1. Which protocol creates a virtual point-to-point
connection to tunnel unencrypted traffic between Cisco routers from a
variety of protocols?
2. What is a disadvantage when both sides of a communication use PAT?
- End-to-end IPv4 traceability is lost.
- The flexibility of connections to the Internet is reduced.
- The security of the communication is negatively impacted.
- Host IPv4 addressing is complicated.
3. What two addresses are specified in a static NAT configuration?
- the outside global and the outside local
- the inside local and the outside global
- the inside global and the outside local
- the inside local and the inside global
4. A company is considering updating the campus WAN
connection. Which two WAN options are examples of the private WAN
architecture? (Choose two.)
- municipal Wi-Fi
- digital subscriber line
- leased line
- Ethernet WAN
- cable
5. Refer to the exhibit. From the perspective of R1, the NAT router, which address is the inside global address?
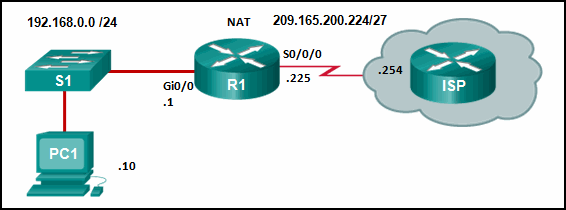
- 192.168.0.10
- 192.168.0.1
- 209.165.200.225
- 209.165.200.254
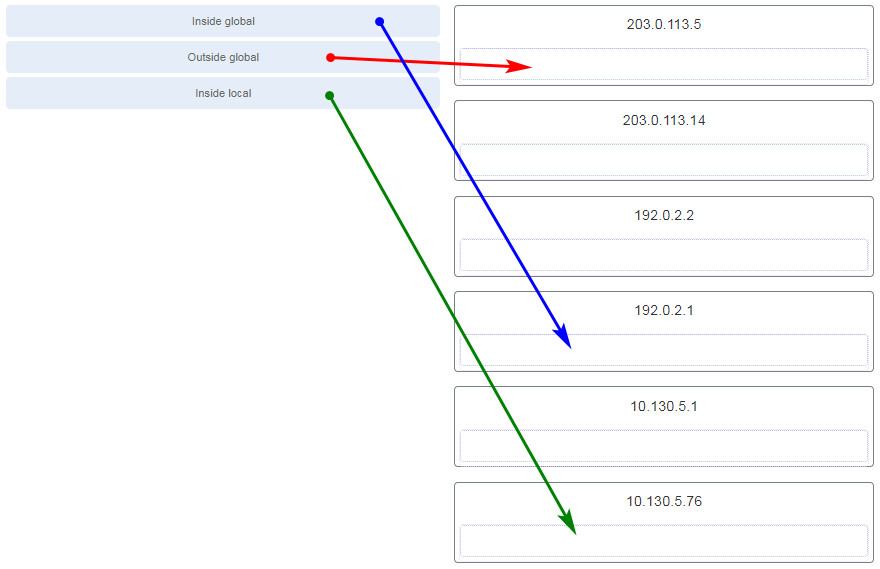
Explanation: There are four types of addresses in NAT terminology.
Inside local address
Inside global address
Outside local address
Outside global address
The inside global address of PC1 is the address that the ISP sees as the
source address of packets, which in this example is the IP address on
the serial interface of R1, 209.165.200.224.
6. Refer to the exhibit. Given the commands as shown, how
many hosts on the internal LAN off R1 can have simultaneous NAT
translations on R1?
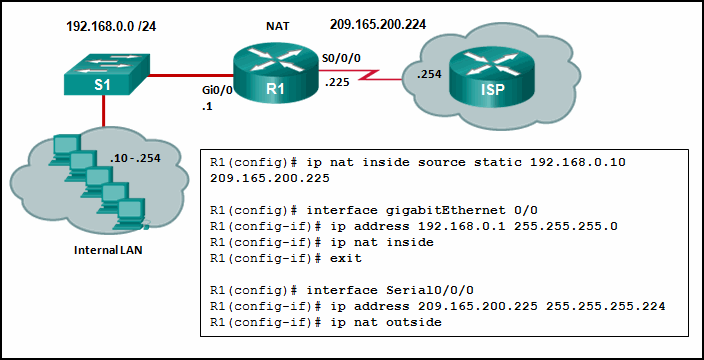
Explanation: The
NAT configuration on R1 is static NAT which translates a single inside
IP address, 192.168.0.10 into a single public IP address,
209.165.200.255. If more hosts need translation, then a NAT pool of
inside global address or overloading should be configured.
7. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator has just
configured address translation and is verifying the configuration. What
three things can the administrator verify? (Choose three.)
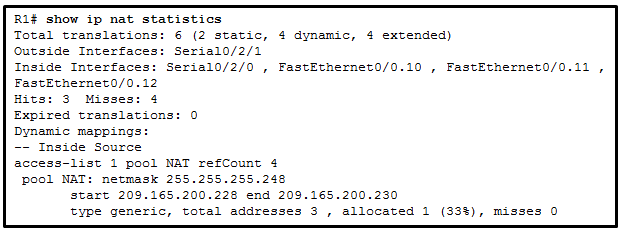
- A standard access list numbered 1 was used as part of the configuration process.
- Three addresses from the NAT pool are being used by hosts.
- Address translation is working.
- One port on the router is not participating in the address translation.
- The name of the NAT pool is refCount.
- Two types of NAT are enabled.
Explanation: The show ip nat statistics, show ip nat translations, and debug ip nat
commands are useful in determining if NAT is working and and also
useful in troubleshooting problems that are associated with NAT. NAT is
working, as shown by the hits and misses count. Because there are four
misses, a problem might be evident. The standard access list numbered 1
is being used and the translation pool is named NAT as evidenced by the
last line of the output. Both static NAT and NAT overload are used as
seen in the Total translations line.
8. Refer to the exhibit. NAT is configured on RT1 and RT2.
The PC is sending a request to the web server. What IPv4 address is the
source IP address in the packet between RT2 and the web server?
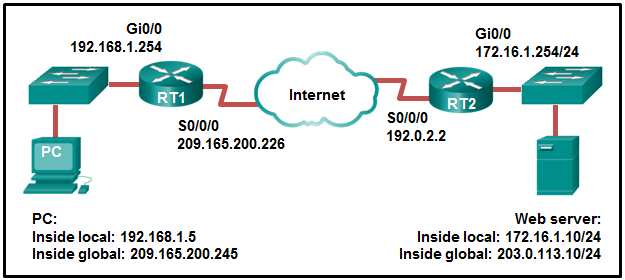
- 192.168.1.5
- 203.0.113.10
- 172.16.1.254
- 172.16.1.10
- 209.165.200.245
- 192.0.2.2
Explanation:
Because the packet is between RT2 and the web server, the source IP
address is the inside global address of PC, 209.165.200.245.
9. Refer to the exhibit. Based on the output that is shown, what type of NAT has been implemented?
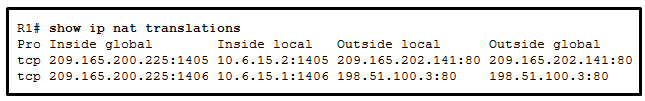
- dynamic NAT with a pool of two public IP addresses
- PAT using an external interface
- static NAT with a NAT pool
- static NAT with one entry
Explanation: The
output shows that there are two inside global addresses that are the
same but that have different port numbers. The only time port numbers
are displayed is when PAT is being used. The same output would be
indicative of PAT that uses an address pool. PAT with an address pool is
appropriate when more than 4,000 simultaneous translations are needed
by the company.
10. Refer to the exhibit. From the perspective of users behind the NAT router, what type of NAT address is 209.165.201.1?
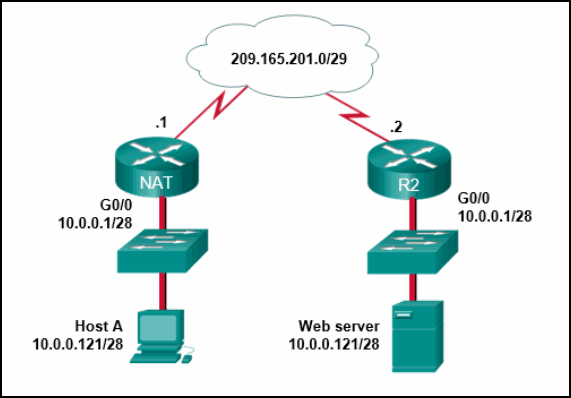
- inside global
- outside global
- outside local
- inside local
Explanation: From
the perspective of users behind NAT, inside global addresses are used by
external users to reach internal hosts. Inside local addresses are the
addresses assigned to internal hosts. Outside global addresses are the
addresses of destinations on the external network. Outside local
addresses are the actual private addresses of destination hosts behind
other NAT devices.
11. Refer to the exhibit. Static NAT is being configured to
allow PC 1 access to the web server on the internal network. What two
addresses are needed in place of A and B to complete the static NAT
configuration? (Choose two.)
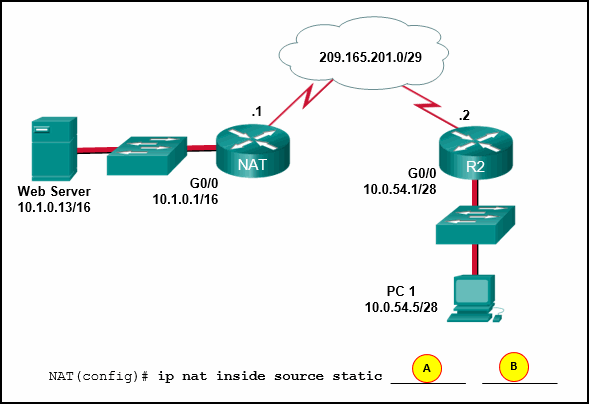
- A = 209.165.201.2
- A = 10.1.0.13
- B = 209.165.201.7
- B = 10.0.254.5
- B = 209.165.201.1
Explanation: Static
NAT is a one-to-one mapping between an inside local address and an
inside global address. By using static NAT, external devices can
initiate connections to internal devices by using the inside global
addresses. The NAT devices will translate the inside global address to
the inside local address of the target host.
12. What is the purpose of the overload keyword in the ip nat inside source list 1 pool NAT_POOL overload command?
- It allows many inside hosts to share one or a few inside global addresses.
- It allows a list of internal hosts to communicate with a specific group of external hosts.
- It allows external hosts to initiate sessions with internal hosts.
- It allows a pool of inside global addresses to be used by internal hosts.
Explanation:
Dynamic NAT uses a pool of inside global addresses that are assigned to
outgoing sessions. If there are more internal hosts than public
addresses in the pool, then an administrator can enable port address
translation with the addition of the overload keyword.
With port address translation, many internal hosts can share a single
inside global address because the NAT device will track the individual
sessions by Layer 4 port number.
13. Refer to the exhibit. Which source address is being used by router R1 for packets being forwarded to the Internet?
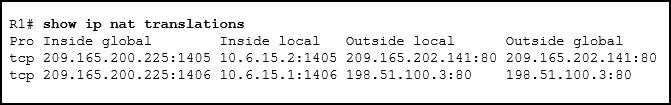
- 10.6.15.2
- 209.165.202.141
- 198.51.100.3
- 209.165.200.225
Explanation: The
source address for packets forwarded by the router to the Internet will
be the inside global address of 209.165.200.225. This is the address
that the internal addresses from the 10.6.15.0 network will be
translated to by NAT.
14. Refer to the exhibit. The NAT configuration applied to the router is as follows:
ERtr(config)# access-list 1 permit 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255
ERtr(config)# ip nat pool corp 209.165.201.6 209.165.201.30 netmask 255.255.255.224
ERtr(config)# ip nat inside source list 1 pool corp overload
ERtr(config)# ip nat inside source static 10.10.10.55 209.165.201.4
ERtr(config)# interface gigabitethernet 0/0
ERtr(config-if)# ip nat inside
ERtr(config-if)# interface serial 0/0/0
ERtr(config-if)# ip nat outside
Based on the configuration and the output shown, what can be determined about the NAT status within the organization?
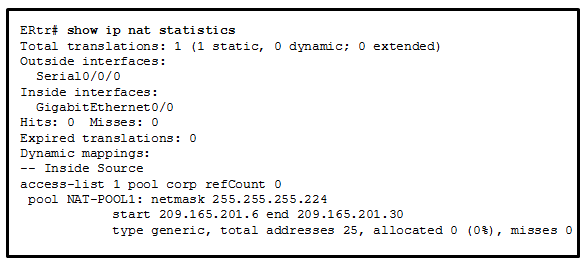
- Static NAT is working, but dynamic NAT is not.
- Dynamic NAT is working, but static NAT is not.
- Not enough information is given to determine if both static and dynamic NAT are working.
- NAT is working.
Explanation: There
is not enough information given because the router might not be attached
to the network yet, the interfaces might not have IP addresses assigned
yet, or the command could have been issued in the middle of the night.
The output does match the given configuration, so no typographical
errors were made when the NAT commands were entered.
15. Which situation describes data transmissions over a WAN connection?
- A network administrator in the office remotely accesses a web server
that is located in the data center at the edge of the campus.
- A manager sends an email to all employees in the department with offices that are located in several buildings.
- An employee prints a file through a networked printer that is located in another building.
- An employee shares a database file with a co-worker who is located in a branch office on the other side of the city.
Explanation: When
two offices across a city are communicating , it is most likely that the
data transmissions are over some type of WAN connection. Data
communications within a campus are typically over LAN connections.
16. Which two technologies are categorized as private WAN infrastructures? (Choose two.)
- Frame Relay
- VPN
- MetroE
- DSL
- cable
Explanation:
Private WAN technologies include leased lines, dialup, ISDN, Frame
Relay, ATM, Ethernet WAN (an example is MetroE), MPLS, and VSAT.
17. Which network scenario will require the use of a WAN?
- Employees need to connect to the corporate email server through a VPN while traveling.
- Employees need to access web pages that are hosted on the corporate web servers in the DMZ within their building.
- Employee workstations need to obtain dynamically assigned IP addresses.
- Employees in the branch office need to share files with the
headquarters office that is located in a separate building on the same
campus network.
Explanation: When
traveling employees need to connect to a corporate email server through a
WAN connection, the VPN will create a secure tunnel between an employee
laptop and the corporate network over the WAN connection. Obtaining
dynamic IP addresses through DHCP is a function of LAN communication.
Sharing files among separate buildings on a corporate campus is
accomplished through the LAN infrastructure. A DMZ is a protected
network inside the corporate LAN infrastructure.
18. What are two hashing algorithms used with IPsec AH to guarantee authenticity? (Choose two.)
Explanation: The
IPsec framework uses various protocols and algorithms to provide data
confidentiality, data integrity, authentication, and secure key
exchange. Two popular algorithms used to ensure that data is not
intercepted and modified (data integrity and authenticity) are MD5 and
SHA.
19. What two algorithms can be part of an IPsec policy to
provide encryption and hashing to protect interesting traffic? (Choose
two.)
Explanation: The
IPsec framework uses various protocols and algorithms to provide data
confidentiality, data integrity, authentication, and secure key
exchange. Two algorithms that can be used within an IPsec policy to
protect interesting traffic are AES, which is an encryption protocol,
and SHA, which is a hashing algorithm.
20. Which VPN solution allows the use of a web browser to establish a secure, remote-access VPN tunnel to the ASA?
- client-based SSL
- site-to-site using an ACL
- clientless SSL
- site-to-site using a preshared key
Explanation: When a
web browser is used to securely access the corporate network, the
browser must use a secure version of HTTP to provide SSL encryption. A
VPN client is not required to be installed on the remote host, so a
clientless SSL connection is used.
21. Which IPsec security function provides assurance that the data received via a VPN has not been modified in transit?
- integrity
- authentication
- confidentiality
- secure key exchange
Explanation:
Integrity is a function of IPsec and ensures data arrives unchanged at
the destination through the use of a hash algorithm. Confidentiality is a
function of IPsec and utilizes encryption to protect data transfers
with a key. Authentication is a function of IPsec and provides specific
access to users and devices with valid authentication factors. Secure
key exchange is a function of IPsec and allows two peers to maintain
their private key confidentiality while sharing their public key.
22. Which two types of VPNs are examples of enterprise-managed remote access VPNs? (Choose two.)
- clientless SSL VPN
- client-based IPsec VPN
- IPsec VPN
- IPsec Virtual Tunnel Interface VPN
- GRE over IPsec VPN
Explanation: Enterprise managed VPNs can be deployed in two configurations:
- Remote Access VPN – This VPN is created dynamically
when required to establish a secure connection between a client and a
VPN server. Remote access VPNs include client-based IPsec VPNs and
clientless SSL VPNs.
- Site-to-site VPN – This VPN is created when
interconnecting devices are preconfigured with information to establish a
secure tunnel. VPN traffic is encrypted only between the
interconnecting devices, and internal hosts have no knowledge that a VPN
is used. Site-to-site VPNs include IPsec, GRE over IPsec, Cisco Dynamic
Multipoint (DMVPN), and IPsec Virtual Tunnel Interface (VTI) VPNs.
23. Which is a requirement of a site-to-site VPN?
- It requires hosts to use VPN client software to encapsulate traffic.
- It requires the placement of a VPN server at the edge of the company network.
- It requires a VPN gateway at each end of the tunnel to encrypt and decrypt traffic.
- It requires a client/server architecture.
Explanation:
Site-to-site VPNs are static and are used to connect entire networks.
Hosts have no knowledge of the VPN and send TCP/IP traffic to VPN
gateways. The VPN gateway is responsible for encapsulating the traffic
and forwarding it through the VPN tunnel to a peer gateway at the other
end which decapsulates the traffic.
24. What is the function of the Diffie-Hellman algorithm within the IPsec framework?
- guarantees message integrity
- allows peers to exchange shared keys
- provides authentication
- provides strong data encryption
Explanation: The
IPsec framework uses various protocols and algorithms to provide data
confidentiality, data integrity, authentication, and secure key
exchange. DH (Diffie-Hellman) is an algorithm used for key exchange. DH
is a public key exchange method that allows two IPsec peers to establish
a shared secret key over an insecure channel.
25. What does NAT overloading use to track multiple internal hosts that use one inside global address?
- port numbers
- IP addresses
- autonomous system numbers
- MAC addresses
Explanation: NAT
overloading, also known as Port Address Translation (PAT), uses port
numbers to differentiate between multiple internal hosts.
26. Question as presented:
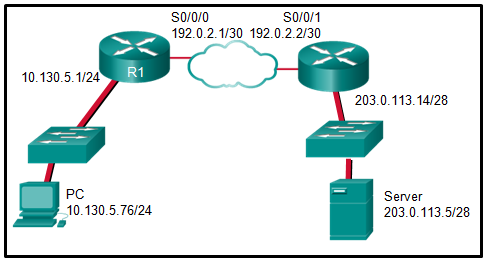
Explanation: The
inside local address is the private IP address of the source or the PC
in this instance. The inside global address is the translated address of
the source or the address as seen by the outside device. Since the PC
is using the outside address of the R1 router, the inside global address
is 192.0.2.1. The outside addressing is simply the address of the
server or 203.0.113.5.
27. Refer to the exhibit. R1 is configured for static NAT. What IP address will Internet hosts use to reach PC1?
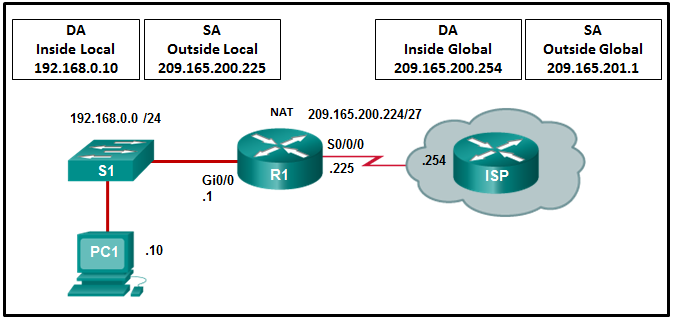
- 192.168.0.1
- 192.168.0.10
- 209.165.201.1
- 209.165.200.225
Explanation: In
static NAT a single inside local address, in this case 192.168.0.10,
will be mapped to a single inside global address, in this case
209.165.200.225. Internet hosts will send packets to PC1 and use as a
destination address the inside global address 209.165.200.225.
28. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is viewing
the output from the command show ip nat translations. Which statement
correctly describes the NAT translation that is occurring on router
RT2?
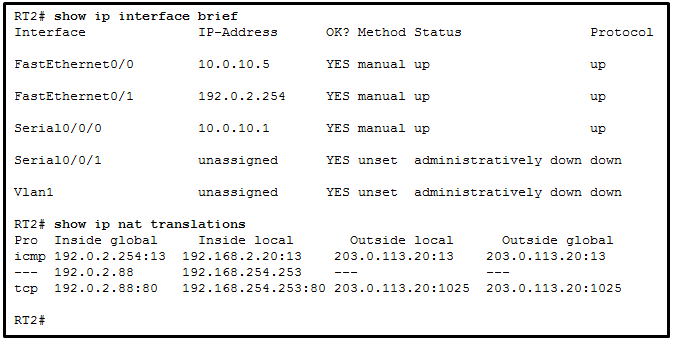
- The traffic from a source IPv4 address of 192.168.254.253 is being translated to 192.0.2.88 by means of static NAT.
- The traffic from a source IPv4 address of 192.0.2.88 is being
translated by router RT2 to reach a destination IPv4 address of
192.168.254.253.
- The traffic from a source IPv4 public address that originates
traffic on the internet would be able to reach private internal IPv4
addresses.
- The traffic from a source IPv4 address of 192.168.2.20 is being
translated by router RT2 to reach a destination IPv4 address of
192.0.2.254.
Explanation:
Because no outside local or outside global address is referenced, the
traffic from a source IPv4 address of 192.168.254.253 is being
translated to 192.0.2.88 by using static NAT. In the output from the
command show ip nat translations, the inside local IP
address of 192.168.2.20 is being translated into an outside IP address
of 192.0.2.254 so that the traffic can cross the public network. A
public IPv4 device can connect to the private IPv4 device
192.168.254.253 by targeting the destination IPv4 address of 192.0.2.88.
29. Which two WAN infrastructure services are examples of private connections? (Choose two.)
- cable
- DSL
- Frame Relay
- T1/E1
- wireless
Explanation: Private WANs can use T1/E1, T3/E3, PSTN, ISDN, Metro Ethernet, MPLS, Frame Relay, ATM, or VSAT technology.
30. Which two statements about the relationship between LANs and WANs are true? (Choose two.)
- Both LANs and WANs connect end devices.
- WANs are typically operated through multiple ISPs, but LANs are typically operated by single organizations or individuals.
- WANs must be publicly-owned, but LANs can be owned by either public or private entities.
- WANs connect LANs at slower speed bandwidth than LANs connect their internal end devices.
- LANs connect multiple WANs together.
Explanation:
Although LANs and WANs can employ the same network media and
intermediary devices, they serve very different areas and purposes. The
administrative and geographical scope of a WAN is larger than that of a
LAN. Bandwidth speeds are slower on WANs because of their increased
complexity. The Internet is a network of networks, which can function
under either public or private management.
31. Which statement describes an important characteristic of a site-to-site VPN?
- It must be statically set up.
- It is ideally suited for use by mobile workers.
- It requires using a VPN client on the host PC.
- After the initial connection is established, it can dynamically change connection information.
- It is commonly implemented over dialup and cable modem networks.
Explanation: A
site-to-site VPN is created between the network devices of two separate
networks. The VPN is static and stays established. The internal hosts of
the two networks have no knowledge of the VPN.
32. How is “tunneling” accomplished in a VPN?
- New headers from one or more VPN protocols encapsulate the original packets.
- All packets between two hosts are assigned to a single physical medium to ensure that the packets are kept private.
- Packets are disguised to look like other types of traffic so that they will be ignored by potential attackers.
- A dedicated circuit is established between the source and destination devices for the duration of the connection.
Explanation:
Packets in a VPN are encapsulated with the headers from one or more VPN
protocols before being sent across the third party network. This is
referred to as “tunneling”. These outer headers can be used to route the
packets, authenticate the source, and prevent unauthorized users from
reading the contents of the packets.
33. Which statement describes a VPN?
- VPNs use open source virtualization software to create the tunnel through the Internet.
- VPNs use logical connections to create public networks through the Internet.
- VPNs use dedicated physical connections to transfer data between remote users.
- VPNs use virtual connections to create a private network through a public network.
Explanation: A VPN
is a private network that is created over a public network. Instead of
using dedicated physical connections, a VPN uses virtual connections
routed through a public network between two network devices.
34. Open the PT Activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then answer the question.
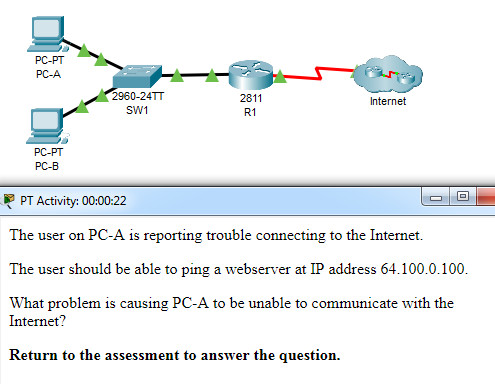
CCNA 3 v7 Modules 6 – 8: WAN Concepts Exam Answers
What problem is causing PC-A to be unable to communicate with the Internet?
- The ip nat inside source command refers to the wrong interface.
- The NAT interfaces are not correctly assigned.
- The static route should not reference the interface, but the outside address instead.
- The access list used in the NAT process is referencing the wrong subnet.
- This router should be configured to use static NAT instead of PAT.
Explanation: The output of show ip nat statistics
shows that the inside interface is FastEthernet0/0 but that no
interface has been designated as the outside interface. This can be
fixed by adding the command ip nat outside to interface Serial0/0/0.
35. What type of address is 64.100.190.189?
36. Which type of VPN routes packets through virtual tunnel interfaces for encryption and forwarding?
- MPLS VPN
- IPsec virtual tunnel interface
- dynamic multipoint VPN
- GRE over IPsec
37. Match the scenario to the WAN solution. (Not all options are used.)
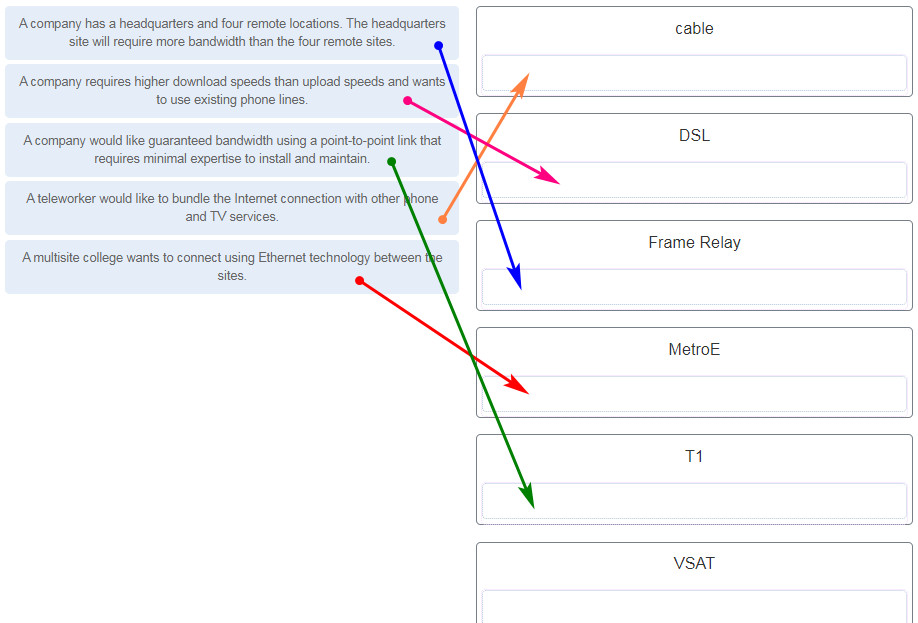 38. Question as presented:
38. Question as presented:
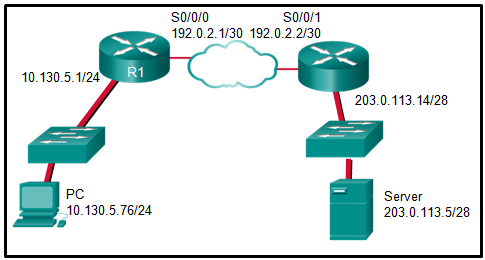 Refer to the exhibit. The PC is sending a packet to the Server
on the remote network. Router R1 is performing NAT overload. From the
perspective of the PC, match the NAT address type with the correct IP
address. (Not all options are used.)
Refer to the exhibit. The PC is sending a packet to the Server
on the remote network. Router R1 is performing NAT overload. From the
perspective of the PC, match the NAT address type with the correct IP
address. (Not all options are used.)
 39. Refer to the exhibit. What has to be done in order to complete the static NAT configuration on R1?
39. Refer to the exhibit. What has to be done in order to complete the static NAT configuration on R1?
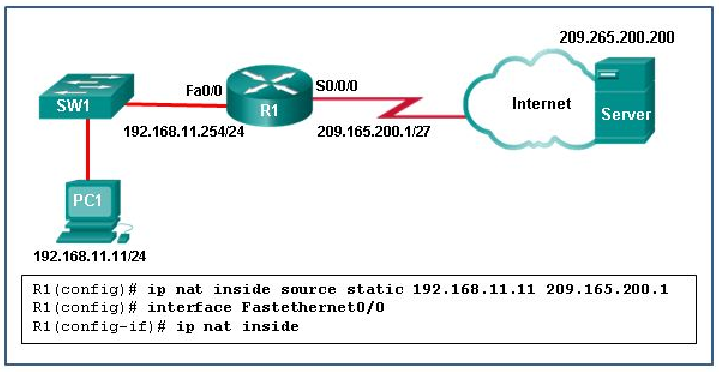
- Interface Fa0/0 should be configured with the command no ip nat inside.
- Interface S0/0/0 should be configured with the command ip nat outside.
- R1 should be configured with the command ip nat inside source static 209.165.200.200 192.168.11.11.
- R1 should be configured with the command ip nat inside source static 209.165.200.1 192.168.11.11.
Explanation: In
order for NAT translations to work properly, both an inside and outside
interface must be configured for NAT translation on the router.
40. In NAT terms, what address type refers to the globally routable IPv4 address of a destination host on the Internet?
- outside global
- inside global
- outside local
- inside local
Explanation: From
the perspective of a NAT device, inside global addresses are used by
external users to reach internal hosts. Inside local addresses are the
addresses assigned to internal hosts. Outside global addresses are the
addresses of destinations on the external network. Outside local
addresses are the actual private addresses of destination hosts behind
other NAT devices.
41. Refer to the exhibit. Which two statements are correct based on the output as shown in the exhibit? (Choose two.)

- The output is the result of the show ip nat translations command.
- The host with the address 209.165.200.235 will respond to requests by using a source address of 192.168.10.10.
- The output is the result of the show ip nat statistics command.
- Traffic with the destination address of a public web server will be sourced from the IP of 192.168.1.10.
- The host with the address 209.165.200.235 will respond to requests by using a source address of 209.165.200.235.
Explanation: The output displayed in the exhibit is the result of the show ip nat translations command. Static NAT entries are always present in the NAT table, while dynamic entries will eventually time out.
42. Which circumstance would result in an enterprise deciding to implement a corporate WAN?
- when the enterprise decides to secure its corporate LAN
- when its employees become distributed across many branch locations
- when the number of employees exceeds the capacity of the LAN
- when the network will span multiple buildings
Explanation: WANs
cover a greater geographic area than LANs do, so having employees
distributed across many locations would require the implementation of
WAN technologies to connect those locations. Customers will access
corporate web services via a public WAN that is implemented by a service
provider, not by the enterprise itself. When employee numbers grow, the
LAN has to expand as well. A WAN is not required unless the employees
are in remote locations. LAN security is not related to the decision to
implement a WAN.
43. What is the function of the Hashed Message Authentication Code (HMAC) algorithm in setting up an IPsec VPN?
- protects IPsec keys during session negotiation
- authenticates the IPsec peers
- creates a secure channel for key negotiation
- guarantees message integrity
Explanation: The
IPsec framework uses various protocols and algorithms to provide data
confidentiality, data integrity, authentication, and secure key
exchange. The Hashed Message Authentication Code (HMAC) is a data
integrity algorithm that uses a hash value to guarantee the integrity of
a message.
44. What algorithm is used with IPsec to provide data confidentiality?
- Diffie-Hellman
- SHA
- MD5
- RSA
- AES
Explanation: The
IPsec framework uses various protocols and algorithms to provide data
confidentiality, data integrity, authentication, and secure key
exchange. Two popular algorithms that are used to ensure that data is
not intercepted and modified (data integrity) are MD5 and SHA. AES is an
encryption protocol and provides data confidentiality. DH
(Diffie-Hellman) is an algorithm that is used for key exchange. RSA is
an algorithm that is used for authentication.
45. Which two technologies provide enterprise-managed VPN solutions? (Choose two.)
- remote access VPN
- Frame Relay
- Layer 2 MPLS VPN
- site-to-site VPN
- Layer 3 MPLS VPN
Explanation: VPNs can be managed and deployed as either of two types:
- Enterprise VPNs – Enterprise-managed VPNs are a
common solution for securing enterprise traffic across the internet.
Site-to-site and remote access VPNs are examples of enterprise managed
VPNs.
- Service Provider VPNs – Service provider managed
VPNs are created and managed over the provider network. Layer 2 and
Layer 3 MPLS are examples of service provider managed VPNs. Other legacy
WAN solutions include Frame Relay and ATM VPNs.
46. Question as presented:
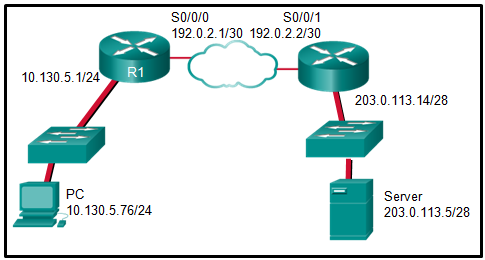
Explanation: The
inside local address is the private IP address of the source or the PC
in this instance. The inside global address is the translated address of
the source or the address as seen by the outside device. Since the PC
is using the outside address of the R1 router, the inside global address
is 192.0.2.1. The outside addressing is simply the address of the
server or 203.0.113.5.
47. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is viewing
the output from the command show ip nat translations. Which statement
correctly describes the NAT translation that is occurring on router
RT2?
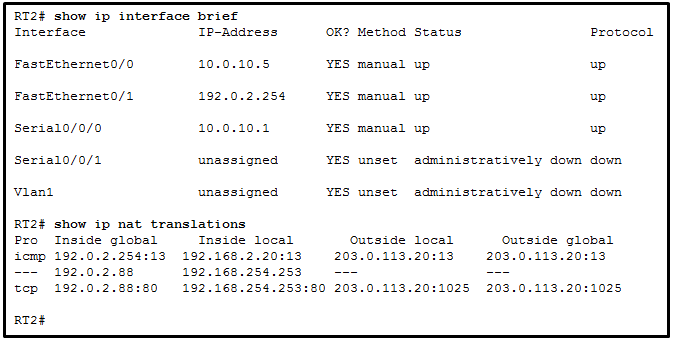
- The traffic from a source IPv4 address of 192.168.254.253 is being translated to 192.0.2.88 by means of static NAT.
- The traffic from a source IPv4 address of 192.0.2.88 is being
translated by router RT2 to reach a destination IPv4 address of
192.168.254.253.
- The traffic from a source IPv4 public address that originates
traffic on the internet would be able to reach private internal IPv4
addresses.
- The traffic from a source IPv4 address of 192.168.2.20 is being
translated by router RT2 to reach a destination IPv4 address of
192.0.2.254.
Explanation:
Because no outside local or outside global address is referenced, the
traffic from a source IPv4 address of 192.168.254.253 is being
translated to 192.0.2.88 by using static NAT. In the output from the
command show ip nat translations, the inside local IP
address of 192.168.2.20 is being translated into an outside IP address
of 192.0.2.254 so that the traffic can cross the public network. A
public IPv4 device can connect to the private IPv4 device
192.168.254.253 by targeting the destination IPv4 address of 192.0.2.88.
48. What type of address is 10.100.126.126?
49. Which type of VPN connects using the Transport Layer Security (TLS) feature?
- SSL VPN
- MPLS VPN
- IPsec virtual tunnel interface
- dynamic multipoint VPN
50. Which two end points can be on the other side of an ASA site-to-site VPN configured using ASDM? (Choose two.)
- DSL switch
- ISR router
- another ASA
- multilayer switch
- Frame Relay switch
51. Which two statements accurately describe an advantage or a
disadvantage when deploying NAT for IPv4 in a network? (Choose two.)
- NAT improves packet handling.
- NAT adds authentication capability to IPv4.
- NAT will impact negatively on switch performance.
- NAT causes routing tables to include more information.
- NAT provides a solution to slow down the IPv4 address depletion.
- NAT introduces problems for some applications that require end-to-end connectivity.
52. A network administrator wants to examine the active NAT
translations on a border router. Which command would perform the task?
- Router# show ip nat translations
- Router# show ip nat statistics
- Router# clear ip nat translations
- Router# debug ip nat translations
53. What are two tasks to perform when configuring static NAT? (Choose two.)
- Configure a NAT pool.
- Create a mapping between the inside local and outside local addresses.
- Identify the participating interfaces as inside or outside interfaces.
- Define the inside global address on the server
- Define the outside global address.
54. What is a disadvantage of NAT?
- There is no end-to-end addressing.
- The router does not need to alter the checksum of the IPv4 packets.
- The internal hosts have to use a single public IPv4 address for external communication.
- The costs of readdressing hosts can be significant for a publicly addressed network.
































0 commentaires:
Enregistrer un commentaire