCOVER message to physical address FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF.
- Send a DHCPREQUEST packet to IP address 255.255.255.255.
- It can provide relay services for multiple UDP services.
- It reduces the response time from a DHCP server.
- It can forward both broadcast and multicast messages on behalf of clients.
- It will allow DHCPDISCOVER messages to pass without alteration.
- When a device that is configured to use DHCP boots, the client broadcasts a DHCPDISCOVER message to identify any available DHCP servers on the network.
- A client must wait for lease expiration before it sends another DHCPREQUEST message.
- If the client receives several DHCPOFFER messages from different servers, it sends a unicast DHCPREQUEST message to the server from which it chooses to obtain the IP information.
- The DHCPDISCOVER message contains the IP address and subnet mask to be assigned, the IP address of the DNS server, and the IP address of the default gateway.
The DHCPDISCOVER message is used to identify any DHCP servers on a network. The DHCPOFFER message is used by a server to offer a lease to a client. The DHCPREQUEST message is used to identify both the specific DHCP server and the lease that the client is accepting.
The DHCPACK message is used by a server to finalize a successful lease with a client.
The DHCPNAK message is used when an offered lease is no longer valid.
188. A network administrator configures a router to send RA messages with M flag as 0 and O flag as 1. Which statement describes the effect of this configuration when a PC tries to configure its IPv6 address?
- It should contact a DHCPv6 server for the prefix, the prefix-length information, and an interface ID that is both random and unique.
- It should use the information that is contained in the RA message and contact a DHCPv6 server for additional information.
- It should use the information that is contained in the RA message exclusively.
- It should contact a DHCPv6 server for all the information that it needs.

- Add the ipv6 dhcp relay command to interface Fa0/0.
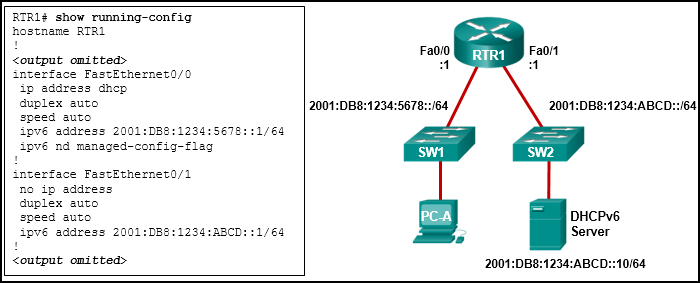
- Change the ipv6 nd managed-config-flag command to ipv6 nd other-config-flag.
- Configure the ipv6 nd managed-config-flag command on interface Fa0/1.
- Add the IPv6 address 2001:DB8:1234:5678::10/64 to the interface configuration of the DHCPv6 server.

- The DNS server address is not on the same network as the clients are on.
- The router is configured for SLAAC operation.
- The GigabitEthernet interface is not activated.
- The clients cannot communicate with the DHCPv6 server, evidenced by the number of active clients being 0.
A stateless DHCPv6 client would send a DHCPv6 INFORMATION-REQUEST message as step 3 in the process.
192. A company uses the SLAAC method to configure IPv6 addresses for the employee workstations. Which address will a client use as its default gateway?
- the global unicast address of the router interface that is attached to the network
- the unique local address of the router interface that is attached to the network
- the all-routers multicast address
- the link-local address of the router interface that is attached to the network

- The router is configured for stateful DHCPv6 operation, but the DHCP pool configuration is incomplete.
- The DHCPv6 server name is ACAD_CLASS.
- Clients would configure the interface IDs above 0010.
- The router is configured for stateless DHCPv6 operation.
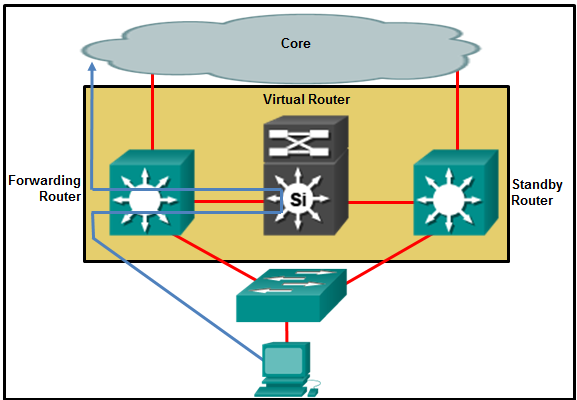
- HSRP uses active and standby routers.
- HSRP is nonproprietary.
- It allows load balancing between a group of redundant routers.
- It uses ICMP messages in order to assign the default gateway to hosts.

- GLBP
- PVST+
- PVST
- STP

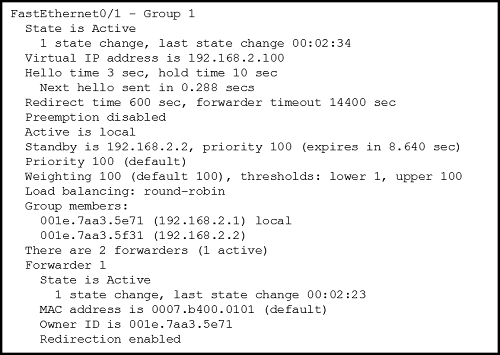
- 192.168.2.0
- 192.168.2.1
- 192.168.2.2
- 192.168.2.100

- MAC address of the virtual router
- MAC address of the standby router
- MAC addresses of both the forwarding and standby routers
- MAC address of the forwarding router
Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) is a Cisco-proprietary protocol that is designed to allow for transparent failover of a first-hop IPv4 device.
199. Which FHRP implementation is a Cisco-proprietary protocol that suppports IPv4 load sharing?
- IRDP
- GLBP
- VRRPv3
- GLBP for IPv6
- 122
- 118
- 119
- 108
- 116
The broadcast DHCPDISCOVER message finds DHCPv4 servers on the network. When the DHCPv4 server receives a DHCPDISCOVER message, it reserves an available IPv4 address to lease to the client and sends the unicast DHCPOFFER message to the requesting client. When the client receives the DHCPOFFER from the server, it sends back a DHCPREQUEST. On receiving the DHCPREQUEST message the server replies with a unicast DHCPACK message. DHCPREPLY and DHCPINFORMATION-REQUEST are DHCPv6 messages.
202. After a host has generated an IPv6 address by using the DHCPv6 or SLAAC process, how does the host verify that the address is unique and therefore usable?
- The host sends an ICMPv6 echo request message to the DHCPv6 or SLAAC-learned address and if no reply is returned, the address is considered unique.
- The host sends an ICMPv6 neighbor solicitation message to the DHCP or SLAAC-learned address and if no neighbor advertisement is returned, the address is considered unique.
- The host checks the local neighbor cache for the learned address and if the address is not cached, it it considered unique.
- The host sends an ARP broadcast to the local link and if no hosts send a reply, the address is considered unique.
- It is used within a group of routers for selecting an active device and a standby device to provide gateway services to a LAN.
- It uses ICMP to allow IPv4 hosts to locate routers that provide IPv4 connectivity to remote IP networks.
- If the virtual router master fails, one router is elected as the virtual router master with the other routers acting as backups.
- It is an open standard protocol.
What is the keyword that is displayed on www.netacad.com?
- DHCP
- switch
- Router
- networking
- Cisco
- IPv6

206. Match the purpose with its DHCP message type. (Not all options are used.)

207. Match the DHCP message types to the order of the stateful DHCPv6 process when a client first connects to an IPv6 network. (Not all options are used.)

208. Match the step number to the sequence of stages that occur during the HSRP failover process. (Not all options are used.)

209. Match the FHRP protocols to the appropriate description. (Not all options are used.)

210. Match the DHCP message types to the order of the DHCPv4 process. (Not all options are used.)

211. The address pool of a DHCP server is configured with 192.168.234.0/27. The network administrator reserves 22 IP addresses for IP phones. How many IP addresses are left in the pool to be assigned to other hosts?
- 10
- 0
- 8
- 21
- 18
- both MAC and IPv4 addresses of the DHCP server
- FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF and IPv4 address of the DHCP server
- FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF and 255.255.255.255
- MAC address of the DHCP server and 255.255.255.255
- Router# show running-config I section_dhcp
- Router# show ip dhcp server statistics
- Router# show ip dhcp binding
- Router# show ip dhcp pool
- better network performance
- better connectivity
- easy IP address management
- easy configuration on ISP firewall
- the IPv4 addresses that are assigned to hosts by the DHCP server
- that DHCPv4 discover messages are still being received by the DHCP server
- the IPv4 addresses that have been excluded from the DHCPv4 pool
- the number of IP addresses remaining in the DHCP pool
- The Cisco router will exclude only the 10.0.15.1 and 10.0.15.15 IP addresses from being leased to DHCP clients.
- The Cisco router will exclude 15 IP addresses from being leased to DHCP clients.
- The Cisco router will automatically create a DHCP pool using a /28 mask.
- The Cisco router will allow only the specified IP addresses to be leased to clients.

218. Refer to the exhibit. Based on the output that is shown, what kind of IPv6 addressing is being configured?

CCNA 2 v7 Modules 7 – 9: Available and Reliable Networks Exam Answers
- stateless DHCPv6
- SLAAC
- static link-local
- stateful DHCPv6
- GLBP
- GLBP for IPv6
- VRRPv3
- VRRPv2
- ip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.100.1 192.168.100.9
ip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.101.254
ip dhcp pool LAN-POOL-100
ip network 192.168.100.0 255.255.254.0
ip default-gateway 192.168.100.1 - dhcp pool LAN-POOL-100
ip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.100.1 192.168.100.9
ip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.100.254
network 192.168.100.0 255.255.254.0
default-router 192.168.101.1 - ip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.100.1 192.168.100.10
ip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.100.254
ip dhcp pool LAN-POOL-100
network 192.168.100.0 255.255.255.0
ip default-gateway 192.168.100.1 - ip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.100.1 192.168.100.10
ip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.101.254
ip dhcp pool LAN-POOL-100
network 192.168.100.0 255.255.254.0
default-router 192.168.100.1
- Workstations are assigned with the IP address 127.0.0.1.
- Workstations are assigned with IP addresses in the 10.0.0.0/8 network.
- Workstations are assigned with IP addresses in the 169.254.0.0/16 network.
- Workstations are assigned with the IP address 0.0.0.0.
- R1(config)# ipv6 dhcp pool
- R1(config-if)# ipv6 enable
- R1(config)# ipv6 unicast-routing
- R1(config-if)# ipv6 nd other-config-flag
- VRRPv3
- GLBP for IPv6
- IRDP
- GLBP

- The ipv6 dhcp relay command should be applied to interface Gig0/0.
- The ipv6 nd managed-config-flag should be applied to interface Gig0/1.
- The ipv6 dhcp relay command should use the link-local address of the DHCP server.
- The ipv6 nd managed-config-flag command should be ipv6 nd other-config-flag .
- View a list of commands entered in a previous session.
- Recall up to 15 command lines by default.
- Set the command history buffer size.
- Recall previously entered commands.
- Save command lines in a log file for future reference.
- load the default Cisco IOS software
- load boot loader software
- low-level CPU initialization
- load a power-on self-test program
- a TFTP server
- a crossover cable
- access to another router
- physical access to the router
- enable secret password
- password password
- username username secret secret
- login block-for seconds attempts number within*seconds*
- show interfaces
- show controllers
- show processes
- show running-config
- on both ends of the connection
- on the full-duplex end of the connection
- only on serial interfaces
- on the half-duplex end of the connection
- config-register
- boot system
- boot loader
- confreg
- BOOT environment variable
- IOS image file
- POST
- startup-config
- NVRAM
- FTP
- HTTP
- NetBEUI
- POP
- SSH
- The no shutdown command is required to place this interface in an UP state.
- It is a logical interface internal to the router.
- Only one loopback interface can be enabled on a router.
- It is assigned to a physical port and can be connected to other devices.
- 64 bytes
- 512 bytes
- 1024 bytes
- 1500 bytes
- after CPU initialization
- after IOS localization
- after flash file system initialization
- after POST execution
- an increase in the number of dropped frames
- an increase in the size of the broadcast domain
- an increase in the number of network collisions
- an increase in the size of the collision domain
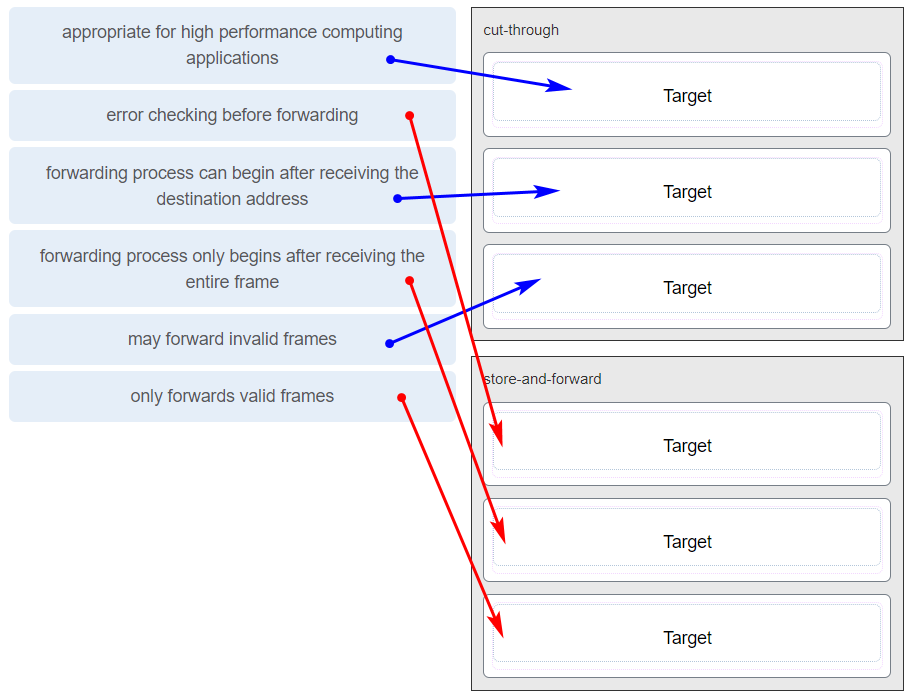
- Error-free fragments are forwarded, so switching occurs with lower latency.
- Frames are forwarded without any error checking.
- Only outgoing frames are checked for errors.
- Buffering is used to support different Ethernet speeds.
- A hub extends a collision domain, and a switch divides collision domains.
- A hub divides collision domains, and a switch divides broadcast domains.
- Each port of a hub is a collision domain, and each port of a switch is a broadcast domain.
- A hub forwards frames, and a switch forwards only packets.
- Frame forwarding decisions are based on MAC address and port mappings in the CAM table.
- Cut-through frame forwarding ensures that invalid frames are always dropped.
- Only frames with a broadcast destination address are forwarded out all active switch ports.
- Unicast frames are always forwarded regardless of the destination MAC address.
- They provide error checking on the data received.
- They store frames received, thus preventing premature frame discarding when network congestion occurs.
- They provide extra memory for a particular port if autonegotiation of speed or duplex fails.
- They hold data temporarily when a collision occurs until normal data transmission resumes.
- high port density
- fast port speed
- large frame buffers
- fast internal switching
- ASIC
- dual processors
- large buffer size
- store-and-forward RAM

CCNA2 v7 SRWE – Modules 1 – 4: Switching Concepts, VLANs, and InterVLAN Routing Exam Answers

CCNA 2 v7 Modules 1 – 4: Switching Concepts, VLANs, and InterVLAN Routing Exam Answers 20
- source MAC address and incoming port number
- destination MAC address and incoming port number
- source IP address and incoming port number
- destination IP address and incoming port number
- cut-through
- FCS
- fragment free
- store-and-forward
CCNA2 v7 SRWE – Modules 1 – 4 Switching Concepts, VLANs, and InterVLAN Routing Exam Answers 23
- 1
- 4
- 8
- 16
- 55
- when connecting a Cisco switch to a non-Cisco switch
- when a neighbor switch uses a DTP mode of dynamic auto
- when a neighbor switch uses a DTP mode of dynamic desirable
- on links that should not be trunking
- on links that should dynamically attempt trunking
- Designed to carry traffic that is generated by users, this type of VLAN is also known as the default VLAN.
- The native VLAN traffic will be untagged across the trunk link.
- This VLAN is necessary for remote management of a switch.
- High priority traffic, such as voice traffic, uses the native VLAN.
- The native VLAN provides a common identifier to both ends of a trunk.
- Switch# delete flash:vlan.dat
- Switch(config-if)# no switchport access vlan 100
- Switch(config-if)# no switchport trunk allowed vlan 100
- Switch(config)# no vlan 100
CCNA 2 v7 Modules 1 – 4 Switching Concepts, VLANs, and InterVLAN Routing Exam 27
- There is a native VLAN mismatch between the switches.
- There is no media connected to the interfaces.
- They are administratively shut down.
- They are configured as trunk interfaces.
- All devices in all VLANs see the frame.
- Devices in VLAN 20 and the management VLAN see the frame.
- Only devices in VLAN 20 see the frame.
- Only devices that are connected to the local switch see the frame.
CCNA2 v7 SRWE – Modules 1 – 4 Switching Concepts, VLANs, and InterVLAN Routing Exam Answers 29
- Allow VLAN 20 on the trunk link.
- Enable DTP on both ends of the trunk.
- Configure all workstations on SW1 to be part of the default VLAN.
- Configure all workstations on SW2 to be part of the native VLAN.
- The ports are disabled.
- The ports are placed in trunk mode.
- The ports are assigned to VLAN1, the default VLAN.
- The ports stop communicating with the attached devices.
CCNA2 v7 Modules 1 – 4 Switching Concepts, VLANs, and InterVLAN Routing Exam Answers 31
CCNA2 v7 Modules 1 – 4 Switching Concepts, VLANs, and InterVLAN Routing Exam Answers 32
- access
- trunk
- native
- auto
CCNA2 v7 Modules 1 – 4 Switching Concepts, VLANs, and InterVLAN Routing Exam Answers 33
- Port Fa0/11 will be shutdown.
- An error message would be displayed.
- Port Fa0/11 will be returned to VLAN 1.
- VLAN 30 will be deleted.
- show vlan brief
- show interfaces Fa0/1 switchport
- show mac address-table interface Fa0/1
- show interfaces trunk
CCNA2 v7 Modules 1 – 4 Switching Concepts, VLANs, and InterVLAN Routing Exam Answers 38
- There is nothing wrong with the configuration.
- Interface Fa0/20 can only have one VLAN assigned.
- The mls qos trust cos command should reference VLAN 35.
- The command used to assign the voice VLAN to the switch port is incorrect.
- Configure the interface as an IEEE 802.1Q trunk.
- Assign the voice VLAN to the switch port.
- Activate spanning-tree PortFast on the interface.
- Ensure that voice traffic is trusted and tagged with a CoS priority value.
- Add a voice VLAN.
- Configure the switch port interface with subinterfaces.
- Assign a data VLAN to the switch port.
- Configure the switch port in access mode.
CCNA2 v7 Modules 1 – 4 Switching Concepts, VLANs, and InterVLAN Routing Exam Answers 38
- Interface G0/2 is not configured as a trunk.
- VLAN 20 has not been created.
- The encapsulation on interface G0/1 is incorrect.
- The DTP mode is incorrectly set to dynamic auto on interface G0/1.
CCNA2 v7 Modules 1 – 4 Switching Concepts, VLANs, and InterVLAN Routing Exam Answers 39
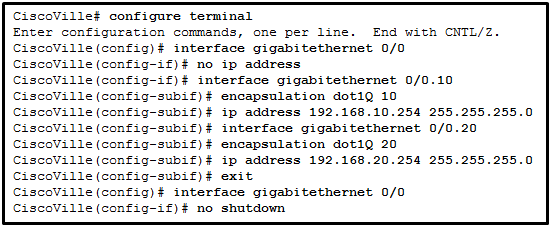
- The gig0/0 interface does not support inter-VLAN routing.
- The no shutdown command has not been configured.
- The IP address on CiscoVille is incorrect.
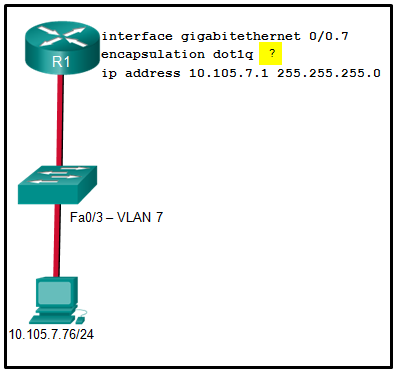
- The encapsulation dot1Q 20 command has not been configured.

CCNA2 v7 Modules 1 – 4 Switching Concepts, VLANs, and InterVLAN Routing Exam Answers 40
- switchport mode access
- no switchport
- switchport mode trunk
- switchport mode dynamic desirable
- A multilayer switch is needed.
- A router with at least two LAN interfaces is needed.
- Two groups of switches are needed, each with ports that are configured for one VLAN.
- A switch with a port that is configured as a trunk is needed when connecting to the router.
- Multiple SVIs are needed.
- A dedicated router is required.
- Router-on-a-stick requires subinterfaces to be configured on the same subnets.
- Router-on-a-stick requires multiple physical interfaces on a router.
- Multiple subinterfaces may impact the traffic flow speed.
CCNA2 v7 Modules 1 – 4 Switching Concepts, VLANs, and InterVLAN Routing Exam Answers 43
- Gi1/1 is in the default VLAN.
- Voice VLAN is not assigned to Gi1/1.
- Gi1/1 is configured as trunk mode.
- Negotiation of trunking is turned on on Gi1/1.
- The trunking encapsulation protocol is configured wrong.

CCNA2 v7 Modules 1 – 4 Switching Concepts, VLANs, and InterVLAN Routing Exam Answers 44
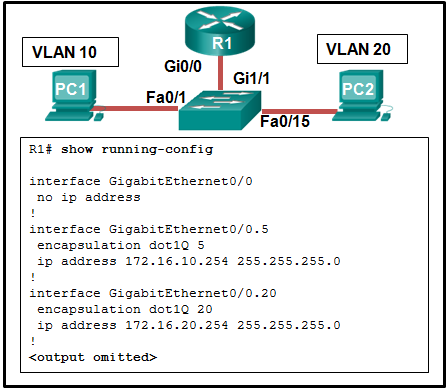
- Gi0/0 is not configured as a trunk port.
- The command interface GigabitEthernet0/0.5 was entered incorrectly.
- There is no IP address configured on the interface Gi0/0.
- The no shutdown command is not entered on subinterfaces.
- The encapsulation dot1Q 5 command contains the wrong VLAN.
CCNA2 v7 Modules 1 – 4 Switching Concepts, VLANs, and InterVLAN Routing Exam Answers 45
- routed port
- access port
- trunk port
- SVI
CCNA2 v7 Modules 1 – 4 Switching Concepts, VLANs, and InterVLAN Routing Exam Answers 46
- Interface Fa0/0 is missing IP address configuration information.
- IP addresses on the subinterfaces are incorrectly matched to the VLANs.
- Each subinterface of Fa0/0 needs separate no shutdown commands.
- Routers do not support 802.1Q encapsulation on subinterfaces.
CCNA2 v7 Modules 1 – 4 Switching Concepts, VLANs, and InterVLAN Routing Exam Answers 47
- The wrong VLAN has been configured on GigabitEthernet 0/0.45.
- The command no shutdown is missing on GigabitEthernet 0/0.30.
- The GigabitEthernet 0/0 interface is missing an IP address.
- There is an incorrect IP address configured on GigabitEthernet 0/0.30.
- It supports trunking.
- It is not assigned to a VLAN.
- It is commonly used as a WAN link.
- It cannot have an IP address assigned to it.
CCNA2 v7 Modules 1 – 4 Switching Concepts, VLANs, and InterVLAN Routing Exam Answers 49
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- It automatically adjusts the port to allow device connections to use either a straight-through or a crossover cable.
- It applies an IPv4 address to the virtual interface.
- It applies an IPv6 address to the virtual interface.
- It permits an IPv6 address to be configured on a switch physical interface.
- It updates the MAC address table for the associated port.
- It applies an IPv4 address to the virtual interface.
- It applies an IPv6 address to the virtual interface.
- It activates a virtual or physical switch interface.
- It permits an IPv6 address to be configured on a switch physical interface.
- It updates the MAC address table for the associated port.
- It enters the global configuration mode.
- It enters configuration mode for a switch virtual interface.
- It applies an IPv4 address to the virtual interface.
- It updates the MAC address table for the associated port.
- It permits an IPv6 address to be configured on a switch physical interface.
- It enters the global configuration mode.
- It saves the running configuration to NVRAM.
- It disables a virtual or physical switch interface.
- It updates the MAC address table for the associated port.
- It saves the startup configuration to the running configuration.
- It disables a virtual or physical switch interface.
- It saves the running configuration to NVRAM.
- It activates a virtual or physical switch interface.
- It updates the MAC address table for the associated port.
- It saves the startup configuration to the running configuration.
- It disables a virtual or physical switch interface.
- It applies an IPv6 address to the virtual interface.
- It applies an IPv4 address to the virtual interface.
- It permits an IPv6 address to be configured on a switch physical interface.
- It updates the MAC address table for the associated port.
- It applies an IPv6 address to the virtual interface.
- It activates a virtual or physical switch interface.
- It applies an IPv4 address to the virtual interface.
- It permits an IPv6 address to be configured on a switch physical interface.
- It updates the MAC address table for the associated port.
- It returns to global configuration mode.
- It returns to privileged mode.
- It configures the default gateway for the switch.
- It enters user mode.
- It saves the startup configuration to the running configuration.
- It enters privileged mode.
- It enters the global configuration mode.
- It enters configuration mode for a switch virtual interface.
- It updates the MAC address table for the associated port.
- It permits an IPv6 address to be configured on a switch physical interface.
- It allows data to flow in both directions at the same time on the interface.
- It allows data to flow in only one direction at a time on the interface
- It automatically adjusts the port to allow device connections to use either a straight-through or a crossover cable.
- It configures the switch as the default gateway.
- It encrypts user-mode passwords when users connect remotely.
- data VLAN
- voice VLAN
- management VLAN
- security VLAN
- data VLAN
- trunk VLAN
- security VLAN
- voice VLAN
- voice VLAN
- trunk VLAN
- security VLAN
- management VLAN
- default VLAN
- native VLAN
- data VLAN
- management VLAN
- voice VLAN
- desirable VLAN
- trunk VLAN
- security VLAN
- data VLAN
- management VLAN
- voice VLAN
- native VLAN
- management VLAN
- security VLAN
- trunk VLAN
- voice VLAN
- management VLAN
- voice VLAN
- security VLAN
- native VLAN
- native VLAN
- voice VLAN
- security VLAN
- management VLAN
- native VLAN
- desirable VLAN
- trunk VLAN
- security VLAN
CCNA2 v7 Modules 1 – 4 Switching Concepts, VLANs, and InterVLAN Routing Exam Answers 70
- IPv6 enable
- clockrate 128000
- end
- no shutdown
CCNA2 v7 Modules 1 – 4 Switching Concepts, VLANs, and InterVLAN Routing Exam Answers 71
- Use SSH version 1.
- Reconfigure the RSA key.
- Configure SSH on a different line.
- Modify the transport input command.
- a firewall that connects to two Internet providers
- a high port density switch
- a router with two Ethernet ports
- a router with three Ethernet ports
- Switching packets is faster with SVI.
- There is no need for a connection to a router.
- Virtual interfaces support subinterfaces.
- SVIs can be bundled into EtherChannels.
- SVIs eliminate the need for a default gateway in the hosts.

CCNA2 v7 Modules 1 – 4 Switching Concepts, VLANs, and InterVLAN Routing Exam Answers 74
- It identifies the subinterface.
- It identifies the VLAN number.
- It identifies the native VLAN number.
- It identifies the type of encapsulation that is used.
- It identifies the number of hosts that are allowed on the interface.
- data
- default
- native
- management
- the VLAN assignment and membership for device MAC addresses
- the VLAN assignment and membership for all switch ports
- the VLAN assignment and trunking encapsulation
- the VLAN assignment and native VLAN

Which message is displayed when 10.10.10.1 is entered into the PC1 Web Browser address bar?
- Local Server
- Test Server
- File Server
- Cisco Server

CCNA 2 v7 Modules 1 – 4: Switching Concepts, VLANs, and InterVLAN Routing Exam Answers
CCNA 2 v7 Final Exam Answers
1. Refer to the exhibit. What will router R1 do with a packet that has a destination IPv6 address of 2001:db8:cafe:5::1?
CCNA 2 v7 Switching Routing and Wireless Essentials-Version 7.00-Final-Answers-1
- forward the packet out GigabitEthernet0/0
- drop the packet
- forward the packet out GigabitEthernet0/1
- forward the packet out Serial0/0/0

CCNA 2 v7 Switching Routing and Wireless Essentials-Version-Final-Answers-2
- ip route 10.10.0.0 255.255.0.0 Serial 0/0/0 100
- ip route 10.10.0.0 255.255.0.0 209.165.200.226 100
- ip route 10.10.0.0 255.255.0.0 209.165.200.225 100
- ip route 10.10.0.0 255.255.0.0 209.165.200.225 50

CCNA 2 v7 Switching Routing and Wireless Essentials-Version-Final-Answers-3
- Add an administrative distance of 254.
- Change the destination network and mask to 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0
- Change the exit interface to S0/0/1.
- Add the next-hop neighbor address of 209.165.200.226.
- ip route 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 S0/0/0
- ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 S0/0/0
- ip route 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 S0/0/0
- ip route 0.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 S0/0/0

CCNA 2 v7 Switching Routing and Wireless Essentials-Version-Final-Answers-5
- ipv6 route 2001:db8:12:10::/64 S0/0/0
- ipv6 route 2001:db8:12:10::/64 S0/0/1 fe80::2
- ipv6 route 2001:db8:12:10::/64 S0/0/0 fe80::2
- ipv6 route 2001:db8:12:10::/64 S0/0/1 2001:db8:12:10::1
- introducing a rogue switch and enabling trunking
- sending spoofed native VLAN information
- sending spoofed IP addresses from the attacking host
- flooding the switch with MAC addresses
- VLAN hopping
- DHCP spoofing
- MAC address table overflow
- VLAN double-tagging
- assigning the ports to the native VLAN
- modifying the default VLAN
- creating SVI interfaces
- adjusting the route metric
- enabling IP routing
- assigning ports to VLANs
- installing a static route
CCNA 2 v7 Switching Routing and Wireless Essentials-Version-Final-Answers-9
- the virtual IP address and the virtual MAC address for the HSRP group 1
- the virtual IP address of the HSRP group 1 and the MAC address of R1
- the virtual IP address of the HSRP group 1 and the MAC address of R2

11. Which statement is correct about how a Layer 2 switch determines how to forward frames?
- Frame forwarding decisions are based on MAC address and port mappings in the CAM table.
- Only frames with a broadcast destination address are forwarded out all active switch ports.
- Cut-through frame forwarding ensures that invalid frames are always dropped.
- The broadcast domain expands to all switches.
- One collision domain exists per switch.
- There is one broadcast domain and one collision domain per switch.
- Frame collisions increase on the segments connecting the switches.
- Unicast frames are always forwarded regardless of the destination MAC address.

14.Refer to the exhibit. How is a frame sent from PCA forwarded to PCC if the MAC address table on switch SW1 is empty?

CCNA 2 v7 Switching Routing and Wireless Essentials-Version-Final-Answers-14
- SW1 forwards the frame directly to SW2. SW2 floods the frame to all ports connected to SW2, excluding the port through which the frame entered the switch.
- SW1 floods the frame on all ports on the switch, excluding the interconnected port to switch SW2 and the port through which the frame entered the switch.
- SW1 floods the frame on all ports on SW1, excluding the port through which the frame entered the switch.
- SW1 drops the frame because it does not know the destination MAC address.
- Because these VLANs are stored in a file that is called vlan.dat that is located in flash memory, this file must be manually deleted.
- These VLANs cannot be deleted unless the switch is in VTP client mode.
- These VLANs are default VLANs that cannot be removed.
- These VLANs can only be removed from the switch by using the no vlan 10 and no vlan 100 commands.

CCNA-2-v7-final-exam-answers-16

CCNA 2 v7 Switching Routing and Wireless Essentials-Version-Final-Answers-17
- STP will block one of the redundant links.
- The switches will load balance and utilize both EtherChannels to forward packets.
- The resulting loop will create a broadcast storm.
- Both port channels will shutdown.
- Configure an ACL and apply it to the VTY lines.
- Configure 802.1x.
- Configure SSH.
- Configure Telnet.
- WPA2 with AES
- WPA2 with TKIP
- WEP
- WPA
- firewall appliance
- wireless router
- switch
- standalone wireless access point

CCNA 2 v7 Switching Routing and Wireless Essentials-Version-Final-Answers-21
- Source MAC: 00E0.FE91.7799
Source IP: 10.1.1.10 - Source MAC: 00E0.FE10.17A3
Source IP: 10.1.1.10 - Source MAC: 00E0.FE10.17A3
Source IP: 192.168.1.1 - Source MAC: 00E0.FE91.7799
Source IP: 10.1.1.1 - Source MAC: 00E0.FE91.7799
Source IP: 192.168.1.1

CCNA 2 v7 Switching Routing and Wireless Essentials-Version-Final-Answers-22
- ip route 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0 s0/0/0
- ip route 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0 s0/0/0 91
- ip route 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0 s0/0/0 121
- ip route 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0 s0/0/0 111
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 serial 0/1/1What is the purpose of this command?

CCNA 2 v7 Switching Routing and Wireless Essentials-Version-Final-Answers-23
- Packets that are received from the Internet will be forwarded to one of the LANs connected to R1 or R2.
- Packets with a destination network that is not 10.10.0.0/16 or is not 10.20.0.0/16 or is not a directly connected network will be forwarded to the Internet.
- Packets from the 10.10.0.0/16 network will be forwarded to network 10.20.0.0/16, and packets from the 10.20.0.0/16 network will be forwarded to network 10.10.0.0/16.
- Packets that are destined for networks that are not in the routing table of HQ will be dropped.
- VTP
- STP
- EtherChannel
- DTP

CCNA 2 v7 Switching Routing and Wireless Essentials-Version-Final-Answers-25
- because VLAN 99 is not a valid management VLAN
- because there is a cabling problem on VLAN 99
- because VLAN 1 is up and there can only be one management VLAN on the switch
- because VLAN 99 has not yet been created
- client
- master
- distribution
- slave
- server
- transparent
- Configure the switch with the name of the new management domain.
- Reset the VTP counters to allow the switch to synchronize with the other switches in the domain.
- Configure the VTP server in the domain to recognize the BID of the new switch.
- Download the VTP database from the VTP server in the new domain.
- Select the correct VTP mode and version.
- Reboot the switch.
- Link types can only be configured on access ports configured with a single VLAN.
- Link types can only be determined if PortFast has been configured.
- Link types are determined automatically.
- Link types must be configured with specific port configuration commands.

CCNA 2 v7 Switching Routing and Wireless Essentials-Version-Final-Answers-29
- fa0/9
- fa0/13
- fa0/10
- fa0/20
- fa0/21
- fa0/11
- It will not perform recursive lookups.
- Ethernet multiaccess interfaces will require fully specified static routes to avoid routing inconsistencies.
- Static routes that use an exit interface will be unnecessary.
- Serial point-to-point interfaces will require fully specified static routes to avoid routing inconsistencies.
- They improve network security.
- They take less time to converge when the network topology changes.
- They improve the efficiency of discovering neighboring networks.
- They use fewer router resources.

CCNA 2 v7 Switching Routing and Wireless Essentials-Version-Final-Answers-32
- S 10.17.2.0/24 [1/0] via 10.16.2.2
- S 0.0.0.0/0 [1/0] via 10.16.2.2
- S 10.17.2.0/24 is directly connected, Serial 0/0/0
- C 10.16.2.0/24 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0
- It disables an unused port.
- It disables all trunk ports.
- It enables portfast on a specific switch interface.
- It checks the source L2 address in the Ethernet header against the sender L2 address in the ARP body.
- FF01::/8
- 2001::/3
- FC00::/7
- FE80::/10
- In a switched network, they are mostly configured between switches at the core and distribution layers.
- The interface vlan command has to be entered to create a VLAN on routed ports.
- They support subinterfaces, like interfaces on the Cisco IOS routers.
- They are used for point-to-multipoint links.
- They are not associated with a particular VLAN.
- The protected edge port function on the backup trunk interfaces has been disabled.
- The allowed VLANs on the backup link were not configured correctly.
- Dynamic Trunking Protocol on the link has failed.
- Inter-VLAN routing also failed when the trunk link failed.
- interface port-channel 2
- channel-group 1 mode desirable
- interface range GigabitEthernet 0/4 – 5
- channel-group 2 mode auto
- The switch will forward the frame out all ports except the incoming port.
- The switch forwards the frame out of the specified port.
- The switch adds a MAC address table entry mapping for the destination MAC address and the ingress port.
- The switch replaces the old entry and uses the more current port.
- Verify that there is not a default route in any of the edge router routing tables.
- Check the configuration on the floating static route and adjust the AD.
- Create a floating static route to that network.
- Check the configuration of the exit interface on the new static route.
- auto
- default
- passive
- desirable
- extended
- on
- Remove the route using the no ip route command.
- Change the administrative distance for that route.
- Change the routing metric for that route.
- Nothing. The static route will go away on its own.

CCNA 2 v7 Switching Routing and Wireless Essentials-Version-Final-Answers-42
- R1 is configured as a DHCPv4 relay agent.
- R1 is operating as a DHCPv4 server.
- R1 will broadcast DHCPv4 requests on behalf of local DHCPv4 clients.
- R1 will send a message to a local DHCPv4 client to contact a DHCPv4 server at 10.10.10.8.

CCNA 2 v7 Switching Routing and Wireless Essentials-Version-Final-Answers-43
- R1(config-if)# ip helper-address 10.1.0.254
- R1(config)# interface G0/0
- R1(config-if)# ip helper-address 10.2.0.250
- R1(config)# interface G0/1
- R2(config-if)# ip helper-address 10.2.0.250
- R2(config)# interface G0/0

CCNA 2 v7 Switching Routing and Wireless Essentials-Version-Final-Answers-43
- The ip helper-address command was applied on the wrong interface.
- R1 is not configured as a DHCPv4 server.
- A DHCP server must be installed on the same LAN as the host that is receiving the IP address.
- The ip address dhcp command was not issued on the interface Gi0/1.
45. What two default wireless router settings can affect network security? (Choose two.)
- The SSID is broadcast.
- MAC address filtering is enabled.
- WEP encryption is enabled.
- The wireless channel is automatically selected.
- A well-known administrator password is set.
46. What is the common term given to SNMP log messages that are generated by network devices and sent to the SNMP server?
- traps
- acknowledgments
- auditing
- warnings
- WIRELESS
- MANAGEMENT
- CONTROLLER
- WLANs
- to restrict access to the WLAN by authorized, authenticated users only
- to monitor the operation of the wireless network
- to reduce outsiders intercepting data or accessing the wireless network by using a well-known address range
- to reduce the risk of interference by external devices such as microwave ovens
- packet acknowledgments and retransmissions
- frame queuing and packet prioritization
- beacons and probe responses
- frame translation to other protocols
- association and re-association of roaming clients
- all PortFast-enabled ports
- only ports that are elected as designated ports
- only ports that attach to a neighboring switch
- all trunk ports that are not root ports
- rogue switches on a network
- CAM table overflow attacks
- MAC address spoofing
- rogue DHCP servers on a network
52. Why is DHCP snooping required when using the Dynamic ARP Inspection feature?
- It relies on the settings of trusted and untrusted ports set by DHCP snooping.
- It uses the MAC address table to verify the default gateway IP address.
- It redirects ARP requests to the DHCP server for verification.
- It uses the MAC-address-to-IP-address binding database to validate an ARP packet.

- Change the administrative distance to 120.
- Add the next hop neighbor address of 192.168.0.36.
- Change the destination network to 192.168.0.34.
- Change the administrative distance to 1.
- 90
- 128
- 2170112
- 2681856
- 2682112
- 3193856
- IP address
- VTP domain
- vty lines
- default VLAN
- default gateway
- loopback address
- ipv6 nd other-config-flag
- prefix-delegation 2001:DB8:8::/48 00030001000E84244E70
- ipv6 dhcp server LAN1
- ipv6 unicast-routing
- dns-server 2001:DB8:8::8
(config)# interface gigabitethernet1/1
(config-if)# switchport mode trunk
(config)# interface gigabitethernet 1/1
(config-if)# no switchport
(config-if)# ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.252
(config)# interface vlan 1
(config-if)# ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0
(config-if)# no shutdown
(config)# interface fastethernet0/4
(config-if)# switchport mode trunk
(config)# ip routing
58. A technician is troubleshooting a slow WLAN and decides to use the split-the-traffic approach. Which two parameters would have to be configured to do this? (Choose two.)
- Configure the 5 GHz band for streaming multimedia and time sensitive traffic.
- Configure the security mode to WPA Personal TKIP/AES for one network and WPA2 Personal AES for the other network
- Configure the 2.4 GHz band for basic internet traffic that is not time sensitive.
- Configure the security mode to WPA Personal TKIP/AES for both networks.
- Configure a common SSID for both split networks.
- Verify that the static route to the server is present in the routing table.
- Check the configuration on the floating static route and adjust the AD.
- Ensure that the old default route has been removed from the company edge routers.
- Create a floating static route to that network.
- the destination MAC address and the incoming port
- the destination MAC address and the outgoing port
- the source and destination MAC addresses and the incoming port
- the source and destination MAC addresses and the outgoing port
- the source MAC address and the incoming port
- the source MAC address and the outgoing port

- PAgP
- DTP
- LACP
- STP
- floating static route
- default static route
- summary static route
- standard static route
- The switch updates the refresh timer for the entry.
- The switch forwards the frame out of the specified port.
- The switch purges the entire MAC address table.
- The switch replaces the old entry and uses the more current port.

- R2(config)# ip route 172.16.2.1 255.255.255.0 172.16.3.1
- R2(config)# ip route 172.16.2.0 255.255.255.0 172.16.2.254
- R2(config)# ip route 172.16.2.0 255.255.255.0 172.16.3.1
- R2(config)# ip route 172.16.3.0 255.255.255.0 172.16.2.254
- EtherChannel
- DTP
- STP
- VTP

- host B
- host C
- host D
- host E
- host F
- host G

- Associate hosts A and B with VLAN 10 instead of VLAN 1.
- Configure either trunk port in the dynamic desirable mode.
- Include a router in the topology.
- Remove the native VLAN from the trunk.
- Add the switchport nonegotiate command to the configuration of SW2.
- It enables BPDU guard on a specific port.
- It disables an unused port.
- It enables portfast on a specific switch interface.
- It disables DTP on a non-trunking interface.
- so that the switch stops forwarding traffic
- so that legitimate hosts cannot obtain a MAC address
- so that the attacker can see frames that are destined for other hosts
- so that the attacker can execute arbitrary code on the switch
- Immediately after successful authentication against an AAA data source
- Immediately after AAA accounting and auditing receives detailed reports
- Immediately after an AAA client sends authentication information to a centralized server
- Immediately after the determination of which resources a user can access
- auto secure MAC addresses
- dynamic secure MAC addresses
- static secure MAC addresses
- sticky secure MAC addresses
- 802.11a
- 802.11b
- 802.11g
- 802.11n
- 802.11ac
- The root bridge BID.
- The role of the ports in all VLANs.
- The status of native VLAN ports.
- The number of broadcasts received on each root port.
- The IP address of the management VLAN interface.

- Trunk1
- Trunk2
- Trunk3
- Trunk4
- EUI-64
- SLAAC
- static
- stateful DHCPv6
- 802.1x
- SSH
- SNMP
- TACACS+
- RADIUS
- to eliminate outsiders scanning for available SSIDs in the area
- to reduce the risk of interference by external devices such as microwave ovens
- to reduce the risk of unauthorized APs being added to the network
- to provide privacy and integrity to wireless traffic by using encryption
- implementing port security
- turning on DHCP snooping
- disabling CDP on edge ports
- implementing port-security on edge ports
- shutdown
- restrict
- warning
- protect
- EtherChannel
- VTP
- HSRP
- DTP

- There is no address on Fa0/0 to use as a default gateway.
- RTA is using the same subnet for VLAN 20 and VLAN 30.
- Dot1q does not support subinterfaces.
- The no shutdown command should have been issued on Fa0/0.20 and Fa0/0.30.
- dynamic desirable – dynamic desirable
- dynamic desirable – trunk
- dynamic auto – dynamic auto
- access – dynamic auto
- dynamic desirable – dynamic auto
- access – trunk
- Verify that there is not a default route in any of the edge router routing tables.
- Create static routes to all internal networks and a default route to the internet.
- Create extra static routes to the same location with an AD of 1.
- Check the statistics on the default route for oversaturation.
- channels 1, 5, and 9
- channels 1, 6, and 11
- channels 1, 7, and 13
- channels 2, 6, and 10
- the company username and password through Active Directory service
- a key that matches the key on the AP
- a user passphrase
- a username and password configured on the AP












0 commentaires:
Enregistrer un commentaire